Environmental social governance (ESG) accounting focuses on measuring a company's performance in areas of environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices, providing investors with data on sustainable business operations. Triple bottom line (TBL) accounting expands financial reporting to include social and environmental outcomes alongside profit, emphasizing people, planet, and profit as equal performance metrics. Explore the distinctions and benefits of each framework to enhance your understanding of sustainable accounting practices.
Why it is important
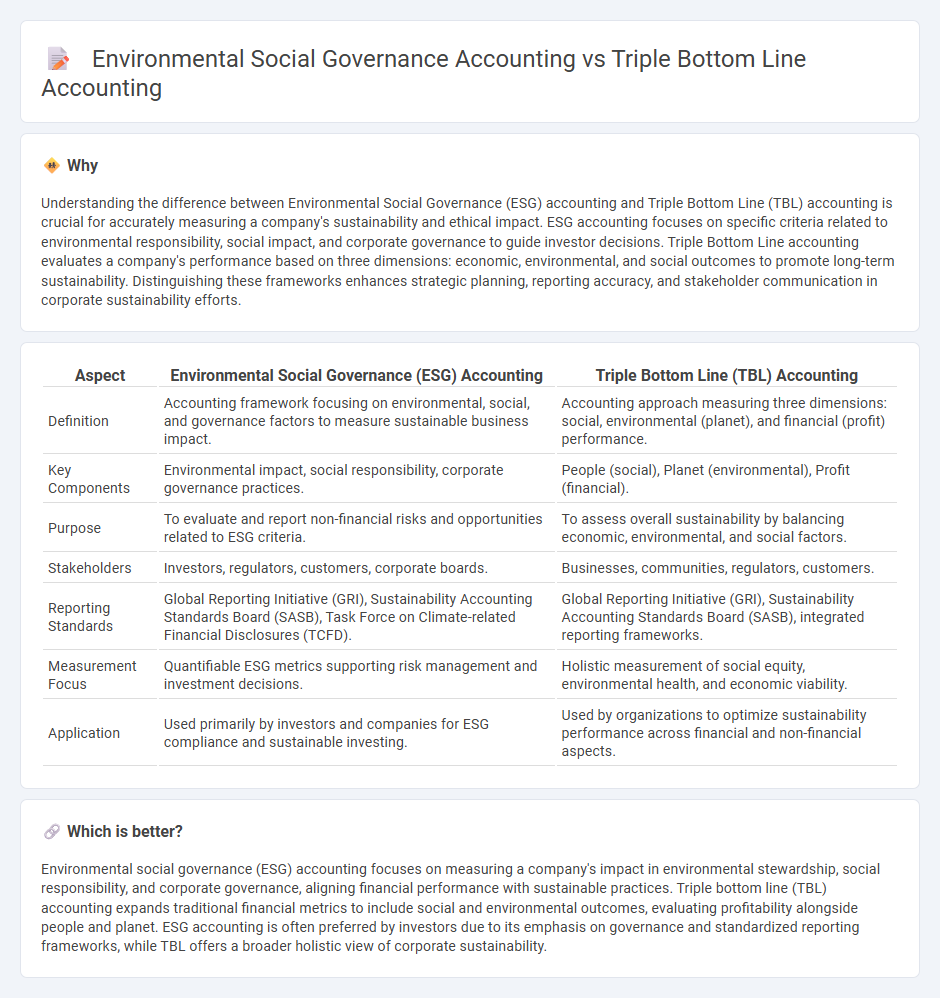
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting and Triple Bottom Line (TBL) accounting is crucial for accurately measuring a company's sustainability and ethical impact. ESG accounting focuses on specific criteria related to environmental responsibility, social impact, and corporate governance to guide investor decisions. Triple Bottom Line accounting evaluates a company's performance based on three dimensions: economic, environmental, and social outcomes to promote long-term sustainability. Distinguishing these frameworks enhances strategic planning, reporting accuracy, and stakeholder communication in corporate sustainability efforts.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Accounting | Triple Bottom Line (TBL) Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting framework focusing on environmental, social, and governance factors to measure sustainable business impact. | Accounting approach measuring three dimensions: social, environmental (planet), and financial (profit) performance. |
| Key Components | Environmental impact, social responsibility, corporate governance practices. | People (social), Planet (environmental), Profit (financial). |
| Purpose | To evaluate and report non-financial risks and opportunities related to ESG criteria. | To assess overall sustainability by balancing economic, environmental, and social factors. |
| Stakeholders | Investors, regulators, customers, corporate boards. | Businesses, communities, regulators, customers. |
| Reporting Standards | Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). | Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), integrated reporting frameworks. |
| Measurement Focus | Quantifiable ESG metrics supporting risk management and investment decisions. | Holistic measurement of social equity, environmental health, and economic viability. |
| Application | Used primarily by investors and companies for ESG compliance and sustainable investing. | Used by organizations to optimize sustainability performance across financial and non-financial aspects. |
Which is better?
Environmental social governance (ESG) accounting focuses on measuring a company's impact in environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and corporate governance, aligning financial performance with sustainable practices. Triple bottom line (TBL) accounting expands traditional financial metrics to include social and environmental outcomes, evaluating profitability alongside people and planet. ESG accounting is often preferred by investors due to its emphasis on governance and standardized reporting frameworks, while TBL offers a broader holistic view of corporate sustainability.
Connection
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting and Triple Bottom Line (TBL) accounting are connected through their shared focus on integrating non-financial performance metrics--environmental, social, and governance factors--into traditional financial reporting. Both frameworks emphasize sustainable business practices by measuring impacts on people, planet, and profit, thereby promoting long-term value creation and responsible corporate behavior. ESG accounting provides detailed criteria that complement the broader TBL approach, enabling organizations to transparently report their sustainability efforts and enhance stakeholder trust.
Key Terms
People, Planet, Profit
Triple bottom line accounting measures organizational success through the integrated lens of People, Planet, and Profit, emphasizing social equity, environmental stewardship, and economic viability. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting centers on corporate policies and practices related to environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance transparency, often aligning with investor criteria. Explore how both frameworks drive sustainable business strategies and impact stakeholder value.
ESG Criteria
Triple bottom line accounting evaluates business performance based on three pillars: social, environmental, and financial outcomes, emphasizing sustainability and long-term value. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting centers specifically on ESG criteria, which include environmental impact, social responsibility, and governance practices to assess corporate behavior and risk. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how each framework drives responsible business strategies and investor decisions.
Sustainability Reporting
Triple bottom line accounting evaluates an organization's performance based on three pillars: economic, environmental, and social outcomes, providing a comprehensive framework for sustainability reporting. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting narrows the focus to measurable environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance factors, aligning closely with investor and regulatory expectations. Discover how integrating TBL and ESG approaches can enhance transparency and drive sustainable business practices.
Source and External Links
The Triple Bottom Line: What Is It and How Does It Work? - The triple bottom line (TBL) is an accounting framework established by John Elkington that measures organizational performance across three dimensions: social, environmental, and financial, also referred to as people, planet, and profit.
What Is the Triple Bottom Line (TBL)? - TBL is a sustainability framework focusing on maximizing the three P's--people (social impact), planet (environmental impact), and profit (financial performance)--to create positive effects for all stakeholders, not just shareholders.
Triple bottom line - The triple bottom line is a framework combining social, environmental, and economic performance measures to broaden how organizations evaluate their overall value and sustainability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com