Continuous audit leverages automated tools to provide real-time monitoring and evaluation of financial transactions, enhancing accuracy and timeliness in detecting discrepancies. System audit, on the other hand, focuses on assessing the overall effectiveness, security, and compliance of an organization's IT infrastructure and control systems. Explore further to understand the distinct benefits and applications of continuous and system audits in modern accounting practices.
Why it is important
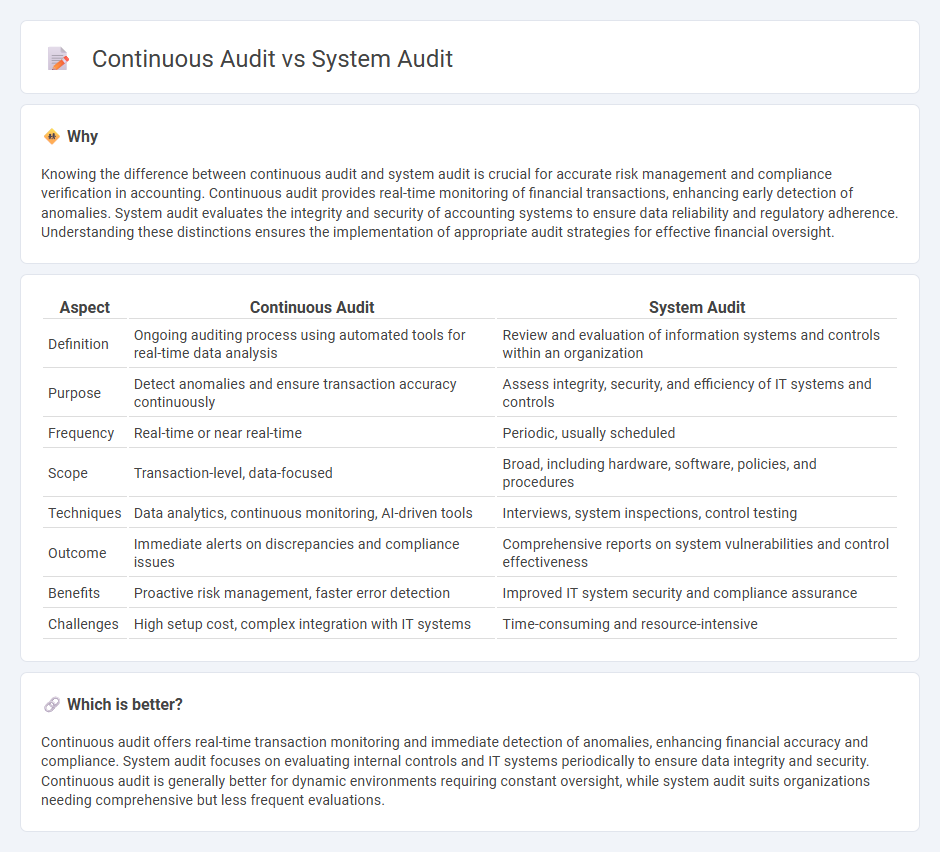
Knowing the difference between continuous audit and system audit is crucial for accurate risk management and compliance verification in accounting. Continuous audit provides real-time monitoring of financial transactions, enhancing early detection of anomalies. System audit evaluates the integrity and security of accounting systems to ensure data reliability and regulatory adherence. Understanding these distinctions ensures the implementation of appropriate audit strategies for effective financial oversight.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Audit | System Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing auditing process using automated tools for real-time data analysis | Review and evaluation of information systems and controls within an organization |
| Purpose | Detect anomalies and ensure transaction accuracy continuously | Assess integrity, security, and efficiency of IT systems and controls |
| Frequency | Real-time or near real-time | Periodic, usually scheduled |
| Scope | Transaction-level, data-focused | Broad, including hardware, software, policies, and procedures |
| Techniques | Data analytics, continuous monitoring, AI-driven tools | Interviews, system inspections, control testing |
| Outcome | Immediate alerts on discrepancies and compliance issues | Comprehensive reports on system vulnerabilities and control effectiveness |
| Benefits | Proactive risk management, faster error detection | Improved IT system security and compliance assurance |
| Challenges | High setup cost, complex integration with IT systems | Time-consuming and resource-intensive |
Which is better?
Continuous audit offers real-time transaction monitoring and immediate detection of anomalies, enhancing financial accuracy and compliance. System audit focuses on evaluating internal controls and IT systems periodically to ensure data integrity and security. Continuous audit is generally better for dynamic environments requiring constant oversight, while system audit suits organizations needing comprehensive but less frequent evaluations.
Connection
Continuous audit and system audit are interconnected through their shared goal of enhancing organizational transparency and accuracy in financial reporting. Continuous audit leverages automated tools to provide real-time or near-real-time data analysis, facilitating ongoing monitoring of transactions and controls within an accounting information system. This constant evaluation supports system audits by identifying risks, control weaknesses, and compliance issues, thereby improving the effectiveness and efficiency of traditional system audit processes.
Key Terms
System Audit:
System audit involves a thorough examination of an organization's information systems, evaluating controls, compliance, and security measures at a specific point in time to identify vulnerabilities and ensure data integrity. It emphasizes comprehensive risk assessment and control effectiveness, often aligning with regulatory standards such as ISO 27001 or COBIT frameworks. Explore how system audits enhance organizational security and governance by diving deeper into best practices and implementation strategies.
Internal Controls
System audit evaluates the design and effectiveness of internal controls at a specific point in time, providing a snapshot of system reliability and risk management. Continuous audit employs automated tools and real-time monitoring to assess internal controls on an ongoing basis, facilitating immediate detection of anomalies and quicker remediation. Explore deeper insights into how these audit approaches enhance internal control frameworks and compliance.
Risk Assessment
System audits evaluate risk assessment at specific points, reviewing controls and identifying vulnerabilities retrospectively. Continuous audits integrate real-time monitoring to detect risk fluctuations promptly, enhancing proactive mitigation strategies. Explore more to understand how continuous audit transforms risk management in dynamic environments.
Source and External Links
What Is A System Audit? - A system audit systematically examines and analyzes an organization's systems, processes, and controls to determine their effectiveness.
How To Become a System Auditor - This guide provides information on the role of a system auditor and the steps to become one, including job duties and salary information.
Information Technology Audit - An examination of management controls within an IT infrastructure to ensure assets are safeguarded and data integrity is maintained.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com