Zero trust accounting implements stringent verification processes to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access, enhancing financial security in digital environments. Cost accounting focuses on tracking, analyzing, and controlling costs to improve budgeting and operational efficiency within organizations. Explore more to understand how these accounting approaches impact business decision-making and security.
Why it is important
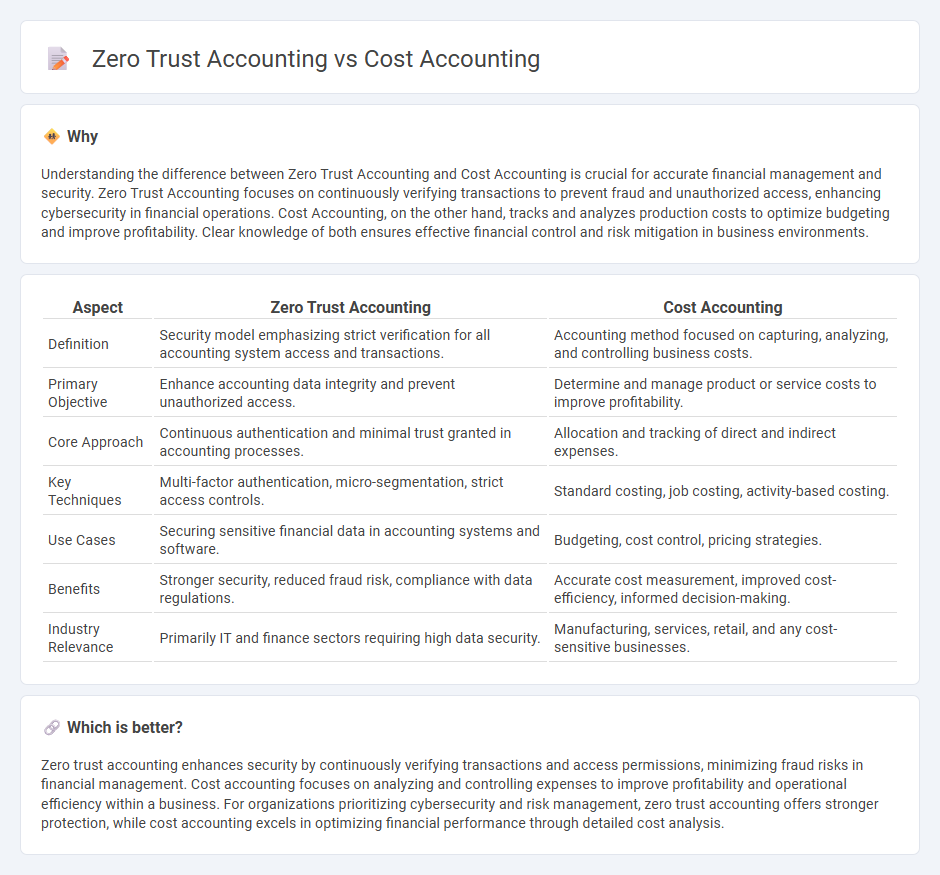
Understanding the difference between Zero Trust Accounting and Cost Accounting is crucial for accurate financial management and security. Zero Trust Accounting focuses on continuously verifying transactions to prevent fraud and unauthorized access, enhancing cybersecurity in financial operations. Cost Accounting, on the other hand, tracks and analyzes production costs to optimize budgeting and improve profitability. Clear knowledge of both ensures effective financial control and risk mitigation in business environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Trust Accounting | Cost Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Security model emphasizing strict verification for all accounting system access and transactions. | Accounting method focused on capturing, analyzing, and controlling business costs. |
| Primary Objective | Enhance accounting data integrity and prevent unauthorized access. | Determine and manage product or service costs to improve profitability. |
| Core Approach | Continuous authentication and minimal trust granted in accounting processes. | Allocation and tracking of direct and indirect expenses. |
| Key Techniques | Multi-factor authentication, micro-segmentation, strict access controls. | Standard costing, job costing, activity-based costing. |
| Use Cases | Securing sensitive financial data in accounting systems and software. | Budgeting, cost control, pricing strategies. |
| Benefits | Stronger security, reduced fraud risk, compliance with data regulations. | Accurate cost measurement, improved cost-efficiency, informed decision-making. |
| Industry Relevance | Primarily IT and finance sectors requiring high data security. | Manufacturing, services, retail, and any cost-sensitive businesses. |
Which is better?
Zero trust accounting enhances security by continuously verifying transactions and access permissions, minimizing fraud risks in financial management. Cost accounting focuses on analyzing and controlling expenses to improve profitability and operational efficiency within a business. For organizations prioritizing cybersecurity and risk management, zero trust accounting offers stronger protection, while cost accounting excels in optimizing financial performance through detailed cost analysis.
Connection
Zero trust accounting enhances cost accounting by implementing stringent data access controls, ensuring accuracy and preventing fraud in financial data management. Integrating zero trust principles helps maintain integrity in cost accounting processes by verifying all transactions and user identities continuously. This connection supports precise cost allocation and financial reporting critical for business decision-making.
Key Terms
**Cost accounting:**
Cost accounting analyzes and controls business expenses to improve profitability by accurately tracking production costs, overhead, and resource allocation. It provides detailed insights into cost behavior, budget management, and financial decision-making processes critical for operational efficiency. Explore expert strategies to enhance your company's financial performance through advanced cost accounting techniques.
Overheads
Cost accounting allocates and tracks overhead expenses such as indirect labor, utilities, and rent to determine product or service profitability. Zero trust accounting applies strict verification and access controls to financial data systems, reducing overhead risks linked to unauthorized access and fraud. Explore how these approaches optimize overhead management and financial security in your organization.
Cost allocation
Cost accounting allocates expenses based on direct and indirect production costs to optimize budgeting and profitability analysis. Zero trust accounting emphasizes granular access controls and real-time verification to allocate costs securely across distributed systems, enhancing auditability and fraud prevention. Explore deeper into how zero trust principles transform cost allocation frameworks for improved financial governance.
Source and External Links
What Is Cost Accounting | A Guide for Businesses - BPM - Cost accounting is a specialized accounting field focusing on analyzing, standardizing, forecasting, and comparing cost data to determine the true cost of products or services, helping businesses improve profitability and operational performance by providing detailed internal cost insights.
Cost Accounting: Types, Functions, and Example - EnKash - Cost accounting helps in cost control, pricing decisions, profitability analysis, budgeting, and performance evaluation through various methods like standard cost accounting, activity-based costing, and marginal costing.
Cost Accounting Defined: What It Is & Why It Matters - NetSuite - Cost accounting tracks and summarizes fixed and variable input costs related to production or service delivery, used internally to control costs and inform pricing, differing from financial accounting by focusing on internal management needs without external reporting requirements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com