Zero trust accounting centers on stringent verification and continuous validation of financial transactions to prevent fraud and ensure data integrity, leveraging advanced security protocols. Tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax laws and regulations, ensuring accurate reporting and optimization of tax liabilities for individuals and businesses. Explore the key differences and applications of zero trust accounting versus tax accounting to enhance financial security and compliance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust accounting and Tax accounting is crucial for accurately managing financial security protocols versus compliance with tax regulations. Zero Trust accounting focuses on strict access controls and continuous verification to protect financial data, while Tax accounting deals with recording and reporting financial transactions to meet tax laws. Accurate knowledge of both ensures robust financial data security and legal adherence in accounting practices. Misunderstanding these can lead to financial vulnerabilities or legal penalties.
Comparison Table
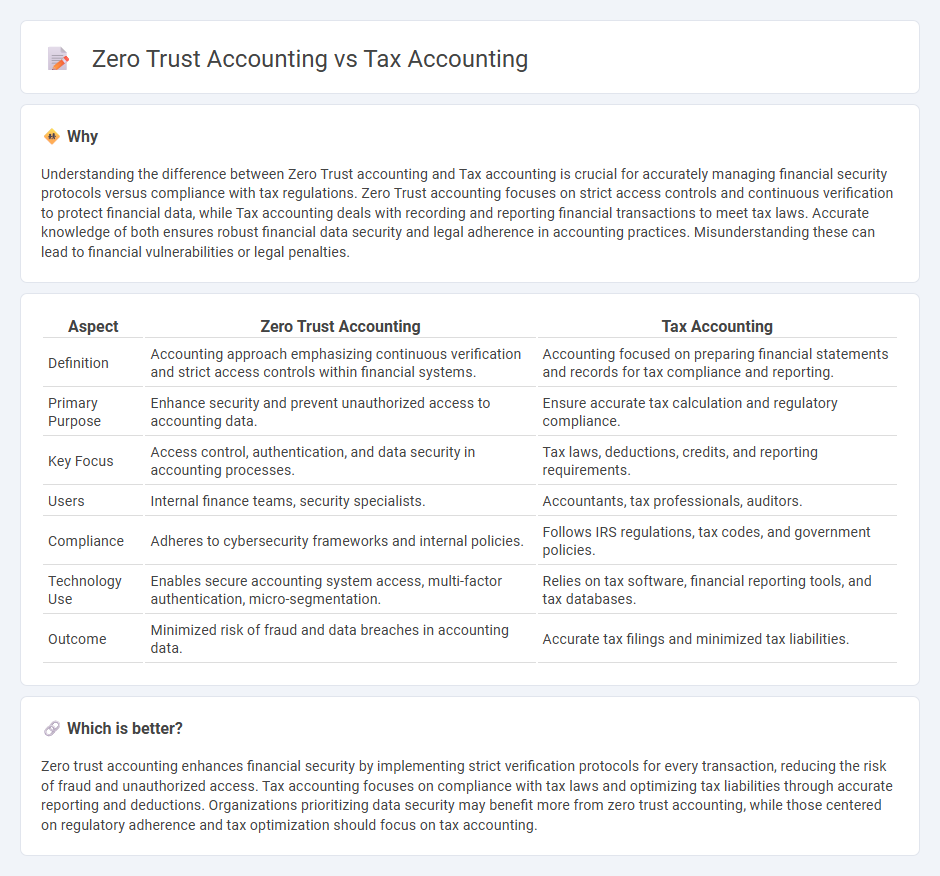
| Aspect | Zero Trust Accounting | Tax Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting approach emphasizing continuous verification and strict access controls within financial systems. | Accounting focused on preparing financial statements and records for tax compliance and reporting. |
| Primary Purpose | Enhance security and prevent unauthorized access to accounting data. | Ensure accurate tax calculation and regulatory compliance. |
| Key Focus | Access control, authentication, and data security in accounting processes. | Tax laws, deductions, credits, and reporting requirements. |
| Users | Internal finance teams, security specialists. | Accountants, tax professionals, auditors. |
| Compliance | Adheres to cybersecurity frameworks and internal policies. | Follows IRS regulations, tax codes, and government policies. |
| Technology Use | Enables secure accounting system access, multi-factor authentication, micro-segmentation. | Relies on tax software, financial reporting tools, and tax databases. |
| Outcome | Minimized risk of fraud and data breaches in accounting data. | Accurate tax filings and minimized tax liabilities. |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting enhances financial security by implementing strict verification protocols for every transaction, reducing the risk of fraud and unauthorized access. Tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax laws and optimizing tax liabilities through accurate reporting and deductions. Organizations prioritizing data security may benefit more from zero trust accounting, while those centered on regulatory adherence and tax optimization should focus on tax accounting.
Connection
Zero trust accounting integrates rigorous access controls and continuous verification methods to enhance data security in tax accounting processes. Tax accounting relies on precise, confidential financial records, making zero trust frameworks essential for protecting sensitive tax data from unauthorized access and fraud. Implementing zero trust principles ensures compliance with tax regulations while safeguarding client information throughout tax reporting and auditing procedures.
Key Terms
**Tax Accounting:**
Tax accounting involves the systematic recording, analysis, and reporting of financial transactions to comply with tax laws and regulations, ensuring accurate calculation of taxable income and tax liabilities. It requires adherence to standards such as GAAP or IFRS, and involves preparing tax returns, conducting audits, and managing tax planning strategies to optimize tax burdens. Explore the key differences and benefits of tax accounting to enhance your financial compliance and strategic planning.
Deferred Tax
Deferred tax arises from temporary differences between tax accounting and financial accounting, impacting the timing of tax recognition on the balance sheet. Zero trust accounting, a security model, does not directly affect deferred tax but emphasizes rigorous access controls to prevent unauthorized financial data manipulation during tax reporting. Explore the distinctions between tax accounting methodologies and zero trust principles to better manage deferred tax implications and safeguard fiscal data.
Taxable Income
Tax accounting centers on accurately reporting taxable income based on IRS guidelines, including deductions and credits to determine tax liability. Zero trust accounting, an emerging cybersecurity approach, ensures data integrity and access control in financial systems to prevent fraud affecting taxable income reporting. Explore more about how zero trust principles enhance the reliability of tax accounting data.
Source and External Links
Tax Accounting | Definition, Types & Examples - This webpage provides an overview of tax accounting, focusing on its definition, types, and examples, highlighting its role in minimizing tax liability and ensuring compliance with tax laws.
Tax Accountant Careers - This page discusses the career aspects of tax accountants, including their duties, required skills, and the importance of staying updated with changing tax laws.
What Is a Tax Accountant? - This article explains the role of a tax accountant in tax filing, planning, and compliance, and how they can help individuals and businesses minimize their tax liability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com