Zero knowledge proofs accounting leverages cryptographic techniques to verify financial transactions without revealing sensitive data, ensuring privacy and security in audit processes. Tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax laws and regulations, emphasizing accurate reporting of income, deductions, and credits to optimize tax liabilities. Explore how integrating zero knowledge proofs can revolutionize confidentiality and trust in tax accounting practices.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between zero knowledge proofs accounting and tax accounting is crucial because zero knowledge proofs enhance data privacy and security by allowing verification without revealing underlying information, while tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax laws and accurate reporting of financial information to authorities. Zero knowledge proofs accounting is pivotal in confidential financial transactions and audits where sensitive data must remain undisclosed. Tax accounting ensures businesses meet legal obligations, avoid penalties, and optimize tax liabilities. Knowing both concepts enables professionals to implement secure, transparent financial practices while adhering to regulatory standards.
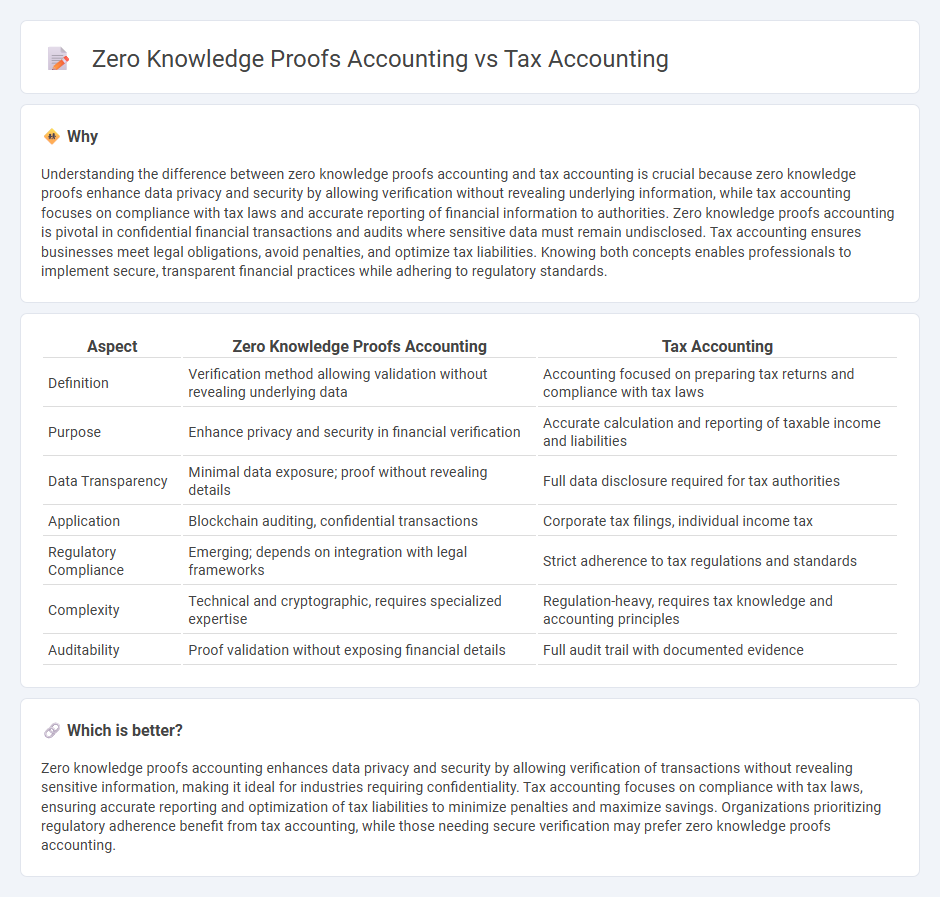
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Knowledge Proofs Accounting | Tax Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Verification method allowing validation without revealing underlying data | Accounting focused on preparing tax returns and compliance with tax laws |
| Purpose | Enhance privacy and security in financial verification | Accurate calculation and reporting of taxable income and liabilities |
| Data Transparency | Minimal data exposure; proof without revealing details | Full data disclosure required for tax authorities |
| Application | Blockchain auditing, confidential transactions | Corporate tax filings, individual income tax |
| Regulatory Compliance | Emerging; depends on integration with legal frameworks | Strict adherence to tax regulations and standards |
| Complexity | Technical and cryptographic, requires specialized expertise | Regulation-heavy, requires tax knowledge and accounting principles |
| Auditability | Proof validation without exposing financial details | Full audit trail with documented evidence |
Which is better?
Zero knowledge proofs accounting enhances data privacy and security by allowing verification of transactions without revealing sensitive information, making it ideal for industries requiring confidentiality. Tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax laws, ensuring accurate reporting and optimization of tax liabilities to minimize penalties and maximize savings. Organizations prioritizing regulatory adherence benefit from tax accounting, while those needing secure verification may prefer zero knowledge proofs accounting.
Connection
Zero knowledge proofs enhance tax accounting by allowing verification of financial data accuracy without revealing sensitive taxpayer information. This cryptographic method ensures compliance and auditability while maintaining confidentiality, reducing the risk of data breaches. Integrating zero knowledge proofs into accounting systems strengthens trust and transparency between taxpayers and tax authorities.
Key Terms
**Tax accounting:**
Tax accounting involves the systematic recording, analysis, and reporting of financial transactions to comply with tax laws and regulations set by authorities such as the IRS. It requires accurate documentation of income, expenses, deductions, and credits to calculate taxable income and ensure proper tax filings. Discover more about the specific methods and benefits of tax accounting to optimize your financial strategy.
Taxable income
Tax accounting calculates taxable income by recording and analyzing all income and deductible expenses according to tax laws, ensuring compliance and accurate tax liability determination. Zero knowledge proofs (ZKP) accounting enhances privacy by verifying the correctness of taxable income computations without revealing the underlying financial data, preserving confidentiality while maintaining trust. Explore how zero knowledge proofs transform taxable income reporting and secure financial transparency.
Deferred tax
Deferred tax in tax accounting involves recognizing future tax liabilities or assets based on temporary differences between accounting and tax bases of assets and liabilities. Zero-knowledge proofs accounting leverages cryptographic methods to validate deferred tax computations without revealing sensitive financial information, enhancing privacy and security in tax reporting. Explore more to understand how zero-knowledge proofs revolutionize deferred tax transparency and compliance in modern tax accounting.
Source and External Links
What Is Tax Accounting? (With Tips and an Example) | Indeed.com - Tax accounting involves specialized methods for preparing public financial statements focused on tax assets, liabilities, and ensuring companies pay the correct amount of taxes and comply with regulations.
Tax Accounting | Definition, Types & Examples - Study.com - Tax accounting is a specialized field aimed at minimizing tax liability and ensuring compliance with tax laws for individuals and organizations through accurate tax return preparation and planning.
Tax Accountant Careers - Tax accountants prepare tax filings, advise clients on tax planning, analyze financial data for tax efficiency, and stay updated on tax law changes to help individuals and businesses manage their tax obligations effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com