Sustainability reporting focuses on a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, providing stakeholders with insights into long-term value creation and ethical practices. Non-financial reporting encompasses a broader range of disclosures, including social responsibility, corporate governance, and employee welfare, going beyond traditional financial metrics. Explore how integrating sustainability reporting enhances transparency and drives strategic decision-making in corporate accounting.
Why it is important
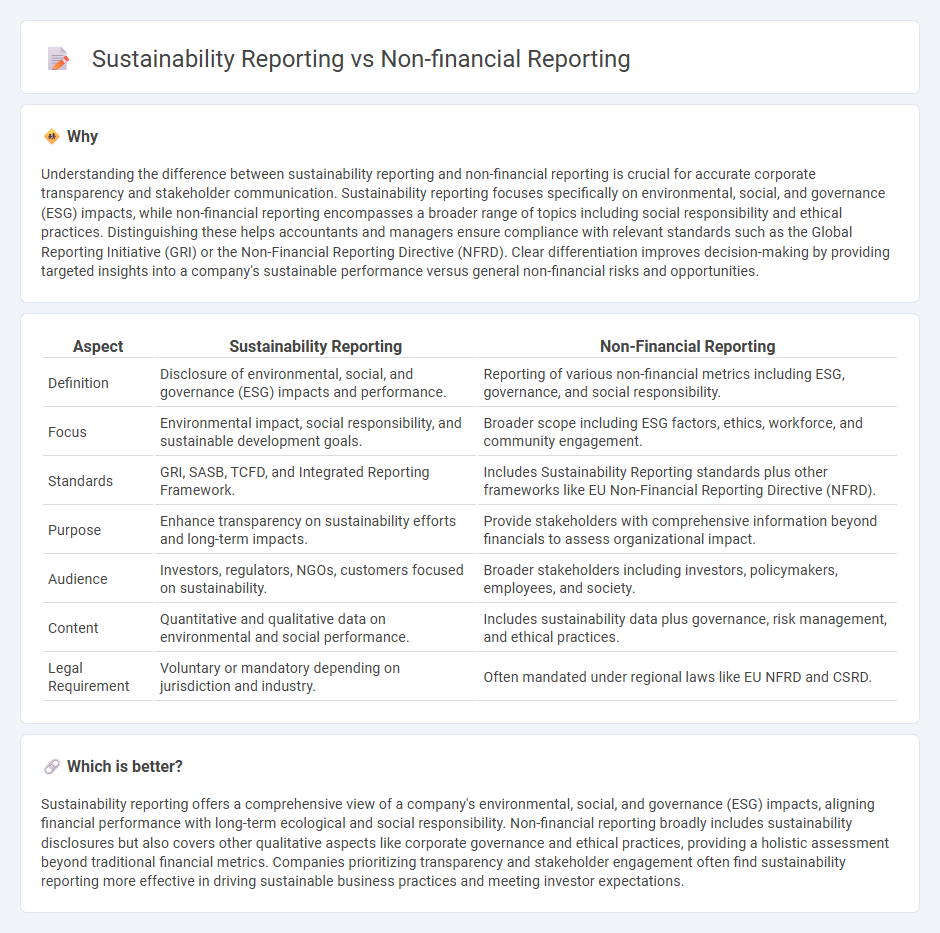
Understanding the difference between sustainability reporting and non-financial reporting is crucial for accurate corporate transparency and stakeholder communication. Sustainability reporting focuses specifically on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, while non-financial reporting encompasses a broader range of topics including social responsibility and ethical practices. Distinguishing these helps accountants and managers ensure compliance with relevant standards such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). Clear differentiation improves decision-making by providing targeted insights into a company's sustainable performance versus general non-financial risks and opportunities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Reporting | Non-Financial Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disclosure of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts and performance. | Reporting of various non-financial metrics including ESG, governance, and social responsibility. |
| Focus | Environmental impact, social responsibility, and sustainable development goals. | Broader scope including ESG factors, ethics, workforce, and community engagement. |
| Standards | GRI, SASB, TCFD, and Integrated Reporting Framework. | Includes Sustainability Reporting standards plus other frameworks like EU Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD). |
| Purpose | Enhance transparency on sustainability efforts and long-term impacts. | Provide stakeholders with comprehensive information beyond financials to assess organizational impact. |
| Audience | Investors, regulators, NGOs, customers focused on sustainability. | Broader stakeholders including investors, policymakers, employees, and society. |
| Content | Quantitative and qualitative data on environmental and social performance. | Includes sustainability data plus governance, risk management, and ethical practices. |
| Legal Requirement | Voluntary or mandatory depending on jurisdiction and industry. | Often mandated under regional laws like EU NFRD and CSRD. |
Which is better?
Sustainability reporting offers a comprehensive view of a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, aligning financial performance with long-term ecological and social responsibility. Non-financial reporting broadly includes sustainability disclosures but also covers other qualitative aspects like corporate governance and ethical practices, providing a holistic assessment beyond traditional financial metrics. Companies prioritizing transparency and stakeholder engagement often find sustainability reporting more effective in driving sustainable business practices and meeting investor expectations.
Connection
Sustainability reporting and non-financial reporting are interconnected as both provide critical insights into a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance beyond traditional financial metrics. These reports offer stakeholders transparent information on corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives, risk management, and long-term value creation, integrating ESG factors into strategic decision-making. The alignment of sustainability metrics with non-financial disclosures enhances accountability and supports compliance with global frameworks such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB).
Key Terms
**Non-Financial Reporting:**
Non-financial reporting encompasses disclosures on environmental impact, social responsibility, governance practices, and ethical standards beyond traditional financial metrics, ensuring transparency for stakeholders. It includes compliance with global frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the EU Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD), which mandate organizations to report on sustainability-related risks and opportunities. Discover more about how non-financial reporting drives corporate accountability and long-term value creation.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
Non-financial reporting encompasses a broad range of disclosures including environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors, whereas sustainability reporting specifically targets the long-term impacts of business practices on environmental and social well-being. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) serves as the foundation for both, emphasizing ethical operations and stakeholder engagement beyond financial performance. Discover detailed differences and best practices to enhance your CSR strategy.
Stakeholder Engagement
Non-financial reporting encompasses a broad spectrum of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, whereas sustainability reporting specifically highlights the impact of organizational operations on ecological and social systems with a greater emphasis on stakeholder engagement. Stakeholder engagement in sustainability reporting involves actively consulting and collaborating with investors, employees, customers, and communities to ensure transparency, accountability, and improved decision-making processes. Explore in-depth analyses of stakeholder engagement's role in enhancing both reporting types to drive sustainable business practices.
Source and External Links
Non-financial reporting: responsible, far-sighted management - Non-financial reporting involves disclosing information that goes beyond financial figures to understand a company's value creation and impact.
Non-financial reporting - This form of reporting focuses on sustainability disclosures, including environmental, social, and human rights impacts of business operations.
Where to Start with Non-Financial Reporting: Navigating the Rise in Regulatory Requirements - Non-financial reporting is essential for compliance and creating a transparent picture of a company's operational impact, requiring careful data management and cross-functional teamwork.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com