Collaborative audit trails enable multiple parties to verify and contribute to financial records, enhancing transparency and reducing discrepancies in accounting processes. Permissioned ledger audits restrict access to authorized users, ensuring data integrity and privacy while maintaining a clear record of all transactions. Explore how integrating these systems can optimize audit accuracy and compliance.
Why it is important
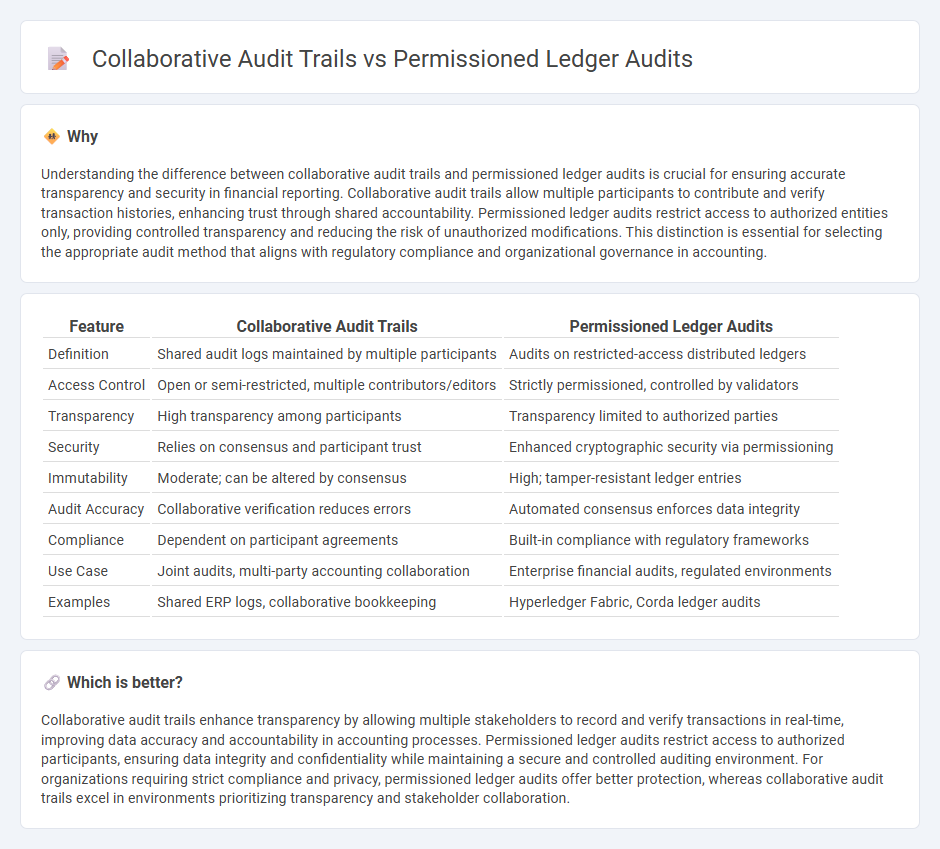
Understanding the difference between collaborative audit trails and permissioned ledger audits is crucial for ensuring accurate transparency and security in financial reporting. Collaborative audit trails allow multiple participants to contribute and verify transaction histories, enhancing trust through shared accountability. Permissioned ledger audits restrict access to authorized entities only, providing controlled transparency and reducing the risk of unauthorized modifications. This distinction is essential for selecting the appropriate audit method that aligns with regulatory compliance and organizational governance in accounting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Collaborative Audit Trails | Permissioned Ledger Audits |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Shared audit logs maintained by multiple participants | Audits on restricted-access distributed ledgers |
| Access Control | Open or semi-restricted, multiple contributors/editors | Strictly permissioned, controlled by validators |
| Transparency | High transparency among participants | Transparency limited to authorized parties |
| Security | Relies on consensus and participant trust | Enhanced cryptographic security via permissioning |
| Immutability | Moderate; can be altered by consensus | High; tamper-resistant ledger entries |
| Audit Accuracy | Collaborative verification reduces errors | Automated consensus enforces data integrity |
| Compliance | Dependent on participant agreements | Built-in compliance with regulatory frameworks |
| Use Case | Joint audits, multi-party accounting collaboration | Enterprise financial audits, regulated environments |
| Examples | Shared ERP logs, collaborative bookkeeping | Hyperledger Fabric, Corda ledger audits |
Which is better?
Collaborative audit trails enhance transparency by allowing multiple stakeholders to record and verify transactions in real-time, improving data accuracy and accountability in accounting processes. Permissioned ledger audits restrict access to authorized participants, ensuring data integrity and confidentiality while maintaining a secure and controlled auditing environment. For organizations requiring strict compliance and privacy, permissioned ledger audits offer better protection, whereas collaborative audit trails excel in environments prioritizing transparency and stakeholder collaboration.
Connection
Collaborative audit trails enable multiple stakeholders to contribute and verify financial data transparently, enhancing accuracy and trust in accounting records. Permissioned ledger audits utilize blockchain technology to restrict access to authorized participants, ensuring data integrity and secure verification of transactions. Together, these systems reinforce accountability and streamline the auditing process by combining shared access with controlled permission protocols.
Key Terms
Access Control
Permissioned ledger audits enforce stringent access control by restricting participation to verified entities, ensuring that only authorized parties can view or modify transaction records. Collaborative audit trails, while also securing data, emphasize shared visibility among stakeholders to enhance transparency and collective verification processes. Explore detailed distinctions in access control mechanisms to optimize your auditing strategy.
Data Integrity
Permissioned ledger audits enhance data integrity by restricting access to authorized participants, ensuring that all entries are traceable and tamper-evident through cryptographic verification and consensus protocols. Collaborative audit trails improve transparency among multiple stakeholders by allowing real-time sharing and verification of transaction data, promoting mutual accountability while safeguarding data accuracy. Explore further to understand how these systems revolutionize secure data management and regulatory compliance.
Traceability
Permissioned ledger audits enable controlled access to transaction records, ensuring high traceability through immutable and cryptographically secured entries. Collaborative audit trails emphasize collective verification and shared data integrity among multiple stakeholders, enhancing transparency and accountability across decentralized environments. Explore how combining these approaches can optimize traceability and audit efficiency in complex operations.
Source and External Links
IA-CCF: Individual Accountability for Permissioned Ledgers - IA-CCF is a permissioned ledger system that provides individual accountability by allowing anyone to audit the ledger with succinct, universally-verifiable receipts to detect inconsistencies and misbehaving replicas, holding individual members accountable beyond traditional Byzantine fault tolerance limits.
Blockchain Technology Could Bring Benefits to the Auditing Industry - This research shows that permissioned blockchains can significantly enhance auditing by improving data integrity, reducing costs by about 70%, and enabling efficient automatic verification of receipts, while also increasing privacy protections in audit information sharing.
ZK Ledger | The Future of Audit - zkLedger uses permissioned blockchains, zero-knowledge proofs, and cryptographic commitments to create a tamper-resistant, privacy-preserving ledger that supports verifiable auditing without revealing sensitive transaction details, offering a modern solution for transparent and secure audits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com