Blockchain bookkeeping enhances transparency and security by recording transactions on a decentralized ledger, reducing the risk of fraud through immutable data entries. Forensic accounting focuses on investigating financial discrepancies, fraud detection, and legal disputes by analyzing complex financial records and transactions. Explore how these two distinct accounting methods transform financial integrity and fraud prevention.
Why it is important
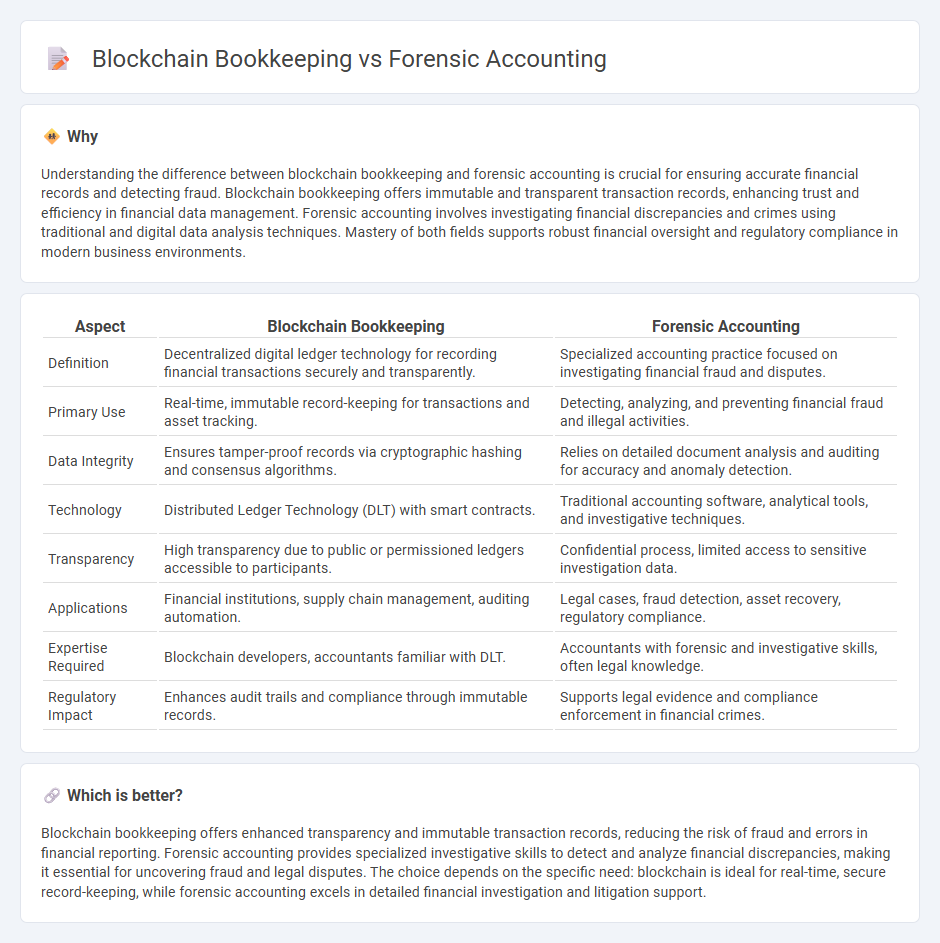
Understanding the difference between blockchain bookkeeping and forensic accounting is crucial for ensuring accurate financial records and detecting fraud. Blockchain bookkeeping offers immutable and transparent transaction records, enhancing trust and efficiency in financial data management. Forensic accounting involves investigating financial discrepancies and crimes using traditional and digital data analysis techniques. Mastery of both fields supports robust financial oversight and regulatory compliance in modern business environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Blockchain Bookkeeping | Forensic Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decentralized digital ledger technology for recording financial transactions securely and transparently. | Specialized accounting practice focused on investigating financial fraud and disputes. |
| Primary Use | Real-time, immutable record-keeping for transactions and asset tracking. | Detecting, analyzing, and preventing financial fraud and illegal activities. |
| Data Integrity | Ensures tamper-proof records via cryptographic hashing and consensus algorithms. | Relies on detailed document analysis and auditing for accuracy and anomaly detection. |
| Technology | Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) with smart contracts. | Traditional accounting software, analytical tools, and investigative techniques. |
| Transparency | High transparency due to public or permissioned ledgers accessible to participants. | Confidential process, limited access to sensitive investigation data. |
| Applications | Financial institutions, supply chain management, auditing automation. | Legal cases, fraud detection, asset recovery, regulatory compliance. |
| Expertise Required | Blockchain developers, accountants familiar with DLT. | Accountants with forensic and investigative skills, often legal knowledge. |
| Regulatory Impact | Enhances audit trails and compliance through immutable records. | Supports legal evidence and compliance enforcement in financial crimes. |
Which is better?
Blockchain bookkeeping offers enhanced transparency and immutable transaction records, reducing the risk of fraud and errors in financial reporting. Forensic accounting provides specialized investigative skills to detect and analyze financial discrepancies, making it essential for uncovering fraud and legal disputes. The choice depends on the specific need: blockchain is ideal for real-time, secure record-keeping, while forensic accounting excels in detailed financial investigation and litigation support.
Connection
Blockchain bookkeeping enhances the transparency and immutability of financial records, which forensic accounting relies on to detect and investigate fraud or discrepancies. By leveraging blockchain's decentralized ledger, forensic accountants gain access to real-time, tamper-proof transaction histories crucial for accurate financial analysis. This integration improves the efficiency and reliability of tracing illicit activities and ensuring regulatory compliance in accounting practices.
Key Terms
Fraud detection
Forensic accounting utilizes investigative techniques and financial analysis to detect and prevent fraud by examining irregularities in traditional financial records and transactions. Blockchain bookkeeping employs decentralized ledgers and cryptographic verification to enhance transparency and immutability, making unauthorized alterations and fraudulent activities more difficult to conceal. Explore the detailed comparison to understand which method best strengthens fraud detection in your financial operations.
Immutable ledger
Forensic accounting leverages traditional investigative techniques to uncover financial discrepancies, while blockchain bookkeeping relies on an immutable ledger that records every transaction with cryptographic proof, ensuring transparency and tamper-resistance. The immutable ledger in blockchain provides a permanent, time-stamped audit trail, making it challenging to alter records without detection and enhancing trust in financial data integrity. Discover how integrating forensic accounting methods with blockchain's immutable ledger can revolutionize auditing and fraud detection.
Transaction verification
Forensic accounting specializes in investigating financial discrepancies through detailed transaction verification to detect fraud, ensuring compliance and accuracy in financial records. Blockchain bookkeeping enhances transaction verification by using decentralized ledger technology, providing immutable, transparent, and real-time validation of every transaction across the network. Explore the evolving synergy between forensic accounting and blockchain capabilities to improve transaction integrity and audit processes.
Source and External Links
Forensic Accounting Career Overview - Forensic accounting involves analyzing financial records to detect crimes like fraud and embezzlement, requiring skills in data analysis and legal proceedings.
What is Forensic Accounting? - Forensic accounting is the process of investigating financial records to uncover fraud and financial misconduct, often involving advanced technology to track suspicious transactions.
Forensic accounting - Forensic accounting specializes in investigating financial crimes, translating complex financial data into understandable terms for legal proceedings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com