Taxonomy alignment in accounting ensures that financial data follows standardized classification systems, enhancing comparability and regulatory compliance. Depreciation methods, such as straight-line or declining balance, systematically allocate the cost of assets over their useful lives, impacting financial statements and tax reporting. Explore more to understand how aligning taxonomy with depreciation methods optimizes financial accuracy and transparency.
Why it is important
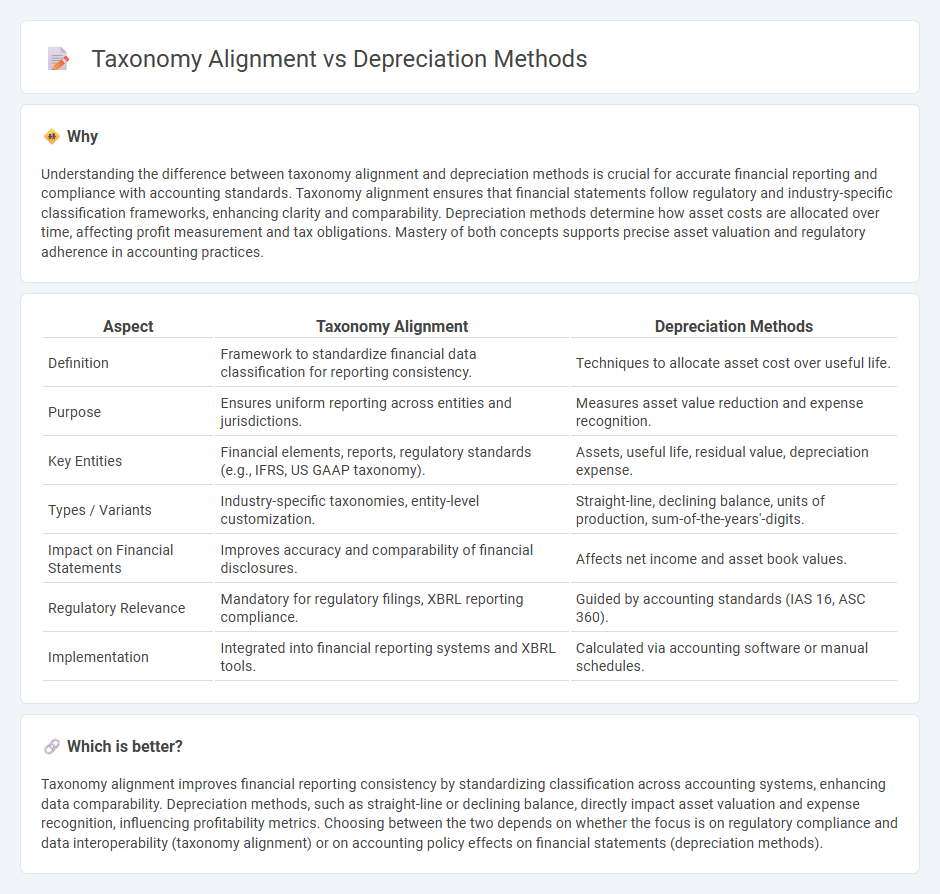
Understanding the difference between taxonomy alignment and depreciation methods is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards. Taxonomy alignment ensures that financial statements follow regulatory and industry-specific classification frameworks, enhancing clarity and comparability. Depreciation methods determine how asset costs are allocated over time, affecting profit measurement and tax obligations. Mastery of both concepts supports precise asset valuation and regulatory adherence in accounting practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Taxonomy Alignment | Depreciation Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Framework to standardize financial data classification for reporting consistency. | Techniques to allocate asset cost over useful life. |
| Purpose | Ensures uniform reporting across entities and jurisdictions. | Measures asset value reduction and expense recognition. |
| Key Entities | Financial elements, reports, regulatory standards (e.g., IFRS, US GAAP taxonomy). | Assets, useful life, residual value, depreciation expense. |
| Types / Variants | Industry-specific taxonomies, entity-level customization. | Straight-line, declining balance, units of production, sum-of-the-years'-digits. |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Improves accuracy and comparability of financial disclosures. | Affects net income and asset book values. |
| Regulatory Relevance | Mandatory for regulatory filings, XBRL reporting compliance. | Guided by accounting standards (IAS 16, ASC 360). |
| Implementation | Integrated into financial reporting systems and XBRL tools. | Calculated via accounting software or manual schedules. |
Which is better?
Taxonomy alignment improves financial reporting consistency by standardizing classification across accounting systems, enhancing data comparability. Depreciation methods, such as straight-line or declining balance, directly impact asset valuation and expense recognition, influencing profitability metrics. Choosing between the two depends on whether the focus is on regulatory compliance and data interoperability (taxonomy alignment) or on accounting policy effects on financial statements (depreciation methods).
Connection
Taxonomy alignment ensures that financial data, including depreciation methods such as straight-line or declining balance, is categorized consistently for regulatory reporting and comparability. Accurate taxonomy mapping facilitates transparent presentation of asset value changes over time, reflecting systematic depreciation in compliance with accounting standards like IFRS or GAAP. This connection enhances data integrity and supports automated financial analysis across accounting systems.
Key Terms
Straight-Line Depreciation
Straight-Line Depreciation allocates asset cost evenly over its useful life, providing straightforward financial consistency aligned with accounting taxonomy standards such as IFRS and US GAAP. This method simplifies asset value tracking and regulatory reporting by matching expense recognition with systematic asset usage, ensuring compliance with taxonomy alignment requirements. Discover how integrating Straight-Line Depreciation can enhance your asset management and financial reporting accuracy.
Reducing Balance Method
The Reducing Balance Method accelerates asset depreciation by applying a fixed percentage to the diminishing book value, optimizing tax benefits and aligning with financial reporting standards. Taxonomy alignment ensures consistency in categorizing and reporting depreciation methods, enhancing comparability and regulatory compliance across industries. Explore how integrating the Reducing Balance Method with taxonomy frameworks can improve asset management and financial transparency.
XBRL (eXtensible Business Reporting Language)
Depreciation methods, including straight-line, declining balance, and units of production, impact financial statements and require precise representation in XBRL for accurate taxonomies alignment. XBRL frameworks facilitate standardized tagging of depreciation data, enhancing comparability and regulatory compliance across jurisdictions. Explore the integration of depreciation methodologies within XBRL taxonomies to optimize financial reporting accuracy and transparency.
Source and External Links
Selecting the Best Depreciation Method: A Complete Guide - This guide discusses the best depreciation methods, including straight-line, accelerated, and units of production, to help choose the most suitable method for assets.
Depreciation Methods: 4 Types with Formulas and Examples - This resource provides an overview of four common depreciation methods: straight-line, declining balance, units of production, and sum of years digits, along with formulas and examples.
Depreciation Methods - 4 Types of ... - This page lists the most common depreciation methods, including straight-line, double declining balance, units of production, and sum of years digits, highlighting their applications.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com