Dark data auditing uncovers hidden and unstructured information within accounting systems that traditional transaction testing often overlooks, enhancing financial accuracy and compliance. Transaction testing systematically examines individual entries and records to ensure transactional accuracy and prevent errors or fraud. Explore more to understand the distinct roles and benefits of dark data auditing and transaction testing in modern accounting practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark data auditing and transaction testing is crucial for accurate financial analysis and risk management. Dark data auditing uncovers hidden, unstructured information that can reveal fraud or compliance issues. Transaction testing focuses on verifying the accuracy and legitimacy of recorded financial transactions. Differentiating these methods ensures comprehensive auditing and strengthens internal controls.
Comparison Table
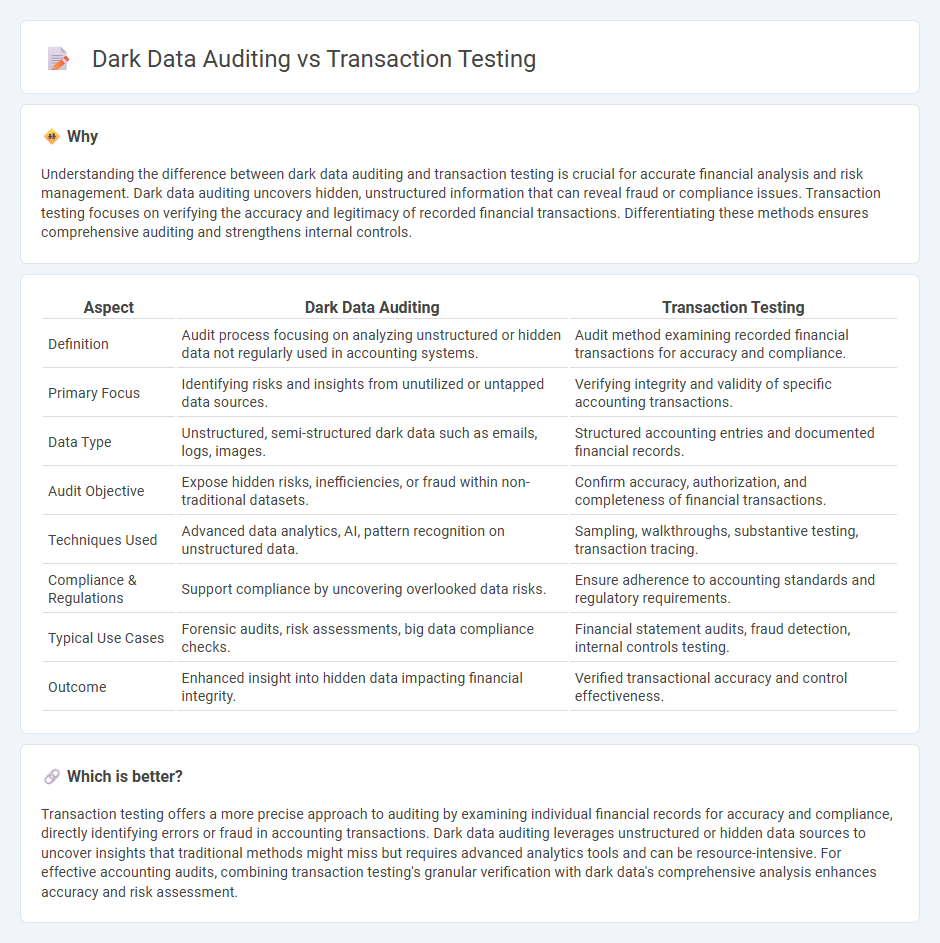
| Aspect | Dark Data Auditing | Transaction Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Audit process focusing on analyzing unstructured or hidden data not regularly used in accounting systems. | Audit method examining recorded financial transactions for accuracy and compliance. |
| Primary Focus | Identifying risks and insights from unutilized or untapped data sources. | Verifying integrity and validity of specific accounting transactions. |
| Data Type | Unstructured, semi-structured dark data such as emails, logs, images. | Structured accounting entries and documented financial records. |
| Audit Objective | Expose hidden risks, inefficiencies, or fraud within non-traditional datasets. | Confirm accuracy, authorization, and completeness of financial transactions. |
| Techniques Used | Advanced data analytics, AI, pattern recognition on unstructured data. | Sampling, walkthroughs, substantive testing, transaction tracing. |
| Compliance & Regulations | Support compliance by uncovering overlooked data risks. | Ensure adherence to accounting standards and regulatory requirements. |
| Typical Use Cases | Forensic audits, risk assessments, big data compliance checks. | Financial statement audits, fraud detection, internal controls testing. |
| Outcome | Enhanced insight into hidden data impacting financial integrity. | Verified transactional accuracy and control effectiveness. |
Which is better?
Transaction testing offers a more precise approach to auditing by examining individual financial records for accuracy and compliance, directly identifying errors or fraud in accounting transactions. Dark data auditing leverages unstructured or hidden data sources to uncover insights that traditional methods might miss but requires advanced analytics tools and can be resource-intensive. For effective accounting audits, combining transaction testing's granular verification with dark data's comprehensive analysis enhances accuracy and risk assessment.
Connection
Dark data auditing uncovers hidden, unstructured information within accounting records that may impact financial accuracy and compliance. Transaction testing systematically examines financial transactions to validate their authenticity and adherence to accounting standards. Integrating dark data auditing with transaction testing enhances the detection of discrepancies, fraud risks, and ensures comprehensive audit quality in accounting processes.
Key Terms
Sampling
Transaction testing utilizes statistical sampling methods to select representative transactions for accuracy and compliance verification, ensuring audit efficiency and reducing resource consumption. Dark data auditing involves exploratory sampling techniques aimed at uncovering hidden or unstructured data that might contain valuable insights or risks previously unassessed. Discover more about how sampling strategies optimize transaction testing and dark data auditing for comprehensive risk management.
Data Integrity
Transaction testing ensures data integrity by validating the accuracy and completeness of data recorded in financial and operational systems, identifying discrepancies or anomalies in real-time. Dark data auditing uncovers and assesses unstructured, unused, or hidden data assets, revealing integrity risks that traditional audits often overlook. Explore detailed methodologies for safeguarding your data integrity through comprehensive transaction testing and dark data auditing.
Anomaly Detection
Transaction testing analyzes financial or operational records to identify irregularities, while dark data auditing uncovers hidden or unused data that may contain anomalies not evident in standard datasets. Anomaly detection in transaction testing often relies on rule-based or statistical methods to flag unusual patterns, whereas dark data auditing employs advanced machine learning techniques to reveal subtle or complex inconsistencies within unstructured or semi-structured data sources. Explore advanced strategies to enhance anomaly detection in both transaction testing and dark data auditing for improved operational insights.
Source and External Links
Transaction Testing - FDIC - Transaction testing is the process of testing individual loans or accounts to ensure adherence to policy, underwriting, risk controls, and reporting accuracy, commonly used during bank examinations to assess loan quality and control effectiveness.
Transaction Testing Services - MBG Corporate Services - Transaction testing validates the integrity and continuity of business transactions by examining specific transactions and internal controls to identify risks like fictitious transactions or conflicts of interest.
Definition of Test of Transaction - AllBusiness.com - Transaction testing in auditing involves verifying transaction amounts and tracing them to financial statements to assess internal control reliability and establish an error rate to determine audit scope.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com