Real-time audits continuously monitor financial transactions and internal controls, providing immediate insights and enabling prompt detection of anomalies. Periodic audits, conducted at scheduled intervals, review financial statements and processes retrospectively, offering a comprehensive overview of compliance and accuracy. Discover how choosing between real-time and periodic audits can enhance your organization's financial oversight.
Why it is important
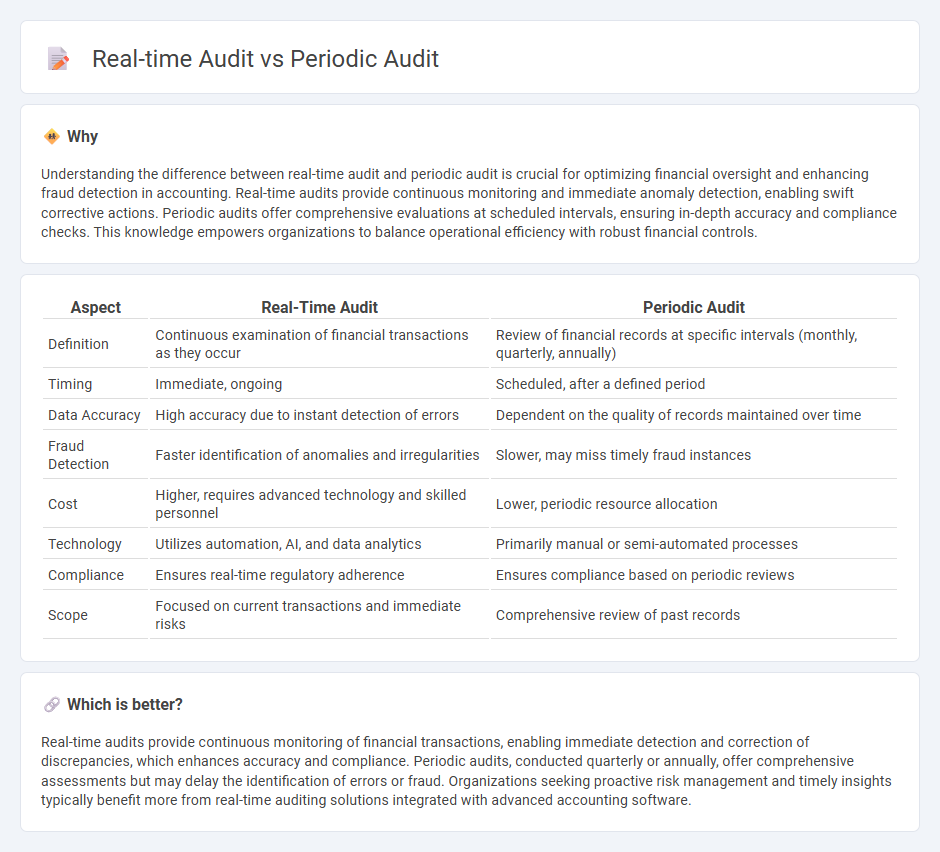
Understanding the difference between real-time audit and periodic audit is crucial for optimizing financial oversight and enhancing fraud detection in accounting. Real-time audits provide continuous monitoring and immediate anomaly detection, enabling swift corrective actions. Periodic audits offer comprehensive evaluations at scheduled intervals, ensuring in-depth accuracy and compliance checks. This knowledge empowers organizations to balance operational efficiency with robust financial controls.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Real-Time Audit | Periodic Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Continuous examination of financial transactions as they occur | Review of financial records at specific intervals (monthly, quarterly, annually) |
| Timing | Immediate, ongoing | Scheduled, after a defined period |
| Data Accuracy | High accuracy due to instant detection of errors | Dependent on the quality of records maintained over time |
| Fraud Detection | Faster identification of anomalies and irregularities | Slower, may miss timely fraud instances |
| Cost | Higher, requires advanced technology and skilled personnel | Lower, periodic resource allocation |
| Technology | Utilizes automation, AI, and data analytics | Primarily manual or semi-automated processes |
| Compliance | Ensures real-time regulatory adherence | Ensures compliance based on periodic reviews |
| Scope | Focused on current transactions and immediate risks | Comprehensive review of past records |
Which is better?
Real-time audits provide continuous monitoring of financial transactions, enabling immediate detection and correction of discrepancies, which enhances accuracy and compliance. Periodic audits, conducted quarterly or annually, offer comprehensive assessments but may delay the identification of errors or fraud. Organizations seeking proactive risk management and timely insights typically benefit more from real-time auditing solutions integrated with advanced accounting software.
Connection
Real-time audit continuously monitors financial transactions to detect anomalies immediately, enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of financial data utilized during periodic audits. Periodic audits rely on accumulated data, often validated by real-time auditing systems, to perform comprehensive assessments of financial statements and internal controls. Integration of both approaches strengthens overall audit effectiveness by combining continuous oversight with detailed, periodic evaluations, ensuring regulatory compliance and risk mitigation.
Key Terms
Audit Frequency
Periodic audits occur at set intervals, such as monthly or annually, providing a snapshot of compliance and financial health at specific points in time. Real-time audits continuously monitor transactions and activities, enabling immediate detection and response to discrepancies or risks. Explore further to understand how audit frequency impacts organizational control and risk management strategies.
Data Timeliness
Periodic audits evaluate data at fixed intervals, providing insights based on historical records that may delay the identification of issues. Real-time audits continuously monitor data streams, enabling immediate detection and response to discrepancies, which enhances operational efficiency and risk management. Explore the advantages of real-time auditing to improve data timeliness in your organization.
Control Monitoring
Periodic audits assess control monitoring effectiveness at set intervals, providing comprehensive but retrospective insights into compliance and risk management. Real-time audits enable continuous control monitoring, allowing for immediate detection and correction of anomalies, enhancing operational agility and reducing exposure to threats. Explore how integrating both methods can optimize your organization's control environment.
Source and External Links
Ensuring AML/BSA Compliance: The Importance of Periodic Audits - Discusses the importance of periodic audits for AML/BSA compliance in financial institutions, emphasizing their role in maintaining regulatory adherence and strategic decision-making.
Periodic Audit: Understanding Its Legal Definition and Importance - Explains the concept of a periodic audit as a tool for assessing compliance with federal awards and ensuring proper use of funds.
What is a Periodic Audit? - Defines a periodic audit as a regular examination of an organization's financial records and compliance with regulations, highlighting its role in identifying potential issues and maintaining operational integrity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com