Carbon accounting focuses on measuring and managing an organization's greenhouse gas emissions to support sustainability goals and regulatory compliance, while financial accounting deals with the systematic recording and reporting of financial transactions to assess economic performance. Both accounting types require precise data collection and analysis but serve different strategic purposes: environmental impact versus financial health. Explore how these accounting practices intersect to drive corporate responsibility and transparency.
Why it is important
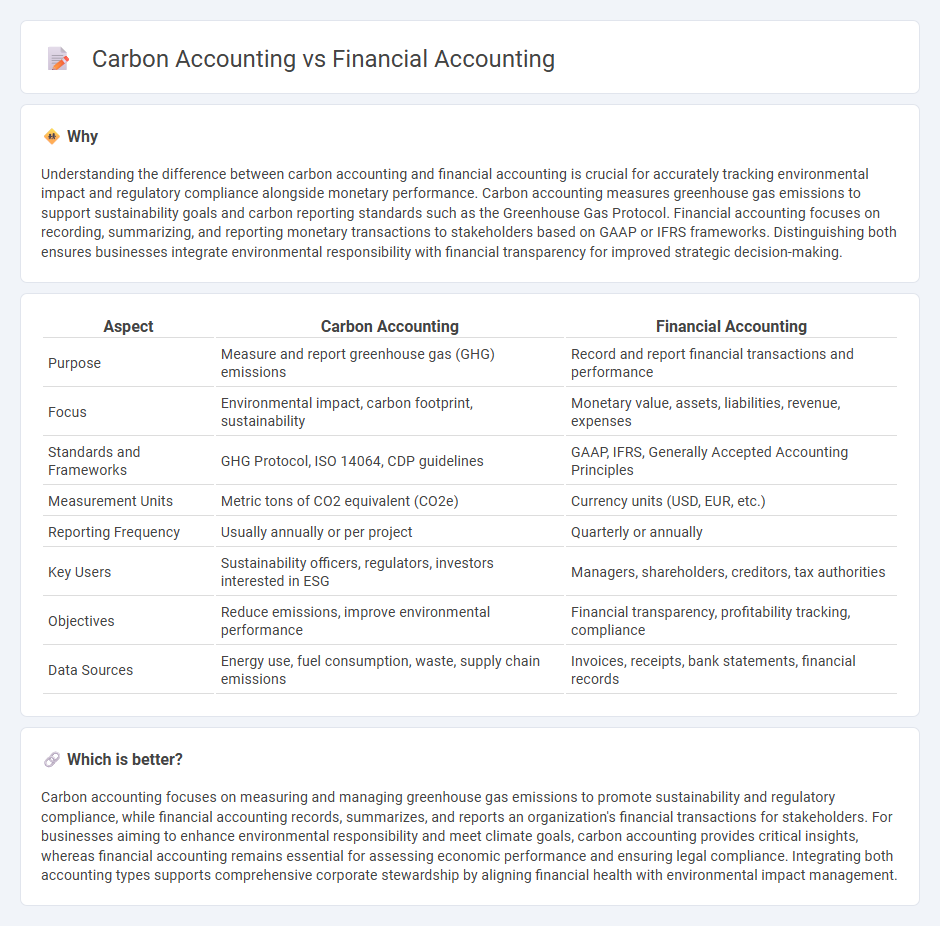
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and financial accounting is crucial for accurately tracking environmental impact and regulatory compliance alongside monetary performance. Carbon accounting measures greenhouse gas emissions to support sustainability goals and carbon reporting standards such as the Greenhouse Gas Protocol. Financial accounting focuses on recording, summarizing, and reporting monetary transactions to stakeholders based on GAAP or IFRS frameworks. Distinguishing both ensures businesses integrate environmental responsibility with financial transparency for improved strategic decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | Financial Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measure and report greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions | Record and report financial transactions and performance |
| Focus | Environmental impact, carbon footprint, sustainability | Monetary value, assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses |
| Standards and Frameworks | GHG Protocol, ISO 14064, CDP guidelines | GAAP, IFRS, Generally Accepted Accounting Principles |
| Measurement Units | Metric tons of CO2 equivalent (CO2e) | Currency units (USD, EUR, etc.) |
| Reporting Frequency | Usually annually or per project | Quarterly or annually |
| Key Users | Sustainability officers, regulators, investors interested in ESG | Managers, shareholders, creditors, tax authorities |
| Objectives | Reduce emissions, improve environmental performance | Financial transparency, profitability tracking, compliance |
| Data Sources | Energy use, fuel consumption, waste, supply chain emissions | Invoices, receipts, bank statements, financial records |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting focuses on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions to promote sustainability and regulatory compliance, while financial accounting records, summarizes, and reports an organization's financial transactions for stakeholders. For businesses aiming to enhance environmental responsibility and meet climate goals, carbon accounting provides critical insights, whereas financial accounting remains essential for assessing economic performance and ensuring legal compliance. Integrating both accounting types supports comprehensive corporate stewardship by aligning financial health with environmental impact management.
Connection
Carbon accounting tracks greenhouse gas emissions in measurable units, providing critical data for sustainability reporting and regulatory compliance. Financial accounting integrates this environmental information into financial statements, impacting asset valuation, risk assessment, and disclosure requirements. The connection ensures businesses transparently report environmental costs alongside traditional financial metrics, enabling more informed decision-making and stakeholder trust.
Key Terms
**Financial Accounting:**
Financial accounting involves recording, summarizing, and reporting an organization's financial transactions to provide an accurate picture of its financial position, primarily through standardized statements like the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow report. It adheres to regulatory frameworks such as GAAP or IFRS to ensure transparency and comparability for stakeholders including investors, regulators, and management. Explore the distinctions between financial and carbon accounting to understand their unique roles and impacts.
Balance Sheet
Financial accounting centers on accurately recording and reporting a company's assets, liabilities, and equity to present a clear snapshot of its financial health on the Balance Sheet. Carbon accounting integrates environmental data, measuring greenhouse gas emissions linked to a company's operations, impacting the reporting of liabilities related to environmental compliance and carbon offset assets. Explore how combining these accounting practices can enhance sustainability reporting and corporate transparency.
Income Statement
Financial accounting focuses on recording and reporting revenue and expenses to determine net income on the income statement, critical for investors and regulatory compliance. Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions associated with a company's operations, often integrating environmental costs and carbon liabilities into financial reporting. Explore how merging these accounting practices can enhance transparency and sustainability performance.
Source and External Links
What Is Financial Accounting? - This webpage provides an overview of financial accounting, including its key principles, careers, and importance in the business world.
Financial accounting - This Wikipedia page covers the objectives, principles, and roles of financial accounting in business operations.
What Is Financial Accounting? - This blog post discusses the importance and functions of financial accounting in business management and decision-making.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com