ESG assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance data to enhance transparency and investor confidence in sustainable practices. Social audits primarily assess labor conditions, human rights adherence, and community impact within organizations to ensure ethical standards. Explore more to understand how ESG assurance and social audits together strengthen corporate accountability.
Why it is important
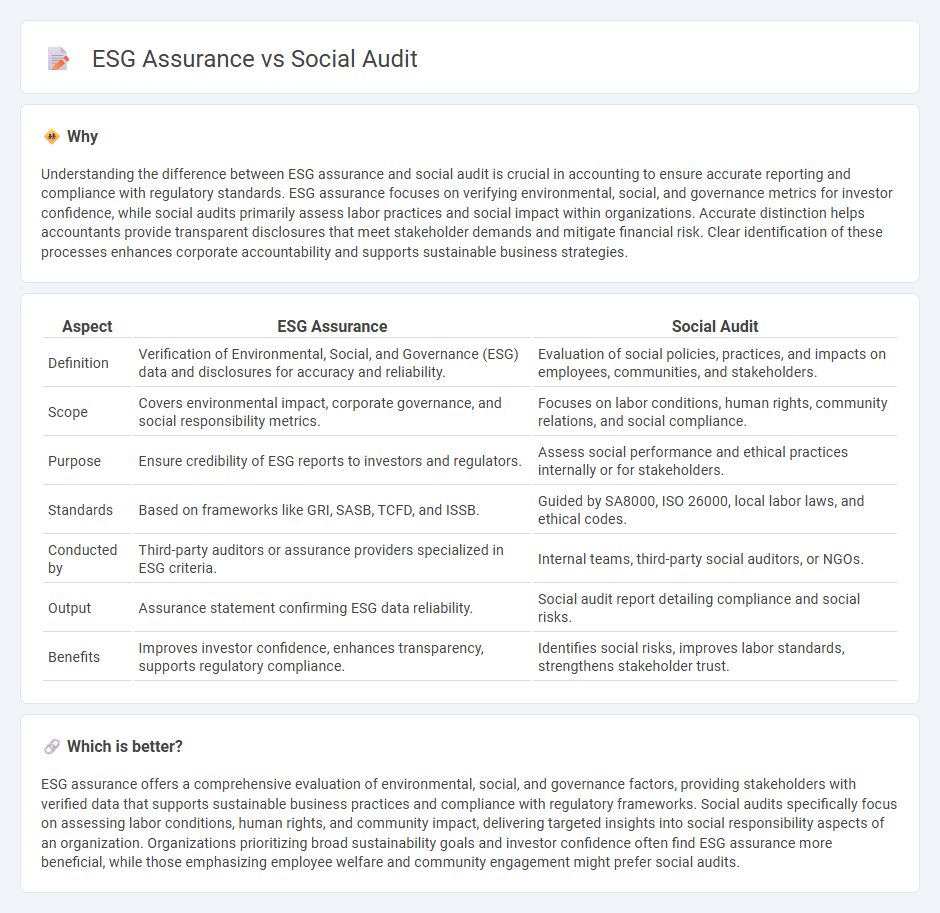
Understanding the difference between ESG assurance and social audit is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate reporting and compliance with regulatory standards. ESG assurance focuses on verifying environmental, social, and governance metrics for investor confidence, while social audits primarily assess labor practices and social impact within organizations. Accurate distinction helps accountants provide transparent disclosures that meet stakeholder demands and mitigate financial risk. Clear identification of these processes enhances corporate accountability and supports sustainable business strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | ESG Assurance | Social Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verification of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) data and disclosures for accuracy and reliability. | Evaluation of social policies, practices, and impacts on employees, communities, and stakeholders. |
| Scope | Covers environmental impact, corporate governance, and social responsibility metrics. | Focuses on labor conditions, human rights, community relations, and social compliance. |
| Purpose | Ensure credibility of ESG reports to investors and regulators. | Assess social performance and ethical practices internally or for stakeholders. |
| Standards | Based on frameworks like GRI, SASB, TCFD, and ISSB. | Guided by SA8000, ISO 26000, local labor laws, and ethical codes. |
| Conducted by | Third-party auditors or assurance providers specialized in ESG criteria. | Internal teams, third-party social auditors, or NGOs. |
| Output | Assurance statement confirming ESG data reliability. | Social audit report detailing compliance and social risks. |
| Benefits | Improves investor confidence, enhances transparency, supports regulatory compliance. | Identifies social risks, improves labor standards, strengthens stakeholder trust. |
Which is better?
ESG assurance offers a comprehensive evaluation of environmental, social, and governance factors, providing stakeholders with verified data that supports sustainable business practices and compliance with regulatory frameworks. Social audits specifically focus on assessing labor conditions, human rights, and community impact, delivering targeted insights into social responsibility aspects of an organization. Organizations prioritizing broad sustainability goals and investor confidence often find ESG assurance more beneficial, while those emphasizing employee welfare and community engagement might prefer social audits.
Connection
ESG assurance and social audit both focus on assessing a company's non-financial performance, with ESG assurance evaluating environmental, social, and governance metrics for investment confidence, while social audits specifically examine workplace conditions, labor rights, and community impact. These processes are interconnected as ESG frameworks increasingly incorporate social audit findings to validate the social criteria within sustainability reports. Integration of social audits into ESG assurance enhances transparency and accountability in corporate social responsibility disclosures.
Key Terms
Stakeholder engagement
Social audit emphasizes direct stakeholder engagement by collecting feedback and assessing community impact, ensuring transparency in social performance metrics. ESG assurance incorporates stakeholder perspectives within a broader environmental, social, and governance framework, validating companies' adherence to comprehensive sustainability standards. Explore the distinctions further to understand how each approach enhances stakeholder trust and corporate accountability.
Materiality
Social audit emphasizes assessing an organization's social impact by measuring stakeholder engagement and community welfare, whereas ESG assurance centers on verifying environmental, social, and governance data for investor transparency. Materiality in social audits involves identifying key social issues affecting specific communities, while ESG assurance prioritizes material risks and opportunities relevant to investors and regulatory compliance. Explore further to understand how integrating materiality enhances both social audits and ESG assurance processes for comprehensive sustainability reporting.
Verification
Social audit evaluates a company's social impact and compliance with labor standards through stakeholder engagement and data collection, whereas ESG assurance verifies environmental, social, and governance disclosures using third-party verification to ensure accuracy and reliability. ESG assurance incorporates robust methodologies like limited or reasonable assurance engagements aligned with international standards such as ISAE 3000, enhancing investor confidence in sustainability reporting. Discover more about the distinctions and methodologies applied for effective verification in social audits and ESG assurance.
Source and External Links
What is Social Auditing? - ESG | The Report - A social audit is a tool used to assess the effects of different programs and policies on communities, enabling those negatively affected to voice concerns and helping organizations remedy issues, thereby promoting sustainability and accountability.
Social audit - Wikipedia - Social audit is a process that measures, understands, reports, and improves an organization's social and ethical performance, with a focus on government accountability, transparency, and citizen participation.
Social Audit - Overview, Rationale, History, Advantages - In business, a social audit formally evaluates a company's corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives and societal impact to assess progress against defined goals, improving public relations and stakeholder trust.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com