Payroll crypto taxation involves complex regulations as digital assets are treated differently than fiat currency by tax authorities, often requiring detailed reporting of transactions and valuations. In contrast, payroll fiat taxation follows established, standardized guidelines with direct withholding of income taxes and social security contributions. Explore the nuances and compliance requirements of payroll crypto versus fiat taxation for a comprehensive understanding.
Why it is important
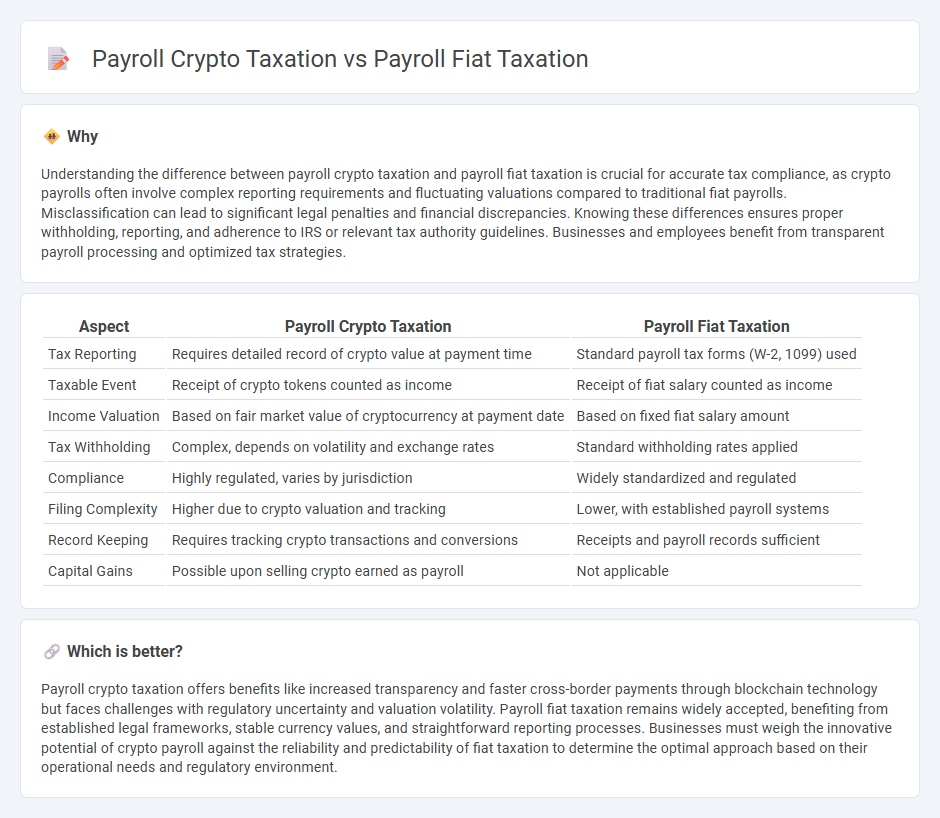
Understanding the difference between payroll crypto taxation and payroll fiat taxation is crucial for accurate tax compliance, as crypto payrolls often involve complex reporting requirements and fluctuating valuations compared to traditional fiat payrolls. Misclassification can lead to significant legal penalties and financial discrepancies. Knowing these differences ensures proper withholding, reporting, and adherence to IRS or relevant tax authority guidelines. Businesses and employees benefit from transparent payroll processing and optimized tax strategies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Payroll Crypto Taxation | Payroll Fiat Taxation |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Reporting | Requires detailed record of crypto value at payment time | Standard payroll tax forms (W-2, 1099) used |
| Taxable Event | Receipt of crypto tokens counted as income | Receipt of fiat salary counted as income |
| Income Valuation | Based on fair market value of cryptocurrency at payment date | Based on fixed fiat salary amount |
| Tax Withholding | Complex, depends on volatility and exchange rates | Standard withholding rates applied |
| Compliance | Highly regulated, varies by jurisdiction | Widely standardized and regulated |
| Filing Complexity | Higher due to crypto valuation and tracking | Lower, with established payroll systems |
| Record Keeping | Requires tracking crypto transactions and conversions | Receipts and payroll records sufficient |
| Capital Gains | Possible upon selling crypto earned as payroll | Not applicable |
Which is better?
Payroll crypto taxation offers benefits like increased transparency and faster cross-border payments through blockchain technology but faces challenges with regulatory uncertainty and valuation volatility. Payroll fiat taxation remains widely accepted, benefiting from established legal frameworks, stable currency values, and straightforward reporting processes. Businesses must weigh the innovative potential of crypto payroll against the reliability and predictability of fiat taxation to determine the optimal approach based on their operational needs and regulatory environment.
Connection
Payroll crypto taxation and payroll fiat taxation are connected through the requirement to accurately report employee compensation for tax compliance, regardless of the payment method. Both systems necessitate tracking income, withholding appropriate taxes, and adhering to regulatory frameworks such as the IRS guidelines for cryptocurrency transactions and traditional fiat wage reporting. Integration of payroll software solutions ensures consistent tax calculations and filing, bridging the gap between digital and fiat currency payroll processes.
Key Terms
Withholding Tax
Payroll fiat taxation involves withholding tax based on traditional currency salaries, where employers deduct a predefined percentage according to local tax laws before disbursing net pay to employees. Payroll crypto taxation requires employers to calculate withholding tax on the fair market value of cryptocurrency payments at the time of salary issuance, which can fluctuate and complicate reporting compliance. Explore the nuances of withholding tax in both payroll fiat and crypto contexts to ensure accurate tax compliance.
Reporting Requirements
Payroll fiat taxation requires employers to report wages, withholdings, and tax payments to government agencies using standardized forms such as W-2 and 941 in the U.S., ensuring compliance with established tax codes. Payroll crypto taxation involves tracking the fair market value of cryptocurrency at the time of payment, reporting it as taxable income, and adhering to additional requirements for virtual assets set by authorities like the IRS. Discover the nuanced reporting requirements and compliance tips for both payroll fiat and crypto taxation to optimize your business processes.
Fair Market Value
Payroll fiat taxation relies on traditional currency values recorded on pay dates, while payroll crypto taxation requires conversion of cryptocurrency earnings to fiat using the Fair Market Value (FMV) at the time of payment. Accurate FMV determination ensures compliance with IRS guidelines and proper reporting of income for crypto payroll, which differs from fixed fiat amounts in payroll systems. Explore deeper insights into how FMV impacts tax liabilities and reporting nuances for crypto payroll.
Source and External Links
Taxation of Digital Assets - Employers must withhold and remit payroll taxes on cryptocurrency payments in the same way as for fiat wages, requiring conversion to U.S. dollars for tax payments, which may trigger capital gains or losses for the employer.
How to Pay In Crypto: Guide for Employers - U.S. employers must calculate the fair market value of crypto wages in USD on the payment date, withhold payroll taxes in U.S. dollars, and report this income on a W-2 or 1099 form for each recipient.
Crypto Payroll: Tax Considerations Under IRS Guidelines - Payroll taxes cannot be paid with cryptocurrency; employers must convert crypto wages to USD for reporting and tax payments, and use the correct fiat value at the time of each transaction to comply with IRS requirements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com