Data lake auditing consolidates vast financial datasets in a centralized repository to enable comprehensive, retrospective analysis of accounting records and transactions. Continuous auditing employs automated tools and real-time monitoring to detect anomalies and ensure compliance throughout ongoing financial processes. Explore the benefits and applications of these auditing approaches to enhance your accounting accuracy and control.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between data lake auditing and continuous auditing is crucial for accounting professionals to ensure accurate financial reporting and compliance with regulatory standards. Data lake auditing involves examining vast, unstructured datasets stored in data lakes, enabling comprehensive historical data analysis. Continuous auditing provides real-time monitoring and evaluation of transactions to detect anomalies and ensure ongoing accuracy. Accurate differentiation enhances fraud prevention, risk management, and decision-making processes in accounting.
Comparison Table
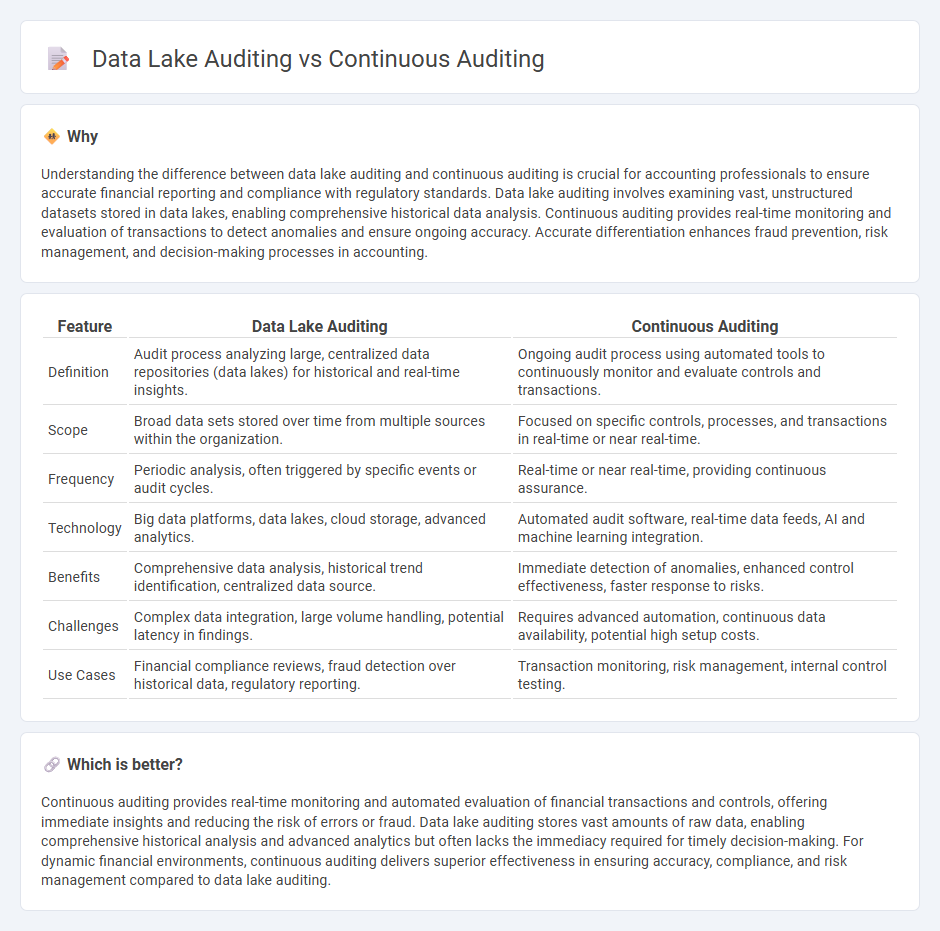
| Feature | Data Lake Auditing | Continuous Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Audit process analyzing large, centralized data repositories (data lakes) for historical and real-time insights. | Ongoing audit process using automated tools to continuously monitor and evaluate controls and transactions. |
| Scope | Broad data sets stored over time from multiple sources within the organization. | Focused on specific controls, processes, and transactions in real-time or near real-time. |
| Frequency | Periodic analysis, often triggered by specific events or audit cycles. | Real-time or near real-time, providing continuous assurance. |
| Technology | Big data platforms, data lakes, cloud storage, advanced analytics. | Automated audit software, real-time data feeds, AI and machine learning integration. |
| Benefits | Comprehensive data analysis, historical trend identification, centralized data source. | Immediate detection of anomalies, enhanced control effectiveness, faster response to risks. |
| Challenges | Complex data integration, large volume handling, potential latency in findings. | Requires advanced automation, continuous data availability, potential high setup costs. |
| Use Cases | Financial compliance reviews, fraud detection over historical data, regulatory reporting. | Transaction monitoring, risk management, internal control testing. |
Which is better?
Continuous auditing provides real-time monitoring and automated evaluation of financial transactions and controls, offering immediate insights and reducing the risk of errors or fraud. Data lake auditing stores vast amounts of raw data, enabling comprehensive historical analysis and advanced analytics but often lacks the immediacy required for timely decision-making. For dynamic financial environments, continuous auditing delivers superior effectiveness in ensuring accuracy, compliance, and risk management compared to data lake auditing.
Connection
Data lake auditing enhances continuous auditing by providing a centralized repository for vast amounts of accounting data, enabling real-time access and analysis. Continuous auditing leverages this constant data flow to detect anomalies and ensure compliance more efficiently. The integration of data lake auditing with continuous auditing streamlines risk management and improves financial accuracy through timely data validation.
Key Terms
Real-time monitoring
Continuous auditing provides real-time monitoring by integrating automated data analysis and transaction verification within an organization's IT systems, enabling immediate detection of anomalies and compliance issues. Data lake auditing involves collecting vast amounts of raw data for retrospective analysis, which may delay real-time insights but supports comprehensive historical audits and data-driven decision-making. Explore more about how continuous auditing enhances proactive risk management and real-time compliance monitoring.
Centralized data repository
Continuous auditing leverages real-time data monitoring to ensure ongoing compliance and accuracy within financial and operational systems, while data lake auditing involves examining large, centralized data repositories that store structured and unstructured data from multiple sources. Centralized data repositories in data lake auditing enable comprehensive visibility and traceability across vast datasets, improving anomaly detection and audit scope. Explore how integrating continuous auditing with data lake strategies enhances data integrity and risk management.
Automated anomaly detection
Continuous auditing leverages real-time data analysis and automated anomaly detection algorithms to identify irregularities promptly, enhancing compliance and risk management. Data lake auditing integrates vast, diverse datasets enabling thorough anomaly detection across structured and unstructured data, supporting comprehensive forensic investigations. Explore the latest advancements in automated anomaly detection techniques for continuous and data lake auditing to optimize your audit processes.
Source and External Links
Continuous audit and monitoring - PwC - Continuous auditing is a method where auditors perform audit-related activities continuously using analytical rules to detect anomalies in transactions in near real-time, enabling earlier risk detection and remediation.
A framework for continuous auditing: Why companies don't need to ... - Continuous auditing automates control and risk assessments on a frequent basis to supplement traditional auditing, allowing more timely identification of risks and control effectiveness.
Continuous Auditing: Advantages & Challenges - DataSnipper - Continuous auditing focuses on auditor-led automated analysis of financial transactions in near real-time, improving accuracy and providing comprehensive data coverage compared to traditional sampling methods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com