Algorithmic compliance leverages automated processes and data-driven algorithms to ensure real-time adherence to accounting standards and regulatory requirements, minimizing human error and enhancing accuracy. Preventive controls focus on designing policies and procedures that proactively deter errors or fraud before transactions are recorded or processed, emphasizing internal checkpoints and authorization protocols. Discover how integrating algorithmic compliance with preventive controls can transform your accounting accuracy and regulatory adherence.
Why it is important
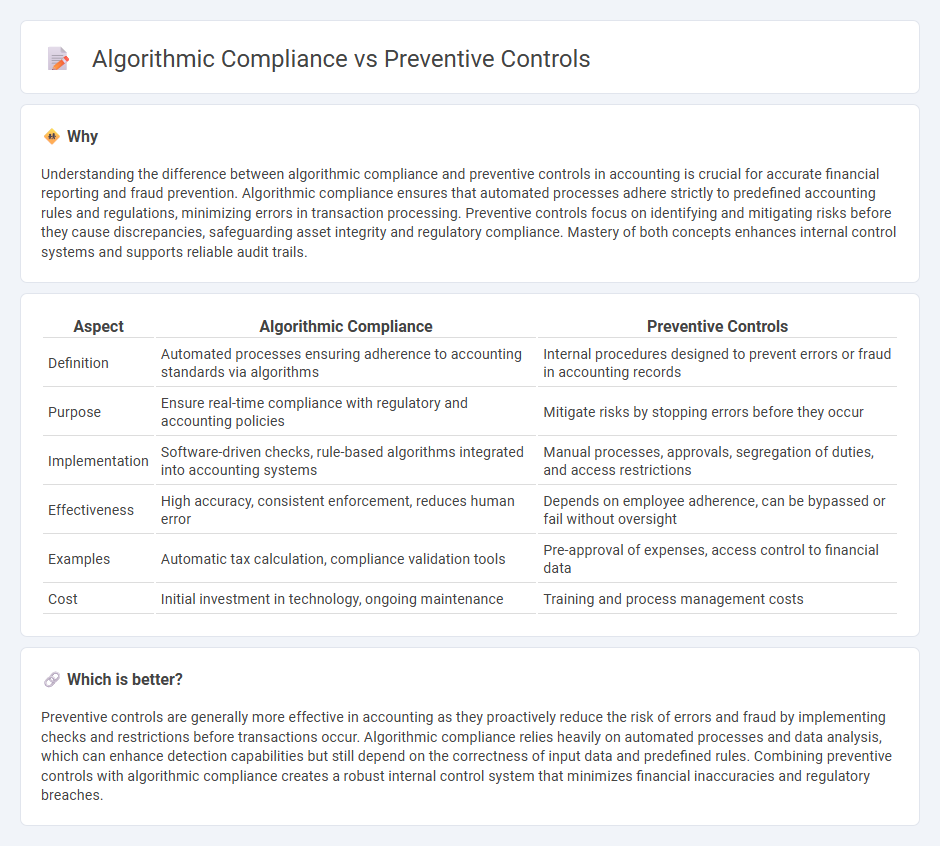
Understanding the difference between algorithmic compliance and preventive controls in accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and fraud prevention. Algorithmic compliance ensures that automated processes adhere strictly to predefined accounting rules and regulations, minimizing errors in transaction processing. Preventive controls focus on identifying and mitigating risks before they cause discrepancies, safeguarding asset integrity and regulatory compliance. Mastery of both concepts enhances internal control systems and supports reliable audit trails.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Compliance | Preventive Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated processes ensuring adherence to accounting standards via algorithms | Internal procedures designed to prevent errors or fraud in accounting records |
| Purpose | Ensure real-time compliance with regulatory and accounting policies | Mitigate risks by stopping errors before they occur |
| Implementation | Software-driven checks, rule-based algorithms integrated into accounting systems | Manual processes, approvals, segregation of duties, and access restrictions |
| Effectiveness | High accuracy, consistent enforcement, reduces human error | Depends on employee adherence, can be bypassed or fail without oversight |
| Examples | Automatic tax calculation, compliance validation tools | Pre-approval of expenses, access control to financial data |
| Cost | Initial investment in technology, ongoing maintenance | Training and process management costs |
Which is better?
Preventive controls are generally more effective in accounting as they proactively reduce the risk of errors and fraud by implementing checks and restrictions before transactions occur. Algorithmic compliance relies heavily on automated processes and data analysis, which can enhance detection capabilities but still depend on the correctness of input data and predefined rules. Combining preventive controls with algorithmic compliance creates a robust internal control system that minimizes financial inaccuracies and regulatory breaches.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance integrates automated rule-based systems to ensure adherence to accounting standards, reducing errors and enhancing data integrity. Preventive controls in accounting utilize these algorithms to detect anomalies and inconsistencies before they affect financial transactions. This synergy minimizes risk and strengthens regulatory compliance through real-time monitoring and enforcement of internal policies.
Key Terms
Segregation of Duties
Segregation of Duties (SoD) is a critical element in both preventive controls and algorithmic compliance frameworks, designed to reduce the risk of fraud and errors by dividing responsibilities among different individuals. Preventive controls enforce SoD through manual checks and policy-driven access restrictions, while algorithmic compliance utilizes automated systems and machine learning to continuously monitor and detect SoD violations in real-time. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances risk management and operational efficiency.
Automated Workflows
Automated workflows leverage algorithmic compliance to ensure real-time adherence to regulatory standards by continuously monitoring processes and flagging deviations. Preventive controls, integrated within these workflows, proactively block non-compliant actions before execution, minimizing operational risks. Explore how combining these strategies enhances compliance efficiency and reduces manual oversight.
Exception Reporting
Preventive controls minimize compliance risks by proactively identifying discrepancies before transactions occur, enhancing regulatory adherence. Algorithmic compliance leverages machine learning models to analyze large datasets, generating exception reports that highlight anomalies and potential violations for further investigation. Discover how integrating exception reporting optimizes compliance frameworks and mitigates operational risks.
Source and External Links
Preventive Controls - Preventive controls are proactive measures designed to prevent errors, losses, or omissions by implementing policies and procedures such as segregation of duties and proper authorizations.
Preventive Controls Rule - The Preventive Controls Rule sets requirements for food facilities to maintain a written food safety plan that includes hazard analysis and preventive controls like process controls and sanitation controls.
Key Facts about Preventive Controls for Human Food - This document outlines key preventive controls for human food, including process controls, food allergen controls, and sanitation controls to reduce or eliminate food safety hazards.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com