Forensic data analytics involves the detailed examination of financial data to detect fraud, irregularities, and compliance issues using advanced techniques such as data mining and predictive modeling. Financial statement audits focus on verifying the accuracy and fairness of an organization's financial reports in accordance with accounting standards and regulatory requirements. Explore the differences and applications to understand how these approaches enhance financial integrity and risk management.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between forensic data analytics and financial statement audits is crucial because forensic analytics focuses on detecting fraud and irregularities using data-driven techniques, while financial statement audits verify the accuracy and compliance of financial reports. Forensic data analytics often involves detailed transaction-level investigations, whereas audits assess overall financial statement integrity according to accounting standards. This distinction enables accountants and auditors to apply the appropriate methodology for risk assessment and assurance. Mastery of both ensures enhanced fraud detection and reliable financial reporting.
Comparison Table
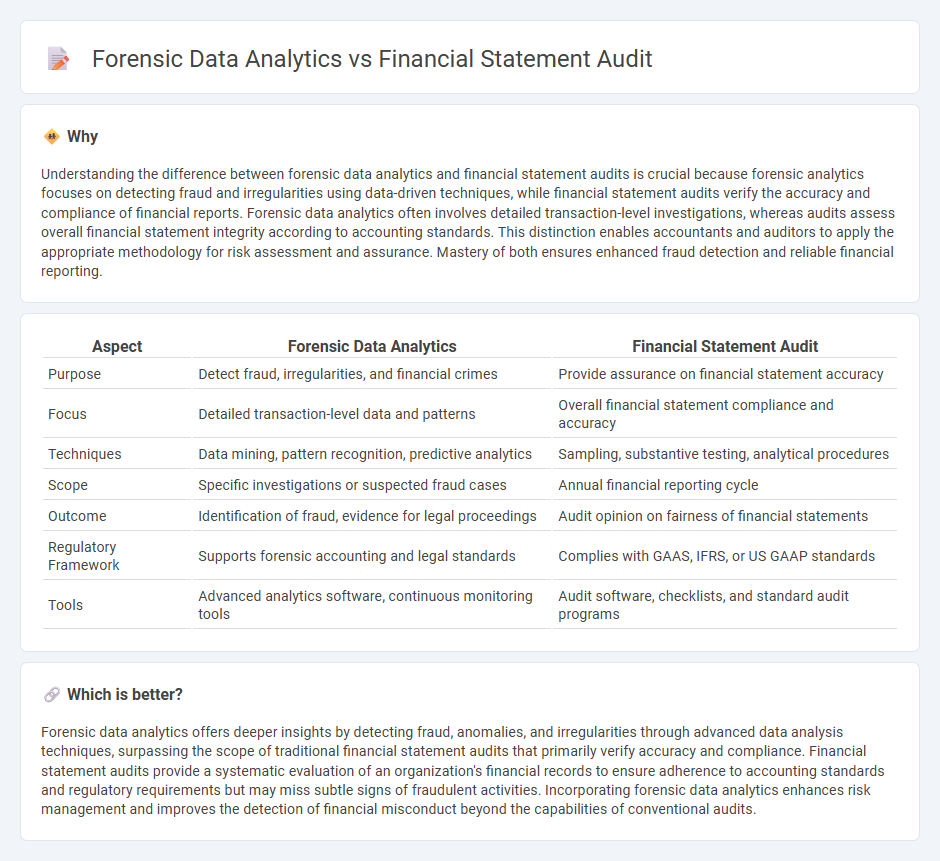
| Aspect | Forensic Data Analytics | Financial Statement Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, irregularities, and financial crimes | Provide assurance on financial statement accuracy |
| Focus | Detailed transaction-level data and patterns | Overall financial statement compliance and accuracy |
| Techniques | Data mining, pattern recognition, predictive analytics | Sampling, substantive testing, analytical procedures |
| Scope | Specific investigations or suspected fraud cases | Annual financial reporting cycle |
| Outcome | Identification of fraud, evidence for legal proceedings | Audit opinion on fairness of financial statements |
| Regulatory Framework | Supports forensic accounting and legal standards | Complies with GAAS, IFRS, or US GAAP standards |
| Tools | Advanced analytics software, continuous monitoring tools | Audit software, checklists, and standard audit programs |
Which is better?
Forensic data analytics offers deeper insights by detecting fraud, anomalies, and irregularities through advanced data analysis techniques, surpassing the scope of traditional financial statement audits that primarily verify accuracy and compliance. Financial statement audits provide a systematic evaluation of an organization's financial records to ensure adherence to accounting standards and regulatory requirements but may miss subtle signs of fraudulent activities. Incorporating forensic data analytics enhances risk management and improves the detection of financial misconduct beyond the capabilities of conventional audits.
Connection
Forensic data analytics enhances financial statement audits by identifying anomalies, patterns, and fraud indicators within large datasets, improving the accuracy and reliability of audit conclusions. Integrating advanced data analysis techniques enables auditors to detect financial misstatements and irregularities more efficiently, strengthening compliance with regulatory standards. This synergy increases the effectiveness of audits, minimizes risk, and supports transparent financial reporting.
Key Terms
Materiality
Financial statement audits emphasize materiality to determine the significance of misstatements affecting users' economic decisions, typically applying quantitative thresholds guided by accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. Forensic data analytics prioritizes materiality based on the context of fraud detection and risk assessment, often requiring a qualitative approach to uncover intentional misrepresentations regardless of amount. Explore in-depth methodologies and their implications for materiality in both fields to enhance your understanding of audit effectiveness and fraud prevention.
Evidence
Financial statement audits primarily rely on sampling methods to gather sufficient, appropriate evidence aimed at providing reasonable assurance that financial records are free from material misstatement. Forensic data analytics focuses on detailed, in-depth examination of transactional data to detect fraud, anomalies, and irregularities, often utilizing advanced algorithms and pattern recognition. Explore how these distinct approaches complement each other in enhancing the integrity of financial information.
Anomaly detection
Financial statement audit primarily emphasizes verifying the accuracy and completeness of financial records through sampling and analytical procedures, while forensic data analytics concentrates on detecting anomalies indicating fraud or irregularities using advanced statistical and machine learning techniques. Anomaly detection in forensic analytics involves identifying outliers and unusual patterns that deviate from expected financial behaviors, enhancing fraud risk assessment beyond traditional audit methods. Explore more to understand how integrating these approaches strengthens financial oversight and fraud prevention.
Source and External Links
What Is a Financial Statement Audit? - A financial statement audit is a professional examination of a company's financial statements to determine if they present a fair and materially correct representation of the business's activity and financial position.
Financial audit - A financial audit is conducted to provide an opinion on whether financial statements are stated in accordance with specified criteria, involving several phases including substantive testing.
Understanding a financial statement audit - This resource explains the process and benefits of a financial statement audit, including how it provides assurance that management has presented a 'true and fair' view of a company's financial performance and position.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com