Cryptocurrency taxation involves tracking digital asset transactions, often treating gains as capital income or ordinary income depending on holding duration and usage, while stock trading taxation primarily categorizes gains as short-term or long-term capital gains with established reporting frameworks. The IRS requires detailed records for both, but crypto taxation includes unique considerations like forks, airdrops, and token swaps, complicating compliance. Explore the nuances of cryptocurrency versus stock trading taxation to optimize your financial strategy effectively.
Why it is important
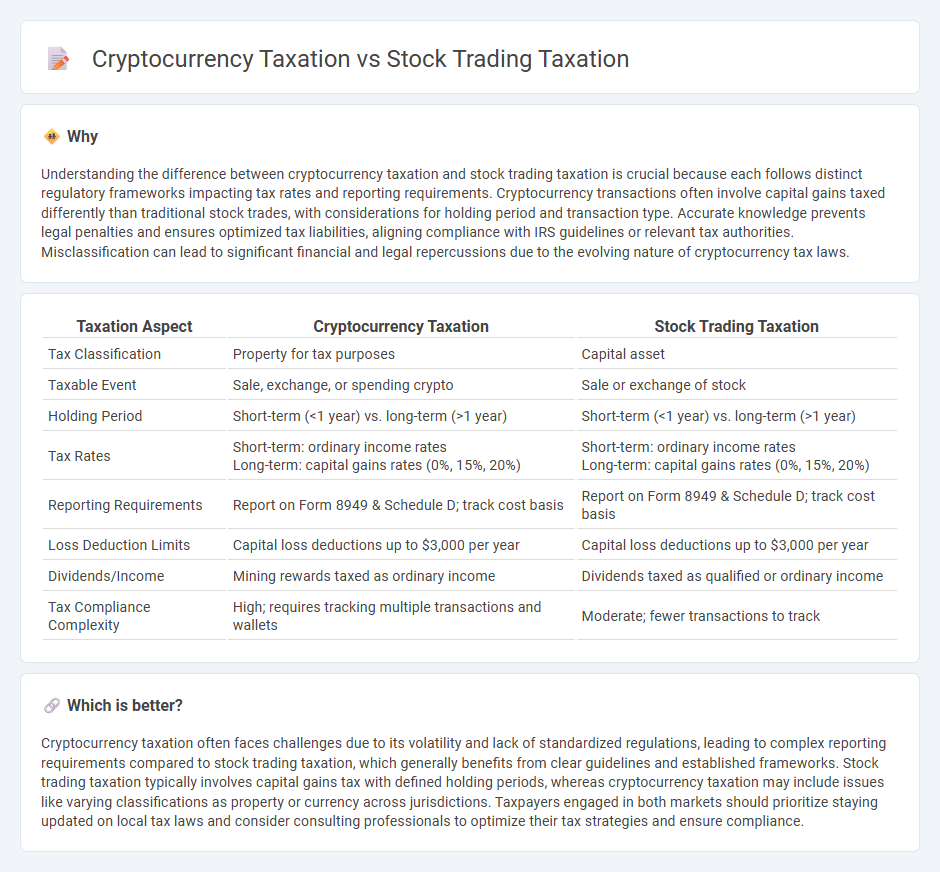
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency taxation and stock trading taxation is crucial because each follows distinct regulatory frameworks impacting tax rates and reporting requirements. Cryptocurrency transactions often involve capital gains taxed differently than traditional stock trades, with considerations for holding period and transaction type. Accurate knowledge prevents legal penalties and ensures optimized tax liabilities, aligning compliance with IRS guidelines or relevant tax authorities. Misclassification can lead to significant financial and legal repercussions due to the evolving nature of cryptocurrency tax laws.
Comparison Table
| Taxation Aspect | Cryptocurrency Taxation | Stock Trading Taxation |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Classification | Property for tax purposes | Capital asset |
| Taxable Event | Sale, exchange, or spending crypto | Sale or exchange of stock |
| Holding Period | Short-term (<1 year) vs. long-term (>1 year) | Short-term (<1 year) vs. long-term (>1 year) |
| Tax Rates |
Short-term: ordinary income rates Long-term: capital gains rates (0%, 15%, 20%) |
Short-term: ordinary income rates Long-term: capital gains rates (0%, 15%, 20%) |
| Reporting Requirements | Report on Form 8949 & Schedule D; track cost basis | Report on Form 8949 & Schedule D; track cost basis |
| Loss Deduction Limits | Capital loss deductions up to $3,000 per year | Capital loss deductions up to $3,000 per year |
| Dividends/Income | Mining rewards taxed as ordinary income | Dividends taxed as qualified or ordinary income |
| Tax Compliance Complexity | High; requires tracking multiple transactions and wallets | Moderate; fewer transactions to track |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency taxation often faces challenges due to its volatility and lack of standardized regulations, leading to complex reporting requirements compared to stock trading taxation, which generally benefits from clear guidelines and established frameworks. Stock trading taxation typically involves capital gains tax with defined holding periods, whereas cryptocurrency taxation may include issues like varying classifications as property or currency across jurisdictions. Taxpayers engaged in both markets should prioritize staying updated on local tax laws and consider consulting professionals to optimize their tax strategies and ensure compliance.
Connection
Cryptocurrency taxation and stock trading taxation intersect through capital gains tax regulations that govern the sale and exchange of assets, requiring accurate reporting of profits and losses to tax authorities such as the IRS. Both taxable events demand meticulous record-keeping of purchase prices, sale prices, and holding periods to determine short-term or long-term capital gains rates, impacting overall tax liability. Compliance with these tax laws is essential to avoid penalties and ensure transparent financial reporting in investment portfolios.
Key Terms
Capital Gains
Capital gains taxation on stock trading typically follows long-term and short-term classifications based on holding periods, with rates varying by income brackets and jurisdictions. Cryptocurrency taxation often treats digital assets as property, applying capital gains rules similarly but with added complexities due to frequent trades, hard forks, and a lack of standardized reporting. Explore detailed guidance and jurisdiction-specific regulations to optimize tax strategies for both investment types.
Cost Basis
Stock trading taxation rules require investors to track the cost basis, including purchase price and any associated fees, to calculate capital gains accurately. Cryptocurrency taxation follows similar principles, but cost basis tracking can be more complex due to frequent transactions, forks, and a lack of standardized reporting. Explore detailed strategies for optimizing cost basis management in both stock and cryptocurrency trading to minimize tax liabilities.
Tax Lot Identification
Stock trading taxation relies heavily on specific Tax Lot Identification methods such as FIFO, LIFO, and Specific Share Identification to calculate capital gains accurately and manage tax liabilities. Cryptocurrency taxation, while adopting similar principles, often requires more scrutiny due to varying IRS guidance and the need to track individual transaction histories across multiple wallets and exchanges. Explore comprehensive strategies to optimize tax outcomes for both stock and cryptocurrency investments.
Source and External Links
Day Trading Taxes: What New Investors Should Consider - This article explains how day trading profits are taxed as ordinary income, lacking the benefits of long-term capital gains rates, and offers strategies to minimize tax liability.
Taxes on Stocks: How They Work, When to Pay - This guide details how stock profits are taxed as either short-term or long-term capital gains, with rates varying based on the holding period and taxpayer's income level.
What is capital gains tax? - This resource explains capital gains tax concepts, including how profits from investments like stocks are taxed after sale, and strategies to minimize these taxes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com