Algorithmic compliance leverages advanced AI and machine learning to automate regulatory adherence, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in accounting processes. In contrast, rules-based compliance relies on predefined standards and manual checks, which can be more rigid and prone to human error. Explore how integrating algorithmic compliance can transform your accounting practices and ensure regulatory precision.
Why it is important
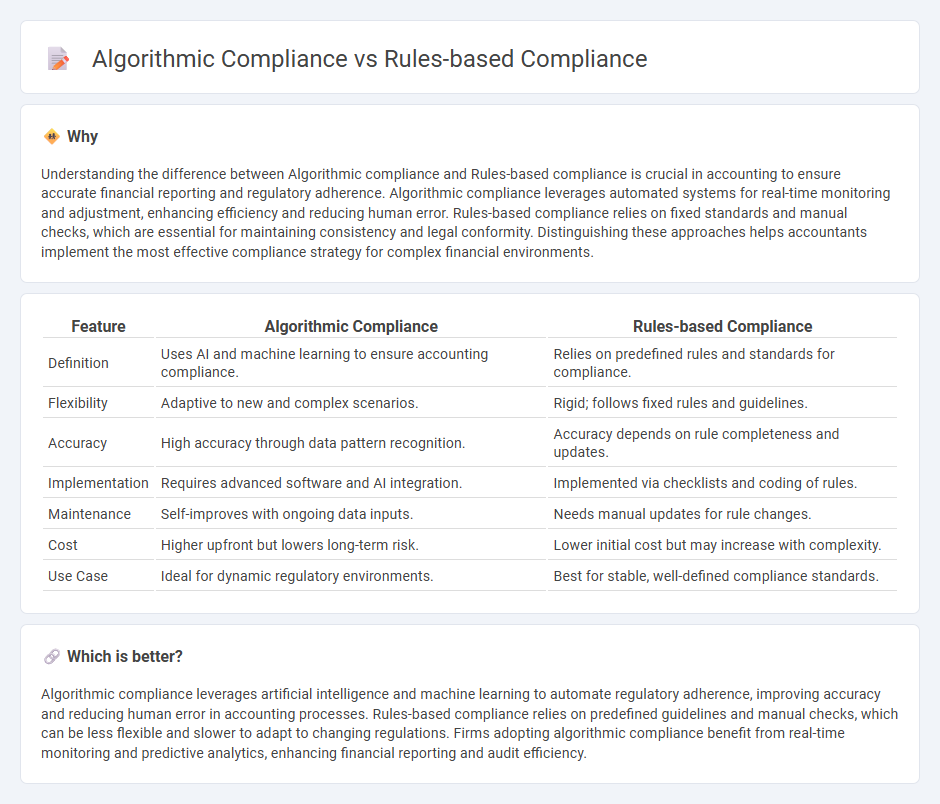
Understanding the difference between Algorithmic compliance and Rules-based compliance is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate financial reporting and regulatory adherence. Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems for real-time monitoring and adjustment, enhancing efficiency and reducing human error. Rules-based compliance relies on fixed standards and manual checks, which are essential for maintaining consistency and legal conformity. Distinguishing these approaches helps accountants implement the most effective compliance strategy for complex financial environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Algorithmic Compliance | Rules-based Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Uses AI and machine learning to ensure accounting compliance. | Relies on predefined rules and standards for compliance. |
| Flexibility | Adaptive to new and complex scenarios. | Rigid; follows fixed rules and guidelines. |
| Accuracy | High accuracy through data pattern recognition. | Accuracy depends on rule completeness and updates. |
| Implementation | Requires advanced software and AI integration. | Implemented via checklists and coding of rules. |
| Maintenance | Self-improves with ongoing data inputs. | Needs manual updates for rule changes. |
| Cost | Higher upfront but lowers long-term risk. | Lower initial cost but may increase with complexity. |
| Use Case | Ideal for dynamic regulatory environments. | Best for stable, well-defined compliance standards. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to automate regulatory adherence, improving accuracy and reducing human error in accounting processes. Rules-based compliance relies on predefined guidelines and manual checks, which can be less flexible and slower to adapt to changing regulations. Firms adopting algorithmic compliance benefit from real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, enhancing financial reporting and audit efficiency.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance enhances rules-based compliance by automating the interpretation and application of accounting regulations through advanced software and machine learning models. This integration ensures real-time monitoring, reduces manual errors, and enforces adherence to complex financial reporting standards such as GAAP and IFRS. Together, they optimize accuracy in financial statements and improve regulatory audit readiness.
Key Terms
GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles)
Rules-based compliance under GAAP relies on detailed, specific guidelines ensuring consistent financial reporting, reducing ambiguity in transactions like revenue recognition or asset valuation. Algorithmic compliance harnesses AI and machine learning to automatically analyze complex accounting data, enhancing accuracy and detecting anomalies in real time, which is particularly useful for large datasets and evolving standards. Explore how integrating both approaches can optimize adherence to GAAP and improve audit efficiencies.
Automated Controls
Rules-based compliance relies on predefined criteria and static rules to enforce regulatory requirements through automated controls, ensuring consistent application across transactions. Algorithmic compliance leverages machine learning and artificial intelligence to adapt controls dynamically, detecting anomalies and evolving risks with greater precision. Explore how integrating both approaches can enhance automated compliance effectiveness and reduce regulatory risks.
Real-time Monitoring
Rules-based compliance relies on predefined criteria to monitor transactions, ensuring adherence to regulatory standards through fixed thresholds and alerts. Algorithmic compliance enhances real-time monitoring by leveraging machine learning models to detect anomalies and evolving risks with greater accuracy and adaptability. Explore the latest advancements in compliance technology to optimize your real-time monitoring strategies.
Source and External Links
Rules Versus Principles Based Regulation - CFA UK - This article discusses the differences between rules-based and principles-based regulation, focusing on their implications for compliance and regulatory frameworks.
Rule-based management - This approach involves establishing and enforcing rules to guide decision-making and behavior within organizations, ensuring compliance with regulations and policies.
Rules-Based Regulation: A Comprehensive Guide - Provides an overview of the clear and specific nature of rules-based regulation, which helps in easy understanding and reduces the risk of non-compliance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com