Sustainable ledgers incorporate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics alongside financial data, enhancing long-term value assessment beyond traditional ledger systems that focus solely on financial transactions. Traditional ledgers offer reliable financial record-keeping but lack the capacity to integrate sustainability factors essential for modern business performance evaluation. Explore how sustainable ledgers can transform accounting practices by aligning financial reporting with corporate responsibility goals.
Why it is important
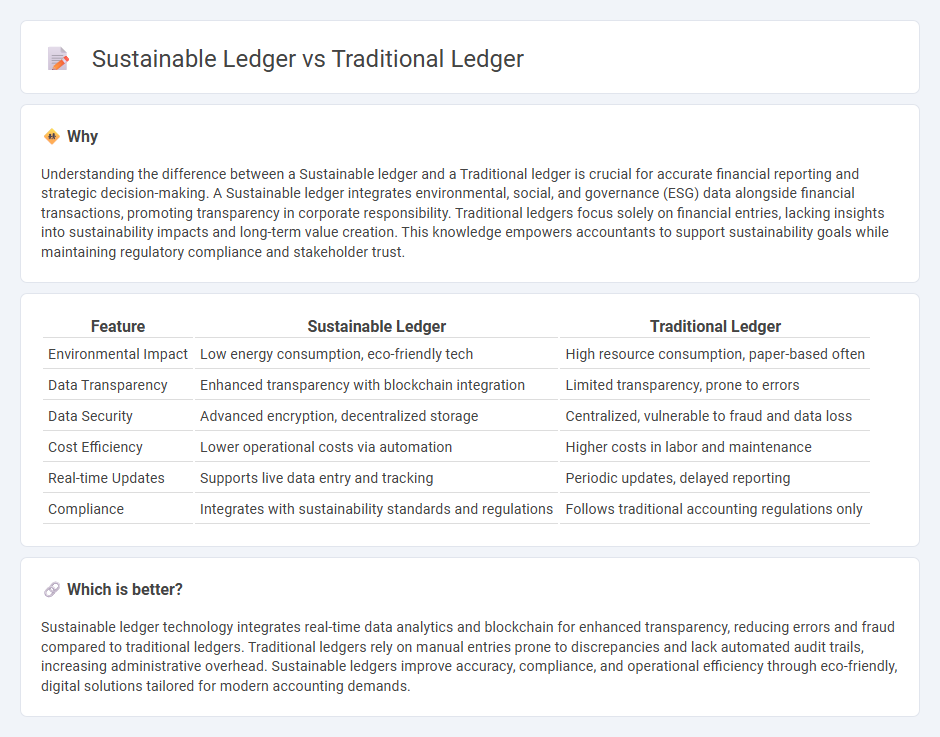
Understanding the difference between a Sustainable ledger and a Traditional ledger is crucial for accurate financial reporting and strategic decision-making. A Sustainable ledger integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data alongside financial transactions, promoting transparency in corporate responsibility. Traditional ledgers focus solely on financial entries, lacking insights into sustainability impacts and long-term value creation. This knowledge empowers accountants to support sustainability goals while maintaining regulatory compliance and stakeholder trust.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Sustainable Ledger | Traditional Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Low energy consumption, eco-friendly tech | High resource consumption, paper-based often |
| Data Transparency | Enhanced transparency with blockchain integration | Limited transparency, prone to errors |
| Data Security | Advanced encryption, decentralized storage | Centralized, vulnerable to fraud and data loss |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs via automation | Higher costs in labor and maintenance |
| Real-time Updates | Supports live data entry and tracking | Periodic updates, delayed reporting |
| Compliance | Integrates with sustainability standards and regulations | Follows traditional accounting regulations only |
Which is better?
Sustainable ledger technology integrates real-time data analytics and blockchain for enhanced transparency, reducing errors and fraud compared to traditional ledgers. Traditional ledgers rely on manual entries prone to discrepancies and lack automated audit trails, increasing administrative overhead. Sustainable ledgers improve accuracy, compliance, and operational efficiency through eco-friendly, digital solutions tailored for modern accounting demands.
Connection
Sustainable ledger integrates environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics into financial records, complementing traditional ledgers by expanding the scope of accounting beyond mere financial transactions. Both systems rely on double-entry bookkeeping principles to ensure accuracy and transparency, facilitating comprehensive reporting for stakeholders. By linking sustainability data with conventional financial information, organizations achieve a holistic view of performance that supports informed decision-making and regulatory compliance.
Key Terms
Double-entry bookkeeping
Traditional ledgers rely on double-entry bookkeeping to ensure accuracy by recording equal debit and credit entries for every transaction, facilitating transparent financial tracking. Sustainable ledgers integrate this method with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, enabling organizations to balance financial performance with sustainability goals. Discover how combining double-entry bookkeeping with sustainability practices drives responsible business decisions.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics
Traditional ledgers primarily track financial transactions without integrating Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics, limiting their scope in sustainability reporting. Sustainable ledgers embed ESG data, enabling organizations to monitor carbon footprints, social impact, and governance compliance in real-time for comprehensive accountability. Explore how sustainable ledgers transform corporate responsibility by visiting our detailed resource.
Carbon accounting
Traditional ledgers record financial transactions without integrating environmental impact data, often overlooking carbon emissions associated with business activities. Sustainable ledgers embed carbon accounting frameworks, enabling organizations to track, report, and manage carbon footprints in real-time, thus enhancing transparency and supporting sustainability goals. Explore how sustainable ledgers revolutionize carbon accounting for improved environmental responsibility.
Source and External Links
Blockchain Ledger Vs Ordinary Ledger: A Detailed ... - A traditional ledger, also called an ordinary ledger, is a financial record book where debits and credits are recorded based on double-entry bookkeeping, summarizing a company's financial transactions to create trial balances and financial statements.
Difference Between A Blockchain Ledger and An Ordinary ... - An ordinary ledger is a document that summarizes classified credits and debits, listing assets, revenues, liabilities, equity, and expenses, often maintained manually or digitally, and serving as the foundation for accounting systems.
Ledgers 101: Understanding Modern Financial Record-Keeping - Traditional ledgers use single-entry or double-entry bookkeeping systems, with double-entry recording each financial transaction twice (debit and credit) to provide accuracy and a comprehensive financial view for businesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com