Zero trust accounting emphasizes real-time verification and strict access controls to enhance data security in financial record-keeping. Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, regardless of cash flow, providing a comprehensive view of financial performance. Explore the key differences and advantages of each approach to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
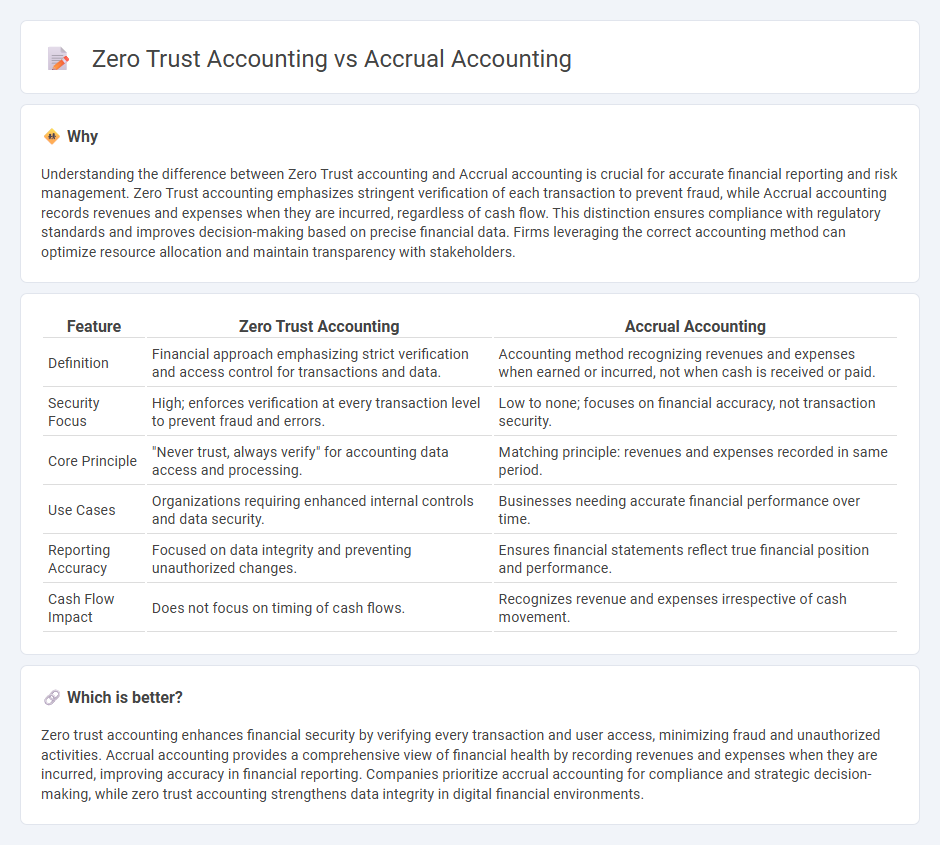
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust accounting and Accrual accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and risk management. Zero Trust accounting emphasizes stringent verification of each transaction to prevent fraud, while Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they are incurred, regardless of cash flow. This distinction ensures compliance with regulatory standards and improves decision-making based on precise financial data. Firms leveraging the correct accounting method can optimize resource allocation and maintain transparency with stakeholders.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Trust Accounting | Accrual Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial approach emphasizing strict verification and access control for transactions and data. | Accounting method recognizing revenues and expenses when earned or incurred, not when cash is received or paid. |
| Security Focus | High; enforces verification at every transaction level to prevent fraud and errors. | Low to none; focuses on financial accuracy, not transaction security. |
| Core Principle | "Never trust, always verify" for accounting data access and processing. | Matching principle: revenues and expenses recorded in same period. |
| Use Cases | Organizations requiring enhanced internal controls and data security. | Businesses needing accurate financial performance over time. |
| Reporting Accuracy | Focused on data integrity and preventing unauthorized changes. | Ensures financial statements reflect true financial position and performance. |
| Cash Flow Impact | Does not focus on timing of cash flows. | Recognizes revenue and expenses irrespective of cash movement. |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting enhances financial security by verifying every transaction and user access, minimizing fraud and unauthorized activities. Accrual accounting provides a comprehensive view of financial health by recording revenues and expenses when they are incurred, improving accuracy in financial reporting. Companies prioritize accrual accounting for compliance and strategic decision-making, while zero trust accounting strengthens data integrity in digital financial environments.
Connection
Zero trust accounting enhances accuracy and security in accrual accounting by rigorously verifying every transaction before recording accrued expenses and revenues. This approach ensures that only validated data is included in financial statements, reducing errors and fraud risks inherent to accrual accounting's reliance on estimated and future transactions. Implementing zero trust principles strengthens internal controls and compliance, supporting reliable accrual-based financial reporting.
Key Terms
Revenue Recognition
Accrual accounting recognizes revenue when earned, matching income with related expenses regardless of cash flow, ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with GAAP standards. Zero trust accounting emphasizes continuous verification and access control over financial data to prevent fraud and unauthorized modifications during revenue recognition processes. Explore how these methodologies impact your organization's financial integrity and compliance by learning more.
Expense Matching
Accrual accounting records expenses when they are incurred, ensuring precise expense matching by recognizing costs in the period they relate to, which enhances financial accuracy. Zero trust accounting emphasizes strict verification and validation of expenses to prevent unauthorized transactions, focusing on security rather than timing of expense recognition. Explore how these methodologies impact financial reporting and internal controls for a comprehensive understanding.
Transaction Verification
Accrual accounting records revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, ensuring accurate financial reporting through recognition of transactions irrespective of cash flow timing. Zero trust accounting emphasizes continuous transaction verification by employing strict access controls, encryption, and real-time authentication to prevent unauthorized financial activities and enhance security. Explore how combining these methods can optimize financial integrity and safeguard sensitive transaction data.
Source and External Links
Accrual-Based Accounting Explained: What It Is, Advantages ... - Accrual accounting records revenues when earned and expenses when incurred, not when cash changes hands, providing a more accurate financial picture and is required by GAAP and SEC for public companies.
Accrual Accounting - Guide, How it Works, Definition - Accrual accounting records revenues earned and expenses incurred regardless of cash payment timing, matching expenses to revenues within the same period for accurate financial reporting.
Accrual Accounting Explained: Examples, Journal Entries, & More - Accrual accounting involves recognizing revenues and expenses when incurred or earned, including prepaid expenses and accruals, to reflect true economic activity in each reporting period.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com