Embedded finance reporting integrates financial data directly within operational systems, enabling real-time insights and streamlined decision-making for businesses. Performance reporting focuses on analyzing financial metrics to evaluate company efficiency, profitability, and strategic progress over specific periods. Explore the key differences and advantages of each reporting method to enhance your accounting practices.
Why it is important
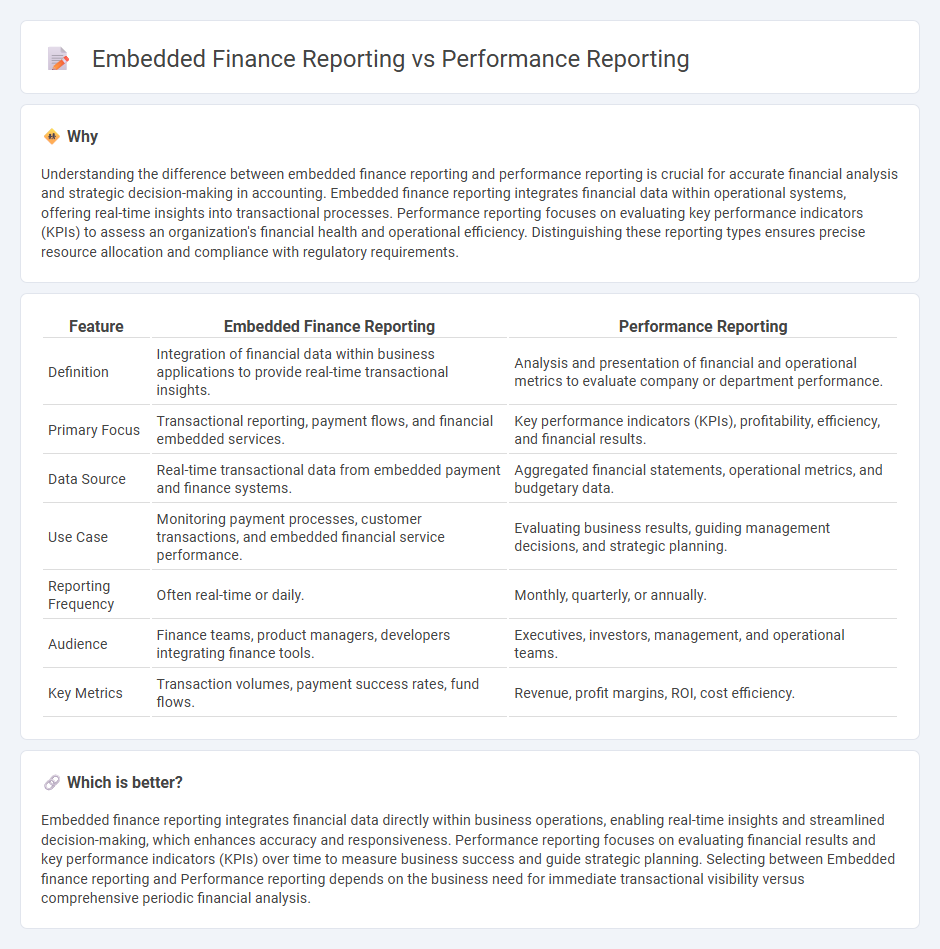
Understanding the difference between embedded finance reporting and performance reporting is crucial for accurate financial analysis and strategic decision-making in accounting. Embedded finance reporting integrates financial data within operational systems, offering real-time insights into transactional processes. Performance reporting focuses on evaluating key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess an organization's financial health and operational efficiency. Distinguishing these reporting types ensures precise resource allocation and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Embedded Finance Reporting | Performance Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of financial data within business applications to provide real-time transactional insights. | Analysis and presentation of financial and operational metrics to evaluate company or department performance. |
| Primary Focus | Transactional reporting, payment flows, and financial embedded services. | Key performance indicators (KPIs), profitability, efficiency, and financial results. |
| Data Source | Real-time transactional data from embedded payment and finance systems. | Aggregated financial statements, operational metrics, and budgetary data. |
| Use Case | Monitoring payment processes, customer transactions, and embedded financial service performance. | Evaluating business results, guiding management decisions, and strategic planning. |
| Reporting Frequency | Often real-time or daily. | Monthly, quarterly, or annually. |
| Audience | Finance teams, product managers, developers integrating finance tools. | Executives, investors, management, and operational teams. |
| Key Metrics | Transaction volumes, payment success rates, fund flows. | Revenue, profit margins, ROI, cost efficiency. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance reporting integrates financial data directly within business operations, enabling real-time insights and streamlined decision-making, which enhances accuracy and responsiveness. Performance reporting focuses on evaluating financial results and key performance indicators (KPIs) over time to measure business success and guide strategic planning. Selecting between Embedded finance reporting and Performance reporting depends on the business need for immediate transactional visibility versus comprehensive periodic financial analysis.
Connection
Embedded finance reporting integrates real-time financial data within operational systems, enabling seamless tracking of transactions and cash flow. Performance reporting leverages this integrated data to analyze key performance indicators (KPIs), profitability, and financial health with enhanced accuracy and timeliness. Together, they provide a comprehensive view of financial performance, improving decision-making and strategic planning.
Key Terms
**Performance reporting:**
Performance reporting delivers detailed insights into key financial and operational metrics, enabling businesses to track progress against strategic goals and identify areas for improvement. It typically includes data on revenue growth, cost management, profitability, and efficiency metrics, which are essential for informed decision-making and stakeholder communication. Explore more to understand how advanced performance reporting tools can drive business success.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Performance reporting emphasizes KPIs such as revenue growth, profit margins, and customer acquisition costs to evaluate overall business success. Embedded finance reporting focuses on transaction volumes, integration depth, user engagement, and financial product adoption rates within non-financial platforms. Discover detailed insights and best practices for optimizing both reporting approaches.
Variance Analysis
Variance analysis in performance reporting centers on comparing actual financial results against budgeted or forecasted figures to identify deviations in revenue, expenses, and profitability. Embedded finance reporting incorporates variance analysis within transactional data from integrated financial services, allowing for real-time insights into payment processing, lending performance, and customer behavior metrics. Explore these reporting techniques to enhance financial decision-making and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Performance Reporting: Definition, Types, Process & More - Performance reporting involves gathering, analyzing, and presenting information about product or project performance while following best practices such as focusing on key information and using visualizations.
What is Reporting Performance? - Reporting performance is the process of tracking, analyzing, and communicating key metrics related to individual, team, or organizational performance.
Performance Reporting: a Complete Guide - Performance reporting collects, analyzes, and reports on user data to compare projections with results, focusing on optimizing project performance and understanding user behavior.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com