Greenwashing detection involves identifying deceptive corporate practices that falsely portray environmental responsibility, while earnings management focuses on manipulating financial reports to influence perceived company performance. Both practices compromise transparency and mislead stakeholders by distorting the true economic and ethical standing of a business. Explore detailed strategies to distinguish between greenwashing and earnings management for improved corporate accountability.
Why it is important
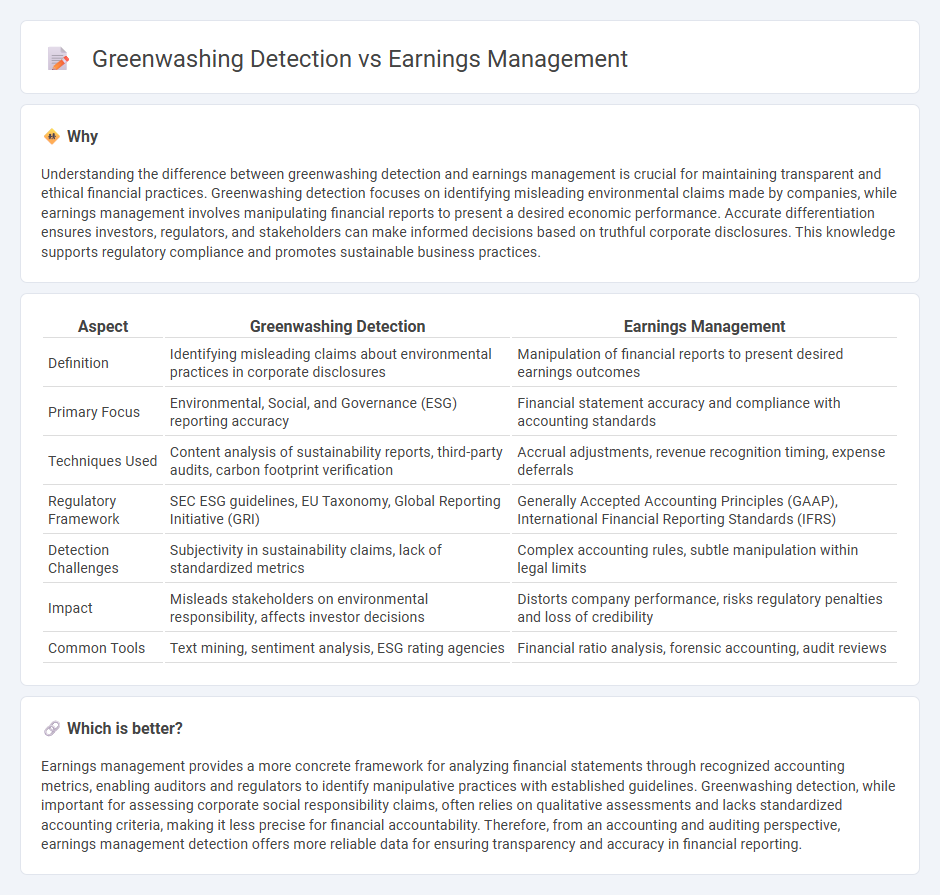
Understanding the difference between greenwashing detection and earnings management is crucial for maintaining transparent and ethical financial practices. Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying misleading environmental claims made by companies, while earnings management involves manipulating financial reports to present a desired economic performance. Accurate differentiation ensures investors, regulators, and stakeholders can make informed decisions based on truthful corporate disclosures. This knowledge supports regulatory compliance and promotes sustainable business practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Greenwashing Detection | Earnings Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Identifying misleading claims about environmental practices in corporate disclosures | Manipulation of financial reports to present desired earnings outcomes |
| Primary Focus | Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting accuracy | Financial statement accuracy and compliance with accounting standards |
| Techniques Used | Content analysis of sustainability reports, third-party audits, carbon footprint verification | Accrual adjustments, revenue recognition timing, expense deferrals |
| Regulatory Framework | SEC ESG guidelines, EU Taxonomy, Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) | Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP), International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) |
| Detection Challenges | Subjectivity in sustainability claims, lack of standardized metrics | Complex accounting rules, subtle manipulation within legal limits |
| Impact | Misleads stakeholders on environmental responsibility, affects investor decisions | Distorts company performance, risks regulatory penalties and loss of credibility |
| Common Tools | Text mining, sentiment analysis, ESG rating agencies | Financial ratio analysis, forensic accounting, audit reviews |
Which is better?
Earnings management provides a more concrete framework for analyzing financial statements through recognized accounting metrics, enabling auditors and regulators to identify manipulative practices with established guidelines. Greenwashing detection, while important for assessing corporate social responsibility claims, often relies on qualitative assessments and lacks standardized accounting criteria, making it less precise for financial accountability. Therefore, from an accounting and auditing perspective, earnings management detection offers more reliable data for ensuring transparency and accuracy in financial reporting.
Connection
Greenwashing detection and earnings management intersect through their impact on financial transparency and corporate accountability. Companies engaging in greenwashing may manipulate earnings reports to present more favorable environmental practices, obscuring true sustainability performance. Effective detection of greenwashing relies on analyzing earnings management patterns that mask environmental liabilities or inflate eco-friendly claims.
Key Terms
Financial Statement Analysis
Earnings management involves manipulating financial statements to present a desired financial position, while greenwashing detection targets misleading environmental claims within corporate disclosures. Financial statement analysis plays a crucial role in identifying inconsistencies or anomalies that may suggest earnings manipulation or insincere sustainability reporting. Explore advanced methodologies and tools used in financial statement analysis to deepen your understanding of detecting earnings management and greenwashing practices.
Non-GAAP Metrics
Non-GAAP metrics often serve as tools for earnings management, allowing companies to present adjusted financial results that may obscure true performance. In greenwashing detection, these non-GAAP figures are scrutinized to identify discrepancies between reported environmental efforts and actual sustainability impact. Explore how advanced data analysis techniques enhance transparency and accuracy in both earnings and greenwashing evaluations.
Sustainability Reporting
Earnings management in sustainability reporting involves manipulating financial data to present a more favorable environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance than actual. Greenwashing detection focuses on identifying misleading claims or exaggerations about a company's sustainability practices to protect stakeholders from false information. Explore advanced techniques and frameworks to enhance transparency and reliability in sustainability disclosures.
Source and External Links
Earnings Management - Definition, Examples, and Types - Earnings management is a practice where companies manipulate financial statements to present a favorable view of their financial performance, often to meet earnings targets or stabilize stock prices.
Earnings Management in Accounting - This practice involves using accounting techniques to smooth out fluctuations in income, making profits appear more stable and consistent for shareholders.
Earnings Management and Manipulation - Earnings management involves accelerating or deferring expenses or revenues to show consistent growth, often through aggressive interpretations of accounting rules.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com