Embedded finance reporting integrates financial services data directly into business operations, enhancing real-time decision-making and operational efficiency. Sustainability reporting focuses on disclosing an organization's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, promoting transparency and long-term value creation. Explore the key differences and benefits of each approach to optimize your accounting strategy.
Why it is important
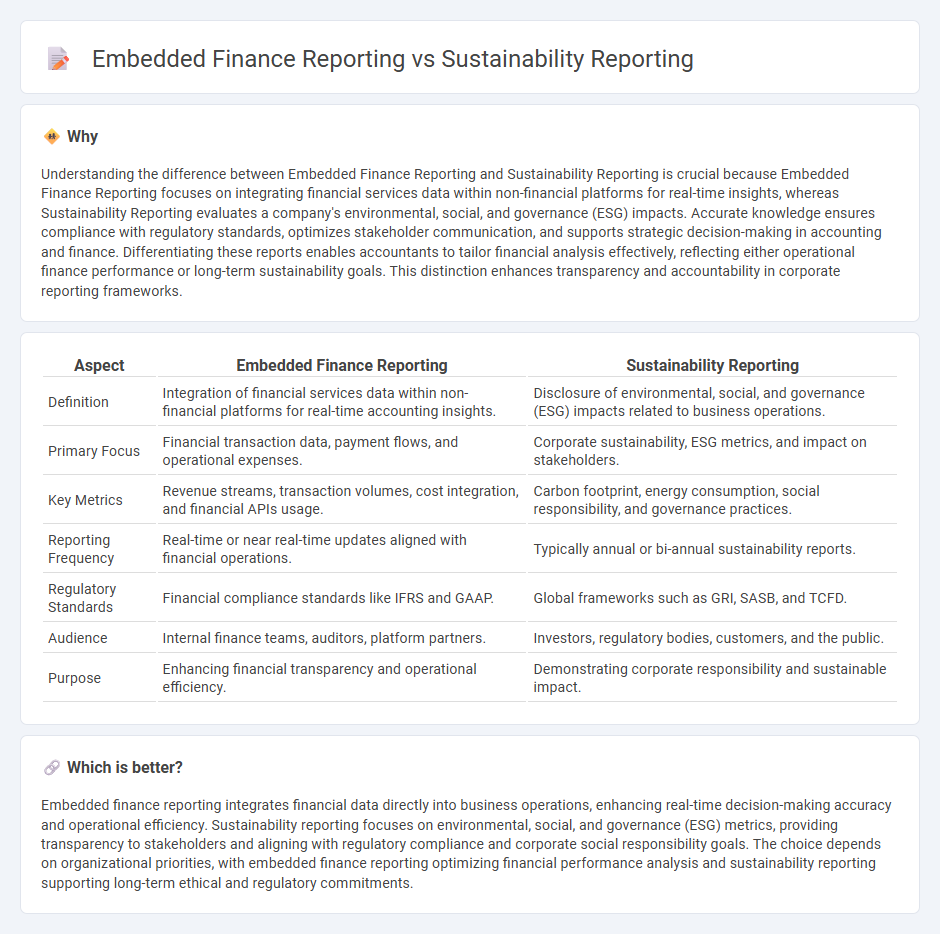
Understanding the difference between Embedded Finance Reporting and Sustainability Reporting is crucial because Embedded Finance Reporting focuses on integrating financial services data within non-financial platforms for real-time insights, whereas Sustainability Reporting evaluates a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts. Accurate knowledge ensures compliance with regulatory standards, optimizes stakeholder communication, and supports strategic decision-making in accounting and finance. Differentiating these reports enables accountants to tailor financial analysis effectively, reflecting either operational finance performance or long-term sustainability goals. This distinction enhances transparency and accountability in corporate reporting frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance Reporting | Sustainability Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of financial services data within non-financial platforms for real-time accounting insights. | Disclosure of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts related to business operations. |
| Primary Focus | Financial transaction data, payment flows, and operational expenses. | Corporate sustainability, ESG metrics, and impact on stakeholders. |
| Key Metrics | Revenue streams, transaction volumes, cost integration, and financial APIs usage. | Carbon footprint, energy consumption, social responsibility, and governance practices. |
| Reporting Frequency | Real-time or near real-time updates aligned with financial operations. | Typically annual or bi-annual sustainability reports. |
| Regulatory Standards | Financial compliance standards like IFRS and GAAP. | Global frameworks such as GRI, SASB, and TCFD. |
| Audience | Internal finance teams, auditors, platform partners. | Investors, regulatory bodies, customers, and the public. |
| Purpose | Enhancing financial transparency and operational efficiency. | Demonstrating corporate responsibility and sustainable impact. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance reporting integrates financial data directly into business operations, enhancing real-time decision-making accuracy and operational efficiency. Sustainability reporting focuses on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, providing transparency to stakeholders and aligning with regulatory compliance and corporate social responsibility goals. The choice depends on organizational priorities, with embedded finance reporting optimizing financial performance analysis and sustainability reporting supporting long-term ethical and regulatory commitments.
Connection
Embedded finance reporting integrates real-time financial data into operational workflows, enabling detailed tracking of resource usage and cost efficiency. Sustainability reporting relies on accurate financial insights to measure environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts effectively, linking financial performance with sustainability goals. The seamless data flow between embedded finance and sustainability reports enhances transparency and supports strategic decision-making in corporate accountability.
Key Terms
**Sustainability Reporting:**
Sustainability reporting centers on measuring and disclosing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, enabling companies to demonstrate commitment to sustainable business practices and regulatory compliance. It involves tracking carbon footprints, resource usage, waste management, and social impact initiatives to provide transparency for stakeholders. Explore how sustainability reporting drives corporate accountability and supports long-term value creation.
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)
Sustainability reporting emphasizes Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics to assess a company's impact on the planet, society, and internal governance structures, providing transparency to investors and stakeholders. Embedded finance reporting integrates financial services within non-financial platforms, highlighting how ESG factors influence financial transactions, risk management, and value creation in real-time. Explore further to understand how these reporting frameworks shape corporate responsibility and financial innovation.
Materiality
Sustainability reporting prioritizes materiality by emphasizing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors that significantly impact a company's long-term value and stakeholder trust. Embedded finance reporting, on the other hand, focuses on financial materiality related to integrated financial services within non-financial platforms, highlighting operational efficiency and user engagement metrics. Discover more about how materiality shapes these distinct reporting frameworks for strategic decision-making.
Source and External Links
What is Sustainability Reporting? - Sustainability reporting allows companies to convey their progress on environmental, social, and governance metrics, providing transparency and assisting in risk management and strategic decision-making.
Sustainability Reporting: Frameworks, Benefits & Challenges - This article discusses the importance of sustainability reporting in publicly disclosing a company's ESG performance, facilitating informed stakeholder decisions and enhancing corporate reputation.
Sustainability Reporting - Sustainability reporting involves disclosing non-financial performance information related to environmental, social, and governance issues, enhancing transparency and corporate accountability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com