Real-time auditing involves continuous monitoring and analysis of financial transactions, allowing businesses to detect errors and discrepancies promptly. Forensic auditing focuses on investigating financial records to uncover fraud, embezzlement, or legal discrepancies after suspicious activities arise. Explore the key differences and applications between real-time and forensic auditing to enhance your organization's financial integrity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between real-time auditing and forensic auditing is crucial for accurate financial oversight and fraud detection. Real-time auditing provides continuous monitoring of financial transactions to ensure compliance and early error identification. Forensic auditing involves detailed examination of financial records to uncover fraud, embezzlement, or legal disputes typically after suspicion arises. Knowing these distinctions enhances an organization's ability to apply the appropriate audit method for risk management and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
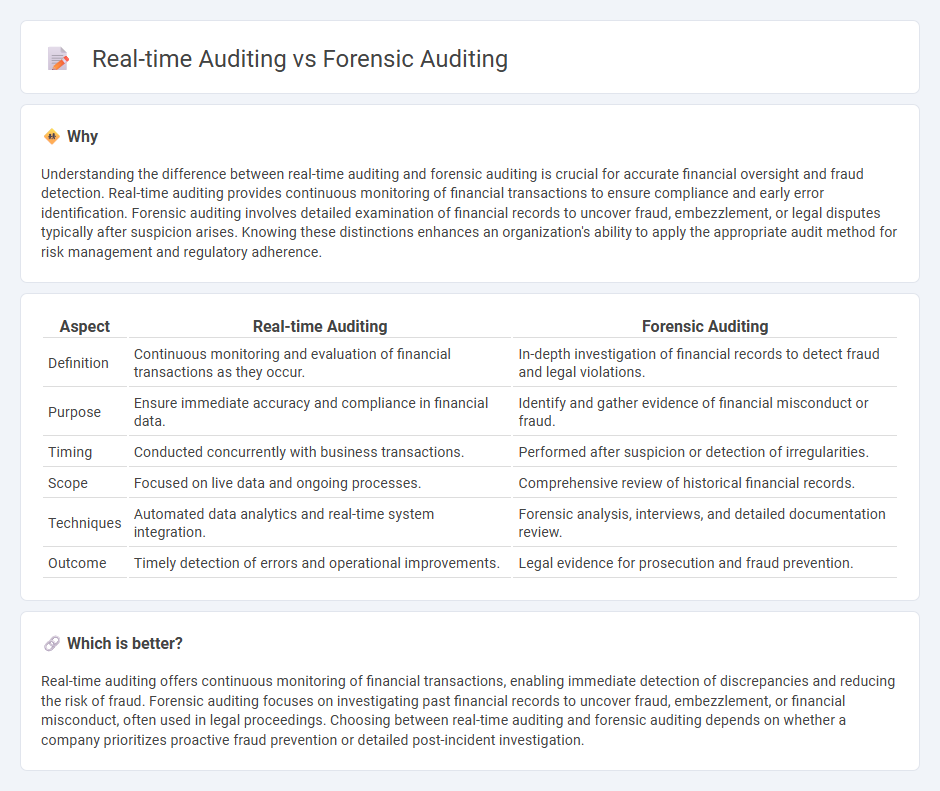
| Aspect | Real-time Auditing | Forensic Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous monitoring and evaluation of financial transactions as they occur. | In-depth investigation of financial records to detect fraud and legal violations. |
| Purpose | Ensure immediate accuracy and compliance in financial data. | Identify and gather evidence of financial misconduct or fraud. |
| Timing | Conducted concurrently with business transactions. | Performed after suspicion or detection of irregularities. |
| Scope | Focused on live data and ongoing processes. | Comprehensive review of historical financial records. |
| Techniques | Automated data analytics and real-time system integration. | Forensic analysis, interviews, and detailed documentation review. |
| Outcome | Timely detection of errors and operational improvements. | Legal evidence for prosecution and fraud prevention. |
Which is better?
Real-time auditing offers continuous monitoring of financial transactions, enabling immediate detection of discrepancies and reducing the risk of fraud. Forensic auditing focuses on investigating past financial records to uncover fraud, embezzlement, or financial misconduct, often used in legal proceedings. Choosing between real-time auditing and forensic auditing depends on whether a company prioritizes proactive fraud prevention or detailed post-incident investigation.
Connection
Real-time auditing enhances forensic auditing by providing immediate access to financial data, enabling quicker detection of anomalies and fraud. Forensic auditing relies on this timely information to perform detailed investigations and gather evidence for legal proceedings. Both auditing processes use advanced data analytics tools to improve accuracy and efficiency in identifying financial discrepancies.
Key Terms
Fraud Detection (Forensic Auditing)
Forensic auditing specializes in investigating and analyzing financial records to detect fraud and gather evidence for legal proceedings, often conducted after suspicious activity is identified. Real-time auditing continuously monitors transactions and financial activities to identify anomalies and potential fraud as they occur, enhancing proactive risk management. Explore how integrating both forensic and real-time auditing can strengthen comprehensive fraud detection strategies.
Continuous Monitoring (Real-time Auditing)
Real-time auditing, centered on continuous monitoring, leverages advanced data analytics and automated processes to detect irregularities as they occur, enhancing fraud prevention and operational efficiency. Unlike forensic auditing, which investigates past financial discrepancies and fraud incidents, continuous monitoring provides ongoing assurance by analyzing transactional data in real time. Explore how integrating continuous monitoring can transform your audit strategy and strengthen compliance frameworks.
Evidence Collection (Forensic Auditing)
Forensic auditing emphasizes meticulous evidence collection to uncover fraud, ensuring that all digital and physical records are preserved following legal standards for admissibility in court. Techniques include thorough document analysis, interviews, and forensic data recovery to trace illicit activities with high accuracy. Explore detailed methods and tools used in forensic auditing to strengthen fraud detection and litigation support.
Source and External Links
Forensic Audits: All You Need to Know - Caseware - Forensic auditing investigates financial records in detail to find fraudulent or illegal activities, typically involving specialists who follow money trails and document evidence that can be used in court cases; the process involves planning, collecting evidence, reporting findings, and possibly court appearances.
Forensic Audit Guide - Definition, Steps, Reasons - A forensic audit is a detailed examination of financial records aimed at uncovering fraud to produce evidence usable in legal proceedings, requiring specialized training and tailored investigation to identify fraud methods, perpetrators, and financial losses.
Forensic auditing | P7 Advanced Audit and Assurance - ACCA Global - Forensic auditing encompasses procedures to gather evidence of fraud or financial wrongdoing, which may include investigating motives, collusion, physical evidence, and suspect behavior, often culminating in expert witness testimony during legal trials.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com