Embedded finance compliance focuses on ensuring adherence to regulatory requirements within integrated financial services, emphasizing real-time transaction monitoring and risk management. Financial statement audits evaluate the accuracy and fairness of a company's financial records, providing assurance on overall financial health and compliance with accounting standards. Explore the key differences and their impact on your financial operations to enhance your accounting practices.
Why it is important
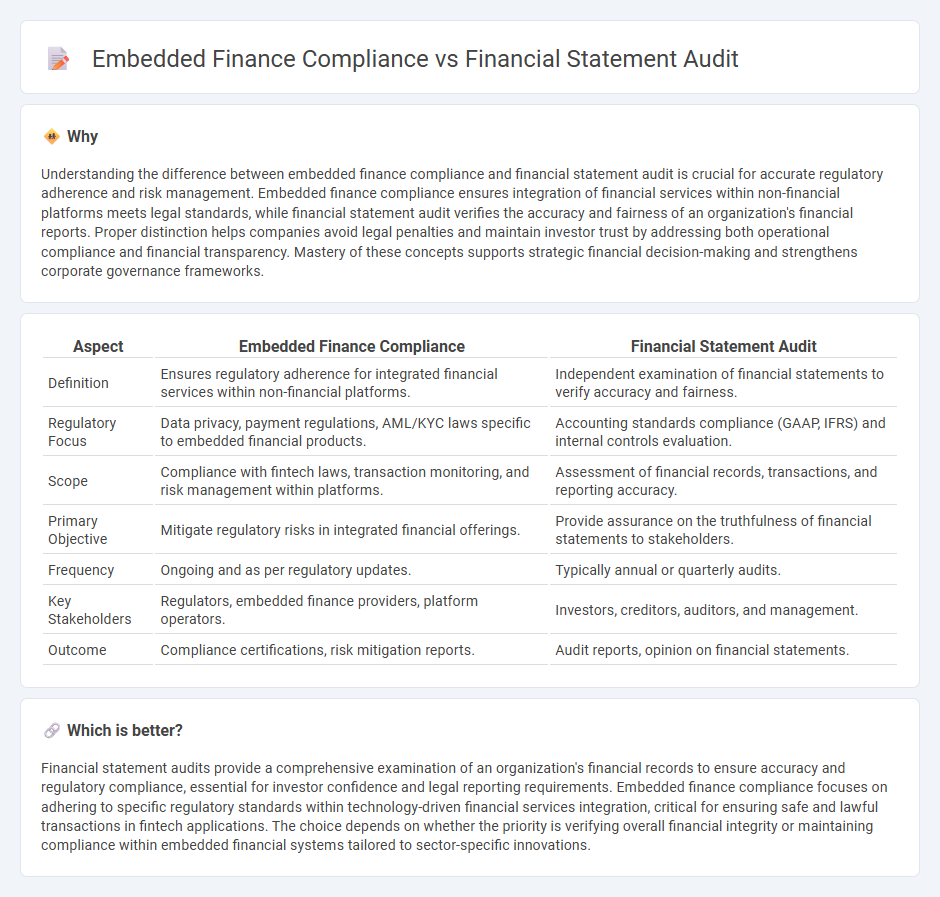
Understanding the difference between embedded finance compliance and financial statement audit is crucial for accurate regulatory adherence and risk management. Embedded finance compliance ensures integration of financial services within non-financial platforms meets legal standards, while financial statement audit verifies the accuracy and fairness of an organization's financial reports. Proper distinction helps companies avoid legal penalties and maintain investor trust by addressing both operational compliance and financial transparency. Mastery of these concepts supports strategic financial decision-making and strengthens corporate governance frameworks.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance Compliance | Financial Statement Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ensures regulatory adherence for integrated financial services within non-financial platforms. | Independent examination of financial statements to verify accuracy and fairness. |
| Regulatory Focus | Data privacy, payment regulations, AML/KYC laws specific to embedded financial products. | Accounting standards compliance (GAAP, IFRS) and internal controls evaluation. |
| Scope | Compliance with fintech laws, transaction monitoring, and risk management within platforms. | Assessment of financial records, transactions, and reporting accuracy. |
| Primary Objective | Mitigate regulatory risks in integrated financial offerings. | Provide assurance on the truthfulness of financial statements to stakeholders. |
| Frequency | Ongoing and as per regulatory updates. | Typically annual or quarterly audits. |
| Key Stakeholders | Regulators, embedded finance providers, platform operators. | Investors, creditors, auditors, and management. |
| Outcome | Compliance certifications, risk mitigation reports. | Audit reports, opinion on financial statements. |
Which is better?
Financial statement audits provide a comprehensive examination of an organization's financial records to ensure accuracy and regulatory compliance, essential for investor confidence and legal reporting requirements. Embedded finance compliance focuses on adhering to specific regulatory standards within technology-driven financial services integration, critical for ensuring safe and lawful transactions in fintech applications. The choice depends on whether the priority is verifying overall financial integrity or maintaining compliance within embedded financial systems tailored to sector-specific innovations.
Connection
Embedded finance compliance ensures that financial services integrated into non-financial platforms adhere to regulatory standards, directly impacting the accuracy and reliability of financial records. Financial statement audits examine these records to verify compliance and detect any discrepancies arising from embedded finance transactions. Effective collaboration between embedded finance compliance and audit processes enhances transparency and mitigates risks in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Financial statement audit:
Financial statement audits provide an independent evaluation of a company's financial records to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS. Auditors assess risks, internal controls, and financial disclosures to enhance the credibility of financial statements for stakeholders. Discover how in-depth financial statement audits safeguard transparency and trust in corporate reporting.
Materiality
Financial statement audit centers on assessing materiality to ensure financial reports accurately reflect a company's financial position, verifying that misstatements could influence stakeholders' decisions. Embedded finance compliance emphasizes materiality in regulatory adherence, ensuring integrated financial services meet legal standards to prevent significant compliance risks. Explore deeper insights into how materiality impacts both financial audits and embedded finance compliance frameworks.
Audit evidence
Audit evidence in financial statement audits centers on verifying accuracy, completeness, and existence of financial records using sources like invoices, bank statements, and contracts. Embedded finance compliance requires gathering evidence on regulatory adherence, data protection, and transaction integrity through system logs, compliance reports, and third-party assessments. Explore detailed methodologies and best practices for collecting and evaluating audit evidence in both domains to enhance audit quality and compliance assurance.
Source and External Links
What Is a Financial Statement Audit? - NetSuite - This webpage provides an overview of financial statement audits, explaining their purpose, process, and benefits for companies.
Financial statement audit definition - AccountingTools - This article defines financial statement audits and discusses their role in enhancing the credibility of a company's financial reports.
What Is an Audited Financial Statement? (And What To Include) - Indeed - This article explains what audited financial statements are and why they are important for companies seeking credibility with stakeholders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com