Real-time audits provide continuous monitoring of financial transactions, ensuring immediate detection of discrepancies and enhancing accuracy in accounting records. Transaction sampling involves reviewing selected subsets of data, offering efficiency in identifying errors or fraud across large volumes of transactions. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which method suits your organization's auditing needs.
Why it is important
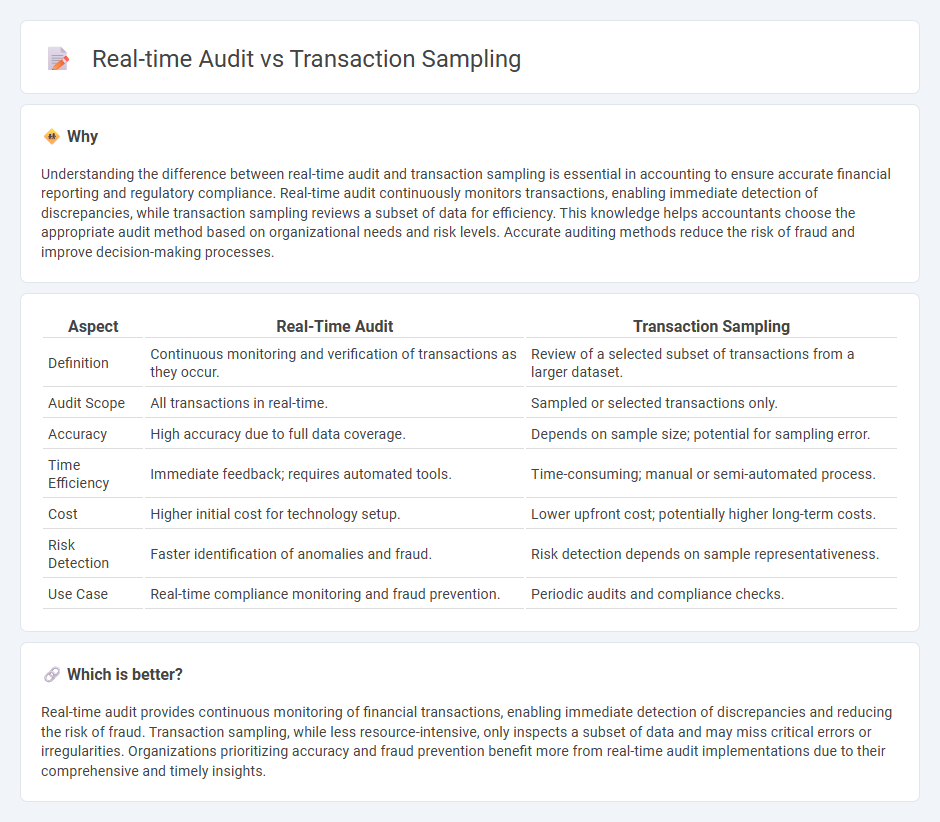
Understanding the difference between real-time audit and transaction sampling is essential in accounting to ensure accurate financial reporting and regulatory compliance. Real-time audit continuously monitors transactions, enabling immediate detection of discrepancies, while transaction sampling reviews a subset of data for efficiency. This knowledge helps accountants choose the appropriate audit method based on organizational needs and risk levels. Accurate auditing methods reduce the risk of fraud and improve decision-making processes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Real-Time Audit | Transaction Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous monitoring and verification of transactions as they occur. | Review of a selected subset of transactions from a larger dataset. |
| Audit Scope | All transactions in real-time. | Sampled or selected transactions only. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy due to full data coverage. | Depends on sample size; potential for sampling error. |
| Time Efficiency | Immediate feedback; requires automated tools. | Time-consuming; manual or semi-automated process. |
| Cost | Higher initial cost for technology setup. | Lower upfront cost; potentially higher long-term costs. |
| Risk Detection | Faster identification of anomalies and fraud. | Risk detection depends on sample representativeness. |
| Use Case | Real-time compliance monitoring and fraud prevention. | Periodic audits and compliance checks. |
Which is better?
Real-time audit provides continuous monitoring of financial transactions, enabling immediate detection of discrepancies and reducing the risk of fraud. Transaction sampling, while less resource-intensive, only inspects a subset of data and may miss critical errors or irregularities. Organizations prioritizing accuracy and fraud prevention benefit more from real-time audit implementations due to their comprehensive and timely insights.
Connection
Real-time audit leverages continuous monitoring of financial transactions to detect anomalies instantly, while transaction sampling focuses on selecting representative subsets of data for detailed examination. Combining these techniques enhances accuracy by enabling auditors to identify irregularities in sampled transactions as they occur, improving the overall reliability of financial reporting. This integration streamlines audit processes, reduces risk, and supports compliance with regulatory standards through timely detection and investigation.
Key Terms
Sample Selection Criteria
Transaction sampling selects transactions based on predetermined criteria such as risk level, transaction size, or time period to provide a representative subset for detailed review. Real-time audit utilizes continuous monitoring and automated alerts, analyzing each transaction as it occurs to detect anomalies instantly. Discover how these methods optimize audit effectiveness by exploring their sample selection strategies in depth.
Continuous Monitoring
Transaction sampling analyzes a subset of financial data to identify anomalies and compliance issues, offering periodic insights into business processes. Real-time audit under continuous monitoring continuously examines all transactions, enabling immediate detection of irregularities and enhancing risk management accuracy. Explore how integrating continuous monitoring transforms audit effectiveness and operational transparency.
Audit Evidence
Transaction sampling provides audit evidence by examining a subset of transactions to infer the accuracy of an entire dataset, offering efficiency in large-scale audits but potential gaps in coverage. Real-time audits deliver continuous, up-to-the-minute verification, enhancing the reliability of audit evidence through immediate detection of anomalies and errors. Explore how these methods impact audit quality and decision-making in dynamic financial environments.
Source and External Links
Transaction sampling in Elastic APM - This page explains how Elastic APM uses transaction sampling to reduce data overhead by making sampling decisions at the root of distributed traces.
Sentry for JavaScript Sampling - Sentry's transaction sampling allows for configurable sample rates and inherits decisions from parent transactions if applicable.
Transaction sampling in Elastic APM Overview - This guide covers Elastic APM's support for head-based probability sampling, where the sampling decision is made at the start of each trace.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com