Real-time expense reconciliation provides instant matching of transactions, enabling businesses to maintain accurate financial records and identify discrepancies promptly. Cash-based reconciliation, on the other hand, aligns expenses strictly when cash flows occur, offering a straightforward snapshot of actual cash movement but potentially delaying insight into outstanding liabilities. Explore the benefits and applications of both methods to optimize your accounting practices.
Why it is important
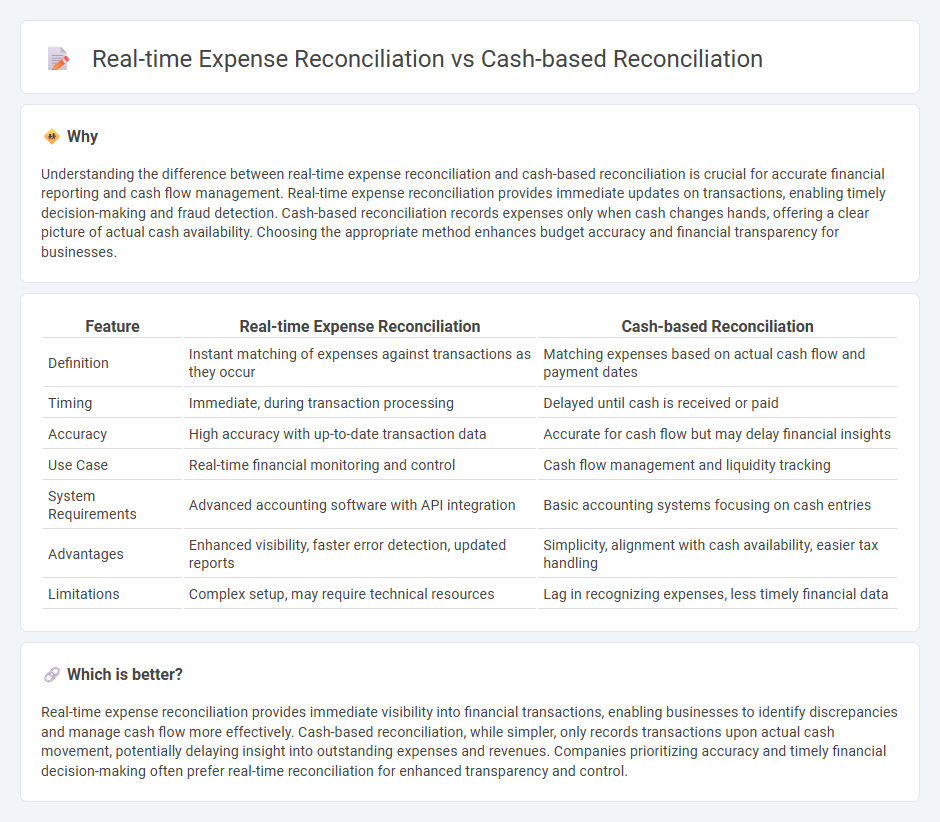
Understanding the difference between real-time expense reconciliation and cash-based reconciliation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and cash flow management. Real-time expense reconciliation provides immediate updates on transactions, enabling timely decision-making and fraud detection. Cash-based reconciliation records expenses only when cash changes hands, offering a clear picture of actual cash availability. Choosing the appropriate method enhances budget accuracy and financial transparency for businesses.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Real-time Expense Reconciliation | Cash-based Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant matching of expenses against transactions as they occur | Matching expenses based on actual cash flow and payment dates |
| Timing | Immediate, during transaction processing | Delayed until cash is received or paid |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with up-to-date transaction data | Accurate for cash flow but may delay financial insights |
| Use Case | Real-time financial monitoring and control | Cash flow management and liquidity tracking |
| System Requirements | Advanced accounting software with API integration | Basic accounting systems focusing on cash entries |
| Advantages | Enhanced visibility, faster error detection, updated reports | Simplicity, alignment with cash availability, easier tax handling |
| Limitations | Complex setup, may require technical resources | Lag in recognizing expenses, less timely financial data |
Which is better?
Real-time expense reconciliation provides immediate visibility into financial transactions, enabling businesses to identify discrepancies and manage cash flow more effectively. Cash-based reconciliation, while simpler, only records transactions upon actual cash movement, potentially delaying insight into outstanding expenses and revenues. Companies prioritizing accuracy and timely financial decision-making often prefer real-time reconciliation for enhanced transparency and control.
Connection
Real-time expense reconciliation enhances cash-based reconciliation by providing immediate updates on cash transactions, ensuring accurate and timely reflection in financial records. This integration reduces discrepancies between actual cash flow and reported expenses, improving liquidity management. Automated synchronization between real-time expense tracking systems and cash-based accounting processes enables better financial control and decision-making.
Key Terms
Timing of Recording
Cash-based reconciliation records transactions only when cash changes hands, ensuring expenses and revenues reflect actual cash flow timing. Real-time expense reconciliation captures transactions instantly at the moment they occur, providing up-to-date financial data and improved accuracy. Explore the key differences between these methods to optimize your financial management strategy.
Data Accuracy
Cash-based reconciliation relies on verifying transactions after cash movements occur, which can introduce delays and potential discrepancies in data accuracy. Real-time expense reconciliation continuously updates records as transactions happen, significantly enhancing accuracy by minimizing errors and providing instant visibility into financial statuses. Explore deeper insights into optimizing financial data accuracy through real-time reconciliation methods.
Transaction Visibility
Cash-based reconciliation records expenses when cash transactions are completed, limiting visibility to actual cash movements and potentially delaying insight into outstanding liabilities. Real-time expense reconciliation captures transactions as they occur, providing immediate visibility into spending patterns and enhancing financial transparency. Discover how improving transaction visibility can optimize your reconciliation process.
Source and External Links
Cash reconciliation definition - AccountingTools - Cash reconciliation is the process of verifying the amount of cash in a cash register at the close of business, comparing cash amounts and receipts, reconciling discrepancies, and submitting for supervisory review to detect errors or fraud.
What is Cash Reconciliation? - DebtBook - Cash reconciliation involves comparing an organization's internal cash records with external financial statements to ensure accuracy, detect discrepancies, investigate differences, adjust records, and document the process to prevent errors and fraud.
How to Perform a Cash Reconciliation: A Step-By-Step Guide for Accountants - Leapfin - Performing cash reconciliation includes determining the period, downloading financial reports (billing system cash reports, payment processor payout reports, bank statements), filtering relevant transactions, and matching cash movements across systems within the accounting period.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com