Carbon accounting focuses specifically on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions, quantifying carbon footprints to help organizations reduce their impact on climate change. Environmental accounting encompasses a broader scope, tracking all environmental costs and benefits, including resource use, pollution, and biodiversity impacts, to support sustainable decision-making. Discover more about how these accounting practices drive environmental responsibility and strategic planning.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and environmental accounting is crucial for accurately measuring and managing an organization's environmental impact. Carbon accounting specifically quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to address climate change, while environmental accounting encompasses a broader evaluation of ecological costs and resource usage. Effective differentiation enables companies to comply with regulations, optimize sustainability strategies, and enhance corporate social responsibility reporting. Precise data from both accounting types supports informed decision-making for reducing overall environmental footprints.
Comparison Table
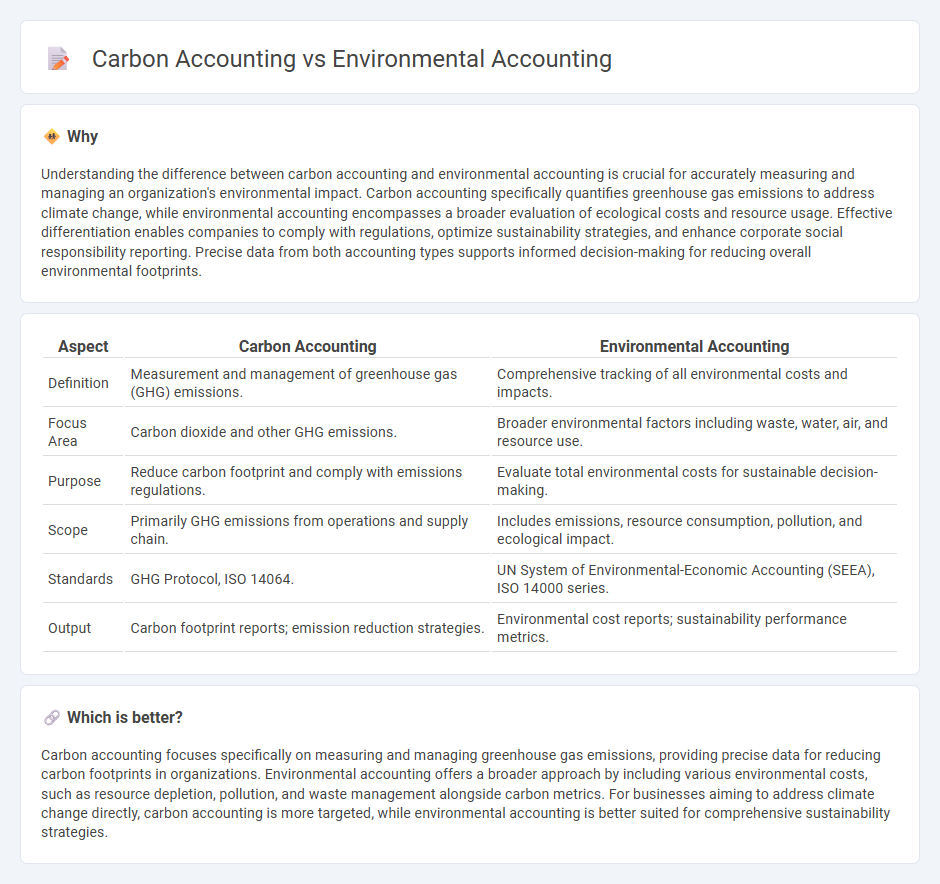
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | Environmental Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement and management of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. | Comprehensive tracking of all environmental costs and impacts. |
| Focus Area | Carbon dioxide and other GHG emissions. | Broader environmental factors including waste, water, air, and resource use. |
| Purpose | Reduce carbon footprint and comply with emissions regulations. | Evaluate total environmental costs for sustainable decision-making. |
| Scope | Primarily GHG emissions from operations and supply chain. | Includes emissions, resource consumption, pollution, and ecological impact. |
| Standards | GHG Protocol, ISO 14064. | UN System of Environmental-Economic Accounting (SEEA), ISO 14000 series. |
| Output | Carbon footprint reports; emission reduction strategies. | Environmental cost reports; sustainability performance metrics. |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting focuses specifically on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions, providing precise data for reducing carbon footprints in organizations. Environmental accounting offers a broader approach by including various environmental costs, such as resource depletion, pollution, and waste management alongside carbon metrics. For businesses aiming to address climate change directly, carbon accounting is more targeted, while environmental accounting is better suited for comprehensive sustainability strategies.
Connection
Carbon accounting is a subset of environmental accounting focused specifically on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions associated with business activities. Both approaches provide data essential for sustainability reporting, regulatory compliance, and strategic decision-making aimed at reducing environmental impact. Integrating carbon accounting within broader environmental accounting frameworks enables organizations to comprehensively track resource consumption, waste generation, and emissions for improved corporate responsibility and environmental performance.
Key Terms
**Environmental Accounting:**
Environmental accounting measures the economic impact of environmental policies and natural resource use, integrating ecological costs into financial decision-making. It captures data on waste management, pollution control, and resource depletion to inform sustainable business practices and regulatory compliance. Explore further to understand how environmental accounting promotes corporate transparency and long-term ecological stewardship.
Natural Resource Valuation
Environmental accounting quantifies the economic value of natural resources and ecosystem services to integrate environmental costs into financial decision-making. Carbon accounting specifically measures greenhouse gas emissions and carbon footprints to manage and reduce carbon impact. Explore how natural resource valuation enhances sustainable business strategies and policy development.
Environmental Liabilities
Environmental accounting encompasses the measurement and reporting of all environmental costs, including liabilities like pollution cleanup and legal penalties. Carbon accounting specifically tracks greenhouse gas emissions and carbon-related liabilities such as carbon taxes or carbon credit obligations. Explore more to understand how each approach addresses environmental liabilities differently and supports sustainability goals.
Source and External Links
Environmental Accounting - Environmental accounting is a field that identifies resource use, measures, and communicates costs of a company's or national economic impact on the environment.
Environmental Accounting - Environmental accounting is a specialized method of evaluating and analyzing the costs incurred by organizations due to their impact on the natural environment.
An Introduction to Environmental Accounting - This primer focuses on the application of environmental accounting as a managerial accounting tool for internal business decisions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com