Carbon accounting focuses on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions to support sustainability and regulatory compliance, while public sector accounting emphasizes transparency, budget control, and financial reporting within governmental entities. Both accounting types utilize specialized frameworks and standards to ensure accurate tracking of relevant data. Explore further to understand their distinct methodologies and applications.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and public sector accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and environmental impact assessment. Carbon accounting focuses on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions to support sustainability goals. Public sector accounting deals with government budgeting, expenditures, and compliance with public financial regulations. Mastery of both ensures organizations meet regulatory requirements and promote transparency in environmental and fiscal responsibilities.
Comparison Table
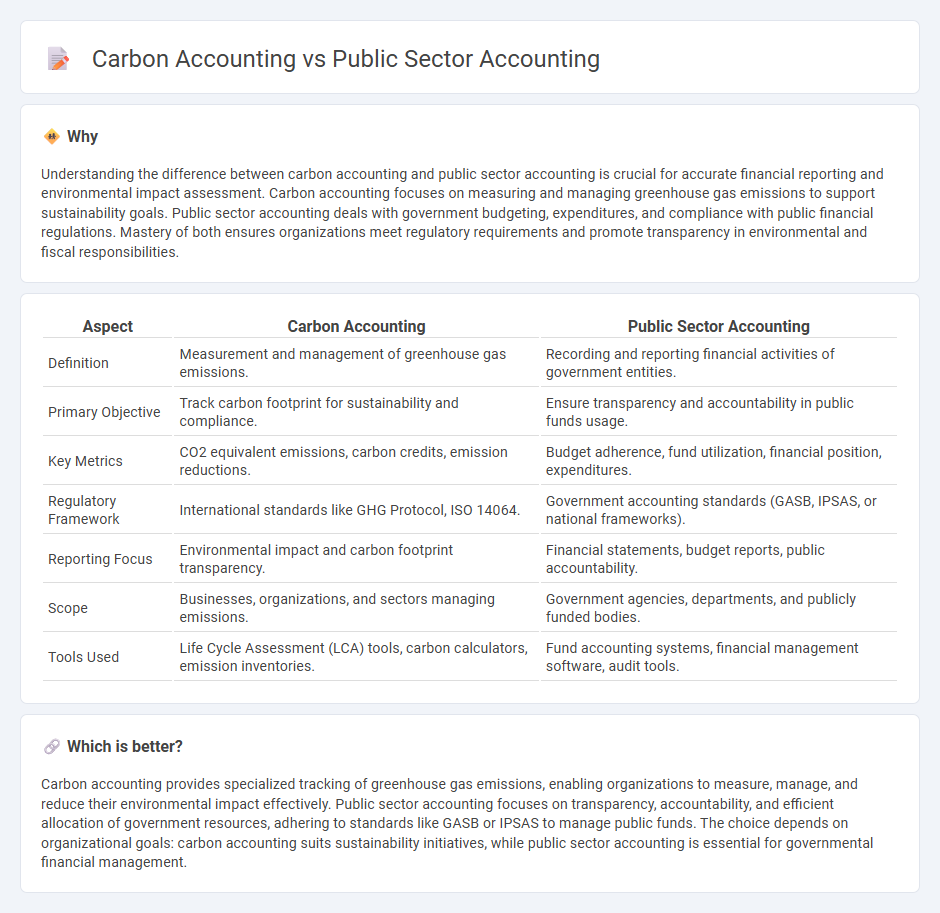
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | Public Sector Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measurement and management of greenhouse gas emissions. | Recording and reporting financial activities of government entities. |
| Primary Objective | Track carbon footprint for sustainability and compliance. | Ensure transparency and accountability in public funds usage. |
| Key Metrics | CO2 equivalent emissions, carbon credits, emission reductions. | Budget adherence, fund utilization, financial position, expenditures. |
| Regulatory Framework | International standards like GHG Protocol, ISO 14064. | Government accounting standards (GASB, IPSAS, or national frameworks). |
| Reporting Focus | Environmental impact and carbon footprint transparency. | Financial statements, budget reports, public accountability. |
| Scope | Businesses, organizations, and sectors managing emissions. | Government agencies, departments, and publicly funded bodies. |
| Tools Used | Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) tools, carbon calculators, emission inventories. | Fund accounting systems, financial management software, audit tools. |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting provides specialized tracking of greenhouse gas emissions, enabling organizations to measure, manage, and reduce their environmental impact effectively. Public sector accounting focuses on transparency, accountability, and efficient allocation of government resources, adhering to standards like GASB or IPSAS to manage public funds. The choice depends on organizational goals: carbon accounting suits sustainability initiatives, while public sector accounting is essential for governmental financial management.
Connection
Carbon accounting integrates environmental impact measurement into financial reporting, enabling public sector entities to track greenhouse gas emissions alongside fiscal data. Public sector accounting incorporates sustainability metrics to align budgeting and resource allocation with climate goals, enhancing transparency and accountability. This connection supports government efforts to meet environmental regulations while maintaining fiscal responsibility.
Key Terms
**Public Sector Accounting:**
Public sector accounting involves the systematic recording, analysis, and reporting of financial transactions within government entities, emphasizing transparency, accountability, and compliance with regulatory standards such as IPSAS (International Public Sector Accounting Standards). It ensures efficient allocation of public resources and supports fiscal policy decision-making through detailed budgetary controls and financial performance assessments. Explore our in-depth resources to understand how public sector accounting drives governmental financial management and policy implementation.
Fund Accounting
Fund accounting in the public sector focuses on tracking and managing resources according to legal and donor restrictions, ensuring transparency and accountability in government finances. Carbon accounting measures greenhouse gas emissions to support environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance, emphasizing the quantification of carbon footprints rather than financial transactions. Explore how integrating fund accounting with carbon accounting can enhance public sector environmental and fiscal responsibility.
Budgetary Control
Budgetary control in public sector accounting emphasizes monitoring government expenditures against allocated budgets to ensure fiscal responsibility and transparency. Carbon accounting focuses on tracking and managing greenhouse gas emissions within budgetary frameworks to align environmental impact with financial planning. Explore how integrating these two accounting practices enhances sustainability and fiscal discipline in public administration.
Source and External Links
Governmental accounting - Wikipedia - Public sector accounting involves managing and recording financial transactions by government entities with a focus on fiscal accountability, fund accounting, legal compliance, transparency, and auditing distinct from private sector accounting focused on profit.
Public Sector Accounting System - A Conceptual Analysis - Public sector accounting records and maintains government financial performance, serving socio-economic development goals with distinct accounting standards different from private and non-profit sectors to ensure transparency.
What Is Government Accounting? - Government accountants track public finances focusing on accountability, tax compliance, fraud detection, and risk assessment to ensure proper use of funds and transparency to taxpayers.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com