Forensic analytics involves the use of advanced data analysis techniques to detect fraud, financial discrepancies, and irregularities within accounting records. Bookkeeping focuses on systematically recording daily financial transactions to maintain accurate and organized financial statements. Explore the differences and applications of forensic analytics and bookkeeping to enhance financial integrity.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between forensic analytics and bookkeeping is crucial for accurately identifying financial discrepancies and preventing fraud. Bookkeeping involves the systematic recording of daily financial transactions, while forensic analytics uses advanced techniques to analyze financial data for legal investigations. Mastery of forensic analytics enables professionals to detect complex fraud schemes that basic bookkeeping cannot reveal. Accurate distinction enhances financial transparency, compliance, and risk management in organizations.
Comparison Table
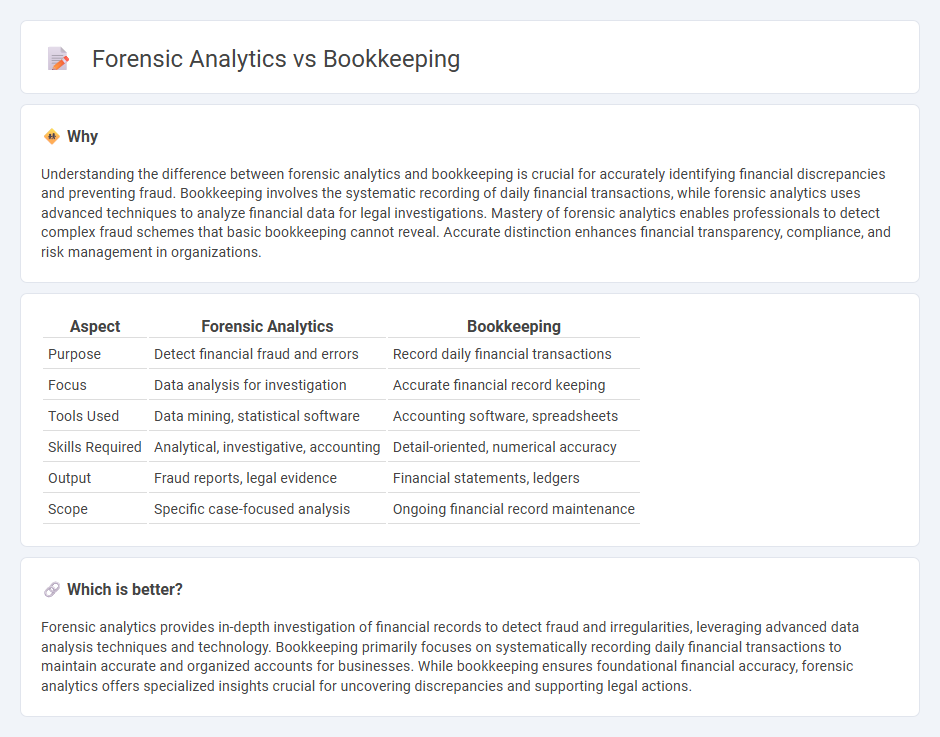
| Aspect | Forensic Analytics | Bookkeeping |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect financial fraud and errors | Record daily financial transactions |
| Focus | Data analysis for investigation | Accurate financial record keeping |
| Tools Used | Data mining, statistical software | Accounting software, spreadsheets |
| Skills Required | Analytical, investigative, accounting | Detail-oriented, numerical accuracy |
| Output | Fraud reports, legal evidence | Financial statements, ledgers |
| Scope | Specific case-focused analysis | Ongoing financial record maintenance |
Which is better?
Forensic analytics provides in-depth investigation of financial records to detect fraud and irregularities, leveraging advanced data analysis techniques and technology. Bookkeeping primarily focuses on systematically recording daily financial transactions to maintain accurate and organized accounts for businesses. While bookkeeping ensures foundational financial accuracy, forensic analytics offers specialized insights crucial for uncovering discrepancies and supporting legal actions.
Connection
Forensic analytics enhances bookkeeping by systematically examining financial records to detect discrepancies, fraud, and errors. Integrating forensic techniques into bookkeeping ensures accurate financial statements and compliance with regulatory standards. This connection strengthens audit quality and supports legal investigations through detailed transaction analysis.
Key Terms
Bookkeeping:
Bookkeeping involves systematically recording daily financial transactions to maintain accurate and up-to-date financial records essential for businesses. It includes tasks such as invoicing, payroll management, and bank reconciliations aimed at ensuring compliance with accounting standards and tax regulations. Discover how mastering bookkeeping contributes to financial transparency and decision-making.
Ledger
Bookkeeping involves the systematic recording and organization of financial transactions in the ledger, ensuring accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Forensic analytics examines ledger data to detect fraud, errors, or irregularities through detailed transaction analysis and pattern recognition. Explore how these disciplines intersect to enhance financial integrity and fraud prevention.
Journal Entries
Bookkeeping involves accurately recording journal entries to maintain a comprehensive financial ledger, ensuring transactions are classified and documented according to accounting standards. Forensic analytics scrutinizes these journal entries to detect anomalies, fraudulent activities, or irregular patterns by analyzing transaction details, dates, and amounts. Explore the key differences and techniques used in journal entry analysis to enhance financial accuracy and fraud detection.
Source and External Links
What is Bookkeeping? 2025 Business Owner's Guide | QuickBooks - Bookkeeping is the process of tracking and recording a business's financial transactions according to accounting principles, with two main types being single-entry and double-entry bookkeeping, helping businesses monitor finances and manage tasks like invoicing and payroll.
The Difference Between Bookkeeping and Accounting - Bookkeeping involves the accurate, consistent recording of daily financial transactions and maintaining the general ledger, serving as the foundation for accounting which focuses on analyzing this data for business insights.
What Is Bookkeeping? Tasks, Skills, and How to Become ... - Coursera - Bookkeeping is the systematic recording and organizing of financial transactions to maintain accurate business records, with single-entry suitable for small businesses and double-entry providing better accuracy for larger operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com