Forensic data analytics in accounting focuses on detecting fraud, financial misstatements, and suspicious transactions by analyzing large datasets with advanced algorithms and patterns. Tax compliance ensures businesses adhere to tax laws, accurately reporting income and deductions to avoid penalties and audits. Explore detailed insights into how these accounting functions protect financial integrity and legal accountability.
Why it is important
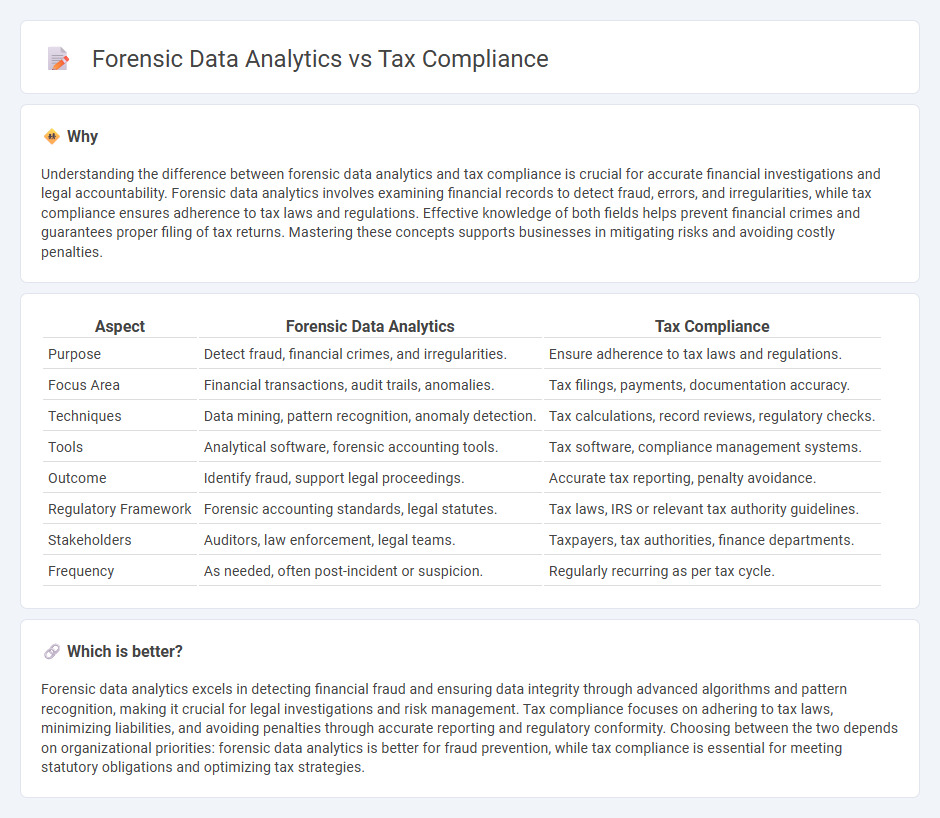
Understanding the difference between forensic data analytics and tax compliance is crucial for accurate financial investigations and legal accountability. Forensic data analytics involves examining financial records to detect fraud, errors, and irregularities, while tax compliance ensures adherence to tax laws and regulations. Effective knowledge of both fields helps prevent financial crimes and guarantees proper filing of tax returns. Mastering these concepts supports businesses in mitigating risks and avoiding costly penalties.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forensic Data Analytics | Tax Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, financial crimes, and irregularities. | Ensure adherence to tax laws and regulations. |
| Focus Area | Financial transactions, audit trails, anomalies. | Tax filings, payments, documentation accuracy. |
| Techniques | Data mining, pattern recognition, anomaly detection. | Tax calculations, record reviews, regulatory checks. |
| Tools | Analytical software, forensic accounting tools. | Tax software, compliance management systems. |
| Outcome | Identify fraud, support legal proceedings. | Accurate tax reporting, penalty avoidance. |
| Regulatory Framework | Forensic accounting standards, legal statutes. | Tax laws, IRS or relevant tax authority guidelines. |
| Stakeholders | Auditors, law enforcement, legal teams. | Taxpayers, tax authorities, finance departments. |
| Frequency | As needed, often post-incident or suspicion. | Regularly recurring as per tax cycle. |
Which is better?
Forensic data analytics excels in detecting financial fraud and ensuring data integrity through advanced algorithms and pattern recognition, making it crucial for legal investigations and risk management. Tax compliance focuses on adhering to tax laws, minimizing liabilities, and avoiding penalties through accurate reporting and regulatory conformity. Choosing between the two depends on organizational priorities: forensic data analytics is better for fraud prevention, while tax compliance is essential for meeting statutory obligations and optimizing tax strategies.
Connection
Forensic data analytics enhances tax compliance by identifying discrepancies and uncovering fraudulent activities within financial records, enabling accurate detection of tax evasion. Advanced analytical tools scrutinize large datasets to detect patterns indicative of non-compliance or manipulation in tax filings. This integration supports regulatory authorities and organizations in ensuring adherence to tax laws and minimizing risks associated with financial misconduct.
Key Terms
**Tax compliance:**
Tax compliance involves adhering to tax laws and regulations by accurately reporting income, expenses, and other financial information to tax authorities. It requires systematic record-keeping, timely filing of tax returns, and ensuring all deductions and credits are properly claimed to avoid penalties. Explore deeper insights into tax compliance strategies and tools to optimize your financial reporting.
Filing requirements
Tax compliance centers on meeting filing requirements by accurately preparing and submitting tax returns in accordance with government regulations to avoid penalties. Forensic data analytics involves analyzing financial records and transactional data to detect inconsistencies, fraud, or errors that may indicate non-compliance or tax evasion. Explore how integrating forensic data analytics enhances accuracy and reliability in fulfilling tax filing obligations.
Tax deductions
Tax compliance ensures accurate reporting and adherence to tax laws, focusing on identifying eligible tax deductions to minimize liabilities. Forensic data analytics investigates anomalies or potential fraud in deduction claims by analyzing transaction patterns and financial records. Explore how integrating both approaches can enhance deduction accuracy and prevent tax-related risks.
Source and External Links
What is tax compliance? - Basware - Tax compliance means adhering to the tax laws and regulations set by governments, ensuring accurate filing, payment, and record-keeping to avoid penalties and maintain trust with stakeholders.
What is Tax Compliance? - TopSource Worldwide - Tax compliance involves fulfilling all legal tax obligations, such as reporting income, filing returns on time, paying taxes owed, and maintaining proper financial records for businesses and individuals.
Tax compliance report | Internal Revenue Service - A tax compliance report is an official document showing whether an individual or business has filed returns and paid taxes on time, often requested by employers, agencies, or financial institutions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com