Continuous audit leverages real-time data analysis and automated tools to provide ongoing assurance of financial transactions and internal controls. Operational audit evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of business processes and management practices, focusing on improving organizational performance. Explore more to understand the key differences and benefits of these auditing approaches.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between continuous audit and operational audit is crucial for optimizing financial oversight and improving organizational efficiency. Continuous audits provide real-time assurance by automatically analyzing transaction data, enabling prompt detection of anomalies and fraud. Operational audits evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of business processes, helping to identify areas for improvement beyond financial accuracy. Distinguishing these audits ensures targeted resource allocation and enhances overall risk management strategies.
Comparison Table
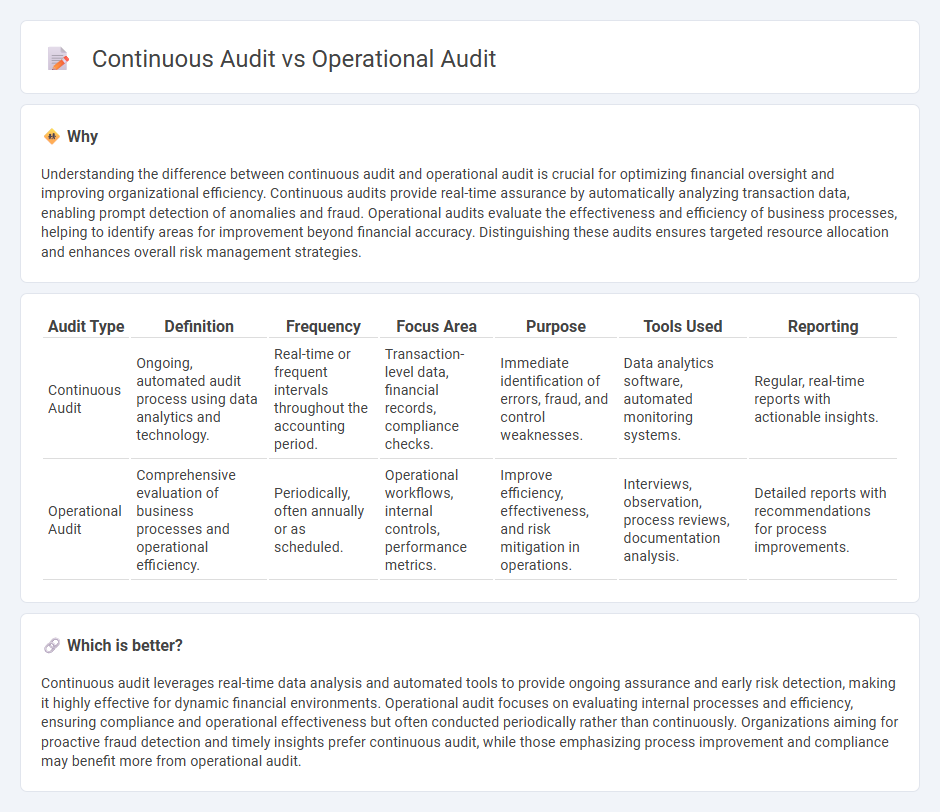
| Audit Type | Definition | Frequency | Focus Area | Purpose | Tools Used | Reporting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Audit | Ongoing, automated audit process using data analytics and technology. | Real-time or frequent intervals throughout the accounting period. | Transaction-level data, financial records, compliance checks. | Immediate identification of errors, fraud, and control weaknesses. | Data analytics software, automated monitoring systems. | Regular, real-time reports with actionable insights. |
| Operational Audit | Comprehensive evaluation of business processes and operational efficiency. | Periodically, often annually or as scheduled. | Operational workflows, internal controls, performance metrics. | Improve efficiency, effectiveness, and risk mitigation in operations. | Interviews, observation, process reviews, documentation analysis. | Detailed reports with recommendations for process improvements. |
Which is better?
Continuous audit leverages real-time data analysis and automated tools to provide ongoing assurance and early risk detection, making it highly effective for dynamic financial environments. Operational audit focuses on evaluating internal processes and efficiency, ensuring compliance and operational effectiveness but often conducted periodically rather than continuously. Organizations aiming for proactive fraud detection and timely insights prefer continuous audit, while those emphasizing process improvement and compliance may benefit more from operational audit.
Connection
Continuous audit leverages real-time data analysis to monitor financial transactions and internal controls, enabling timely detection of anomalies. Operational audit assesses the efficiency and effectiveness of business processes, often utilizing insights generated from continuous audit reports. The integration of continuous audit's ongoing review with operational audit's process evaluation enhances comprehensive risk management and organizational performance.
Key Terms
Scope
Operational audit evaluates an organization's overall efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance by examining processes, controls, and risk management within a defined period. Continuous audit focuses on real-time or near-real-time assessment through automated tools that monitor transactions and controls continuously. Explore in-depth insights to understand how scope distinctions impact audit outcomes and organizational decision-making.
Frequency
Operational audits are typically conducted periodically, such as annually or quarterly, providing a comprehensive assessment of business processes and internal controls at specific intervals. Continuous audits utilize automated tools and real-time data analysis to monitor operations on an ongoing basis, enabling immediate detection of discrepancies and risks. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how audit frequency impacts organizational efficiency and risk management.
Automation
Operational audits evaluate business processes and controls at specific intervals to ensure compliance and efficiency, often relying on manual data collection and analysis. Continuous audits leverage automation technologies like AI and real-time data monitoring to provide ongoing assurance and early detection of anomalies. Explore how integrating automation enhances audit accuracy and speed in your organization.
Source and External Links
Operational Audit: Overview and Guide - This resource provides an overview of operational audits, their purpose, and the process involved in conducting them to optimize internal processes and achieve business goals.
Guide To Operational Auditing - This guide explains the definition, process, advantages, and disadvantages of operational auditing, offering insights into how it enhances organizational efficiency.
Operational Auditing - This Wikipedia entry describes operational auditing as a systematic review of an organization's effectiveness, efficiency, and economy of operations, highlighting its characteristics and objectives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com