Embedded finance reconciliation streamlines financial transactions by integrating payment processes directly within digital platforms, ensuring real-time accuracy and reducing errors. Settlement reconciliation focuses on verifying and matching settled transactions between parties to confirm the completion and correctness of payments. Explore the distinctions and benefits of each reconciliation type to optimize your accounting workflows.
Why it is important
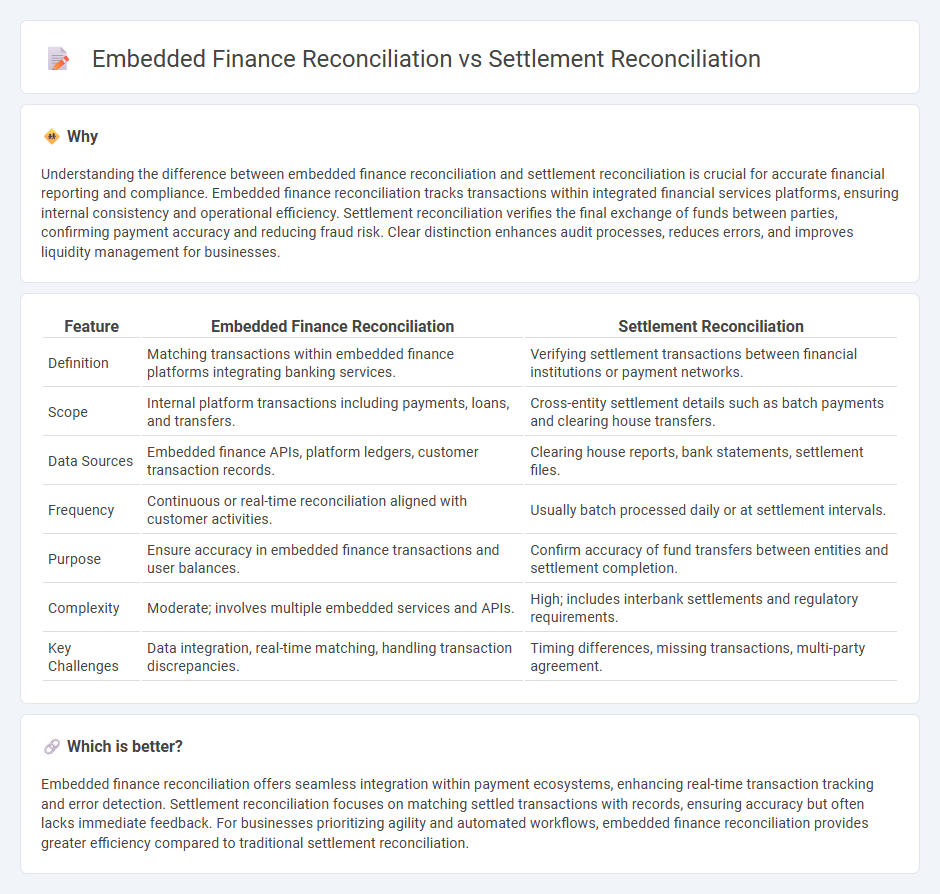
Understanding the difference between embedded finance reconciliation and settlement reconciliation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance. Embedded finance reconciliation tracks transactions within integrated financial services platforms, ensuring internal consistency and operational efficiency. Settlement reconciliation verifies the final exchange of funds between parties, confirming payment accuracy and reducing fraud risk. Clear distinction enhances audit processes, reduces errors, and improves liquidity management for businesses.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Embedded Finance Reconciliation | Settlement Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Matching transactions within embedded finance platforms integrating banking services. | Verifying settlement transactions between financial institutions or payment networks. |
| Scope | Internal platform transactions including payments, loans, and transfers. | Cross-entity settlement details such as batch payments and clearing house transfers. |
| Data Sources | Embedded finance APIs, platform ledgers, customer transaction records. | Clearing house reports, bank statements, settlement files. |
| Frequency | Continuous or real-time reconciliation aligned with customer activities. | Usually batch processed daily or at settlement intervals. |
| Purpose | Ensure accuracy in embedded finance transactions and user balances. | Confirm accuracy of fund transfers between entities and settlement completion. |
| Complexity | Moderate; involves multiple embedded services and APIs. | High; includes interbank settlements and regulatory requirements. |
| Key Challenges | Data integration, real-time matching, handling transaction discrepancies. | Timing differences, missing transactions, multi-party agreement. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance reconciliation offers seamless integration within payment ecosystems, enhancing real-time transaction tracking and error detection. Settlement reconciliation focuses on matching settled transactions with records, ensuring accuracy but often lacks immediate feedback. For businesses prioritizing agility and automated workflows, embedded finance reconciliation provides greater efficiency compared to traditional settlement reconciliation.
Connection
Embedded finance reconciliation streamlines the integration of financial services within non-financial platforms, ensuring real-time tracking of transactions and balances. Settlement reconciliation verifies and matches payment settlements against recorded transactions, reducing discrepancies and errors. Both processes are interconnected by enhancing accuracy and transparency in financial reporting, ultimately improving operational efficiency in accounting systems.
Key Terms
Clearing
Settlement reconciliation focuses on verifying and matching payment transactions after trade execution to ensure accurate fund transfers between parties, primarily involving clearinghouses and custodians. Embedded finance reconciliation integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, streamlining clearing by automating transaction validation and fund settlements within ecosystems like e-commerce or fintech apps. Explore advanced reconciliation techniques to improve settlement efficiency and reduce operational risks in clearing processes.
Ledger
Settlement reconciliation involves matching transactional records between trading parties to ensure accuracy and completeness, focusing on clearing payments and confirming settlements in the ledger. Embedded finance reconciliation integrates financial services directly within platforms, requiring real-time ledger updates to manage diverse payment flows, fees, and commissions dynamically. Explore how ledger technologies optimize both reconciliation types for enhanced financial transparency and efficiency.
API Integration
Settlement reconciliation involves matching transaction records from multiple parties to ensure accuracy and completeness in financial settlements, often requiring robust API integration for real-time data exchange between banks, payment gateways, and merchants. Embedded finance reconciliation integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, using APIs to seamlessly track and manage transactions within the host application, enabling streamlined payment processing and detailed financial reporting. Explore how advanced API integration enhances reconciliation precision and efficiency in both settlement and embedded finance contexts.
Source and External Links
What Is Settlement Reconciliation Definition & Meaning - Emagia - Settlement reconciliation is a financial process that involves comparing and verifying financial records between two parties, such as businesses and financial institutions, to ensure consistency, identify discrepancies, and balance accounts for accuracy and transparency.
Payment Reconciliation: Definition, Types, and How It Works - Payment reconciliation involves gathering internal and external transaction records, matching them, identifying and resolving discrepancies, and documenting the process to ensure account accuracy and catch errors like timing differences or data entry mistakes.
Settlement Reconciliation Software, Automate Matching - Ledge - Automated settlement reconciliation software streamlines the matching and verification process across multiple payment sources and accounts in real time, helping to manage high volumes of transactions with fewer errors and providing comprehensive financial insights.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com