Payroll crypto taxation involves tracking and reporting employee compensation paid in cryptocurrencies, requiring compliance with IRS guidelines on fair market value and taxable income recognition. Payroll accruals focus on accounting for earned wages and related liabilities within the correct financial period, ensuring accurate financial statements according to GAAP standards. Explore more to understand the complexities and best practices in managing payroll crypto taxation versus payroll accruals.
Why it is important
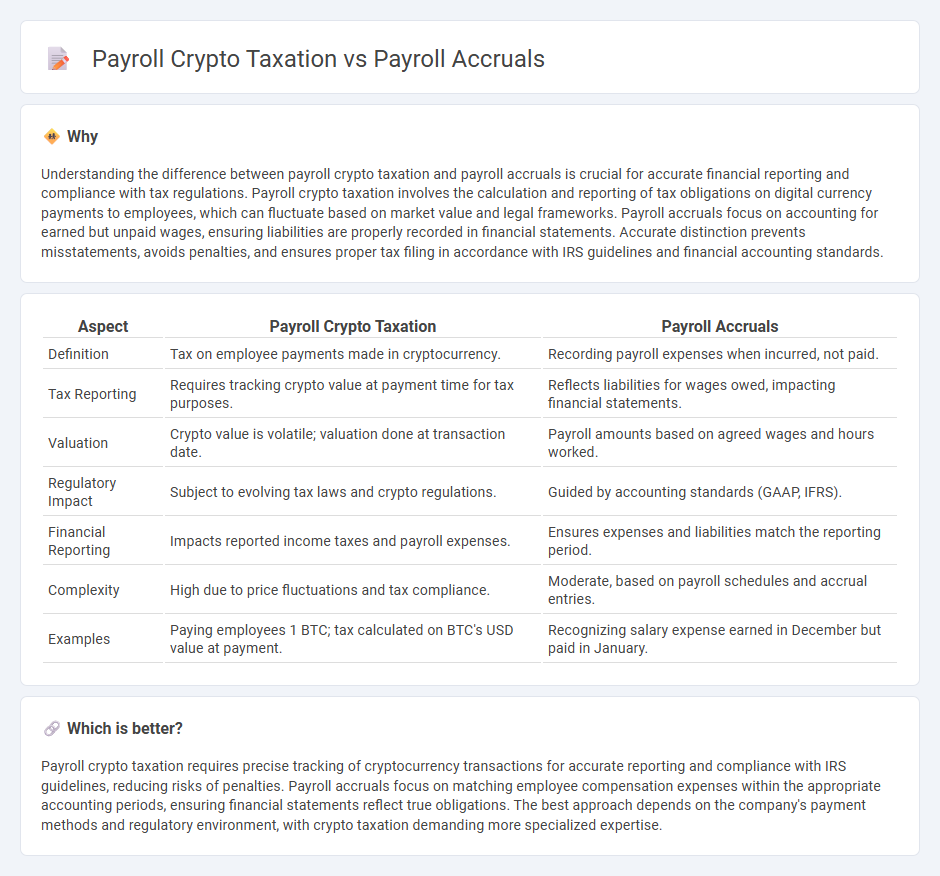
Understanding the difference between payroll crypto taxation and payroll accruals is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with tax regulations. Payroll crypto taxation involves the calculation and reporting of tax obligations on digital currency payments to employees, which can fluctuate based on market value and legal frameworks. Payroll accruals focus on accounting for earned but unpaid wages, ensuring liabilities are properly recorded in financial statements. Accurate distinction prevents misstatements, avoids penalties, and ensures proper tax filing in accordance with IRS guidelines and financial accounting standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Payroll Crypto Taxation | Payroll Accruals |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Tax on employee payments made in cryptocurrency. | Recording payroll expenses when incurred, not paid. |
| Tax Reporting | Requires tracking crypto value at payment time for tax purposes. | Reflects liabilities for wages owed, impacting financial statements. |
| Valuation | Crypto value is volatile; valuation done at transaction date. | Payroll amounts based on agreed wages and hours worked. |
| Regulatory Impact | Subject to evolving tax laws and crypto regulations. | Guided by accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS). |
| Financial Reporting | Impacts reported income taxes and payroll expenses. | Ensures expenses and liabilities match the reporting period. |
| Complexity | High due to price fluctuations and tax compliance. | Moderate, based on payroll schedules and accrual entries. |
| Examples | Paying employees 1 BTC; tax calculated on BTC's USD value at payment. | Recognizing salary expense earned in December but paid in January. |
Which is better?
Payroll crypto taxation requires precise tracking of cryptocurrency transactions for accurate reporting and compliance with IRS guidelines, reducing risks of penalties. Payroll accruals focus on matching employee compensation expenses within the appropriate accounting periods, ensuring financial statements reflect true obligations. The best approach depends on the company's payment methods and regulatory environment, with crypto taxation demanding more specialized expertise.
Connection
Payroll crypto taxation involves accurately reporting employee compensation paid in cryptocurrency, requiring mastery of IRS guidelines on virtual currency valuation and tax withholding. Payroll accruals record the expenses related to employee compensation, including crypto payments, ensuring financial statements reflect unpaid wages and tax liabilities. Integrating these processes ensures compliance with tax regulations and precise financial reporting in blockchain-based payroll systems.
Key Terms
Accrued Liabilities
Payroll accruals represent the accounting practice of recording employee compensation expenses as accrued liabilities before payment, ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards. In contrast, payroll crypto taxation involves tracking and reporting employee earnings paid in cryptocurrency, which requires understanding of tax regulations related to digital assets and the valuation of accrued payroll liabilities in crypto terms. Explore detailed insights on managing accrued payroll liabilities and navigating the complexities of crypto payroll taxation.
Fair Market Value (Crypto)
Payroll accruals involve recognizing employee compensation expenses in accounting records before payment is made, ensuring accurate financial reporting. Payroll crypto taxation requires determining the Fair Market Value (FMV) of cryptocurrency at the time of payment to calculate taxable income correctly, as the IRS treats crypto as property. Explore how precise FMV assessments impact compliance and reporting in payroll crypto taxation for deeper insights.
Tax Withholding
Payroll accruals involve recording expenses for employee wages and benefits incurred during a period but paid later, ensuring accurate financial reporting and tax withholding compliance. Payroll crypto taxation presents unique challenges in tax withholding, as cryptocurrencies can fluctuate in value and may require distinct treatment under IRS guidelines for accurate payroll tax calculation. Explore the complexities and best practices for managing tax withholding in payroll accruals and crypto compensation to ensure regulatory compliance.
Source and External Links
What Is Accrued Payroll? Definition + Calculation - Accrued payroll is the unpaid compensation a business owes employees including wages, bonuses, employer taxes, and accrued paid time off, calculated by summing all outstanding payroll liabilities for the pay period.
What is Accrued Payroll? - Accrued payroll represents the total wages and benefits employees have earned during a pay period but have not yet received, including regular pay, commissions, PTO, and employer contributions.
Biweekly Payroll Accrual Month-End Process - Payroll accrual involves estimating unpaid employee salary and wages at month-end based on unpaid days or hours worked, ensuring expenses are recorded in the correct accounting period, especially when payroll is processed after month-end.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com