Dynamic discounting enables businesses to optimize cash flow by offering early payment discounts directly to suppliers, reducing reliance on external financing. Factoring involves selling accounts receivable to third parties at a discount to obtain immediate funds, often at higher costs and with credit risk transfer. Explore the benefits and applications of dynamic discounting versus factoring to enhance your company's financial strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dynamic discounting and factoring is crucial for optimizing cash flow management and reducing financing costs in accounting. Dynamic discounting allows buyers to offer early payment discounts to suppliers, enhancing supplier relationships while improving working capital efficiency. Factoring involves selling accounts receivable to a third party at a discount, providing immediate cash but at a higher cost and potential loss of control over receivables. Proper knowledge of both methods enables accountants to choose the most cost-effective and strategic financing tool for their organization's liquidity needs.
Comparison Table
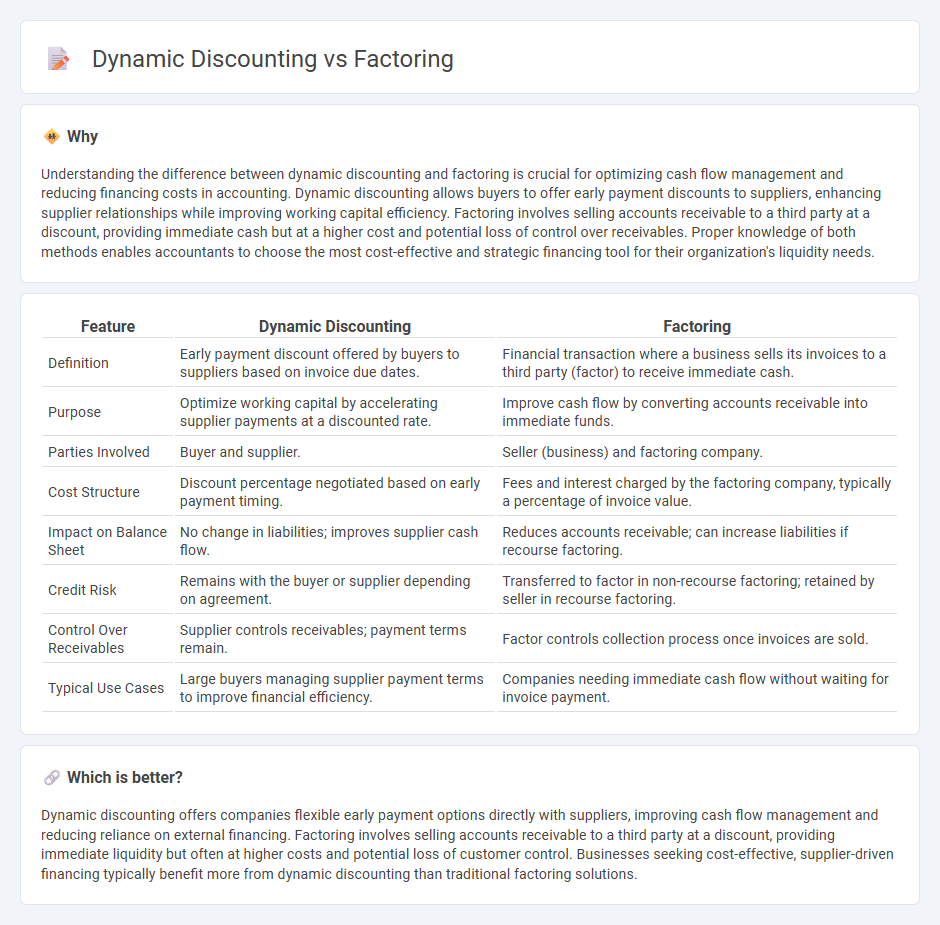
| Feature | Dynamic Discounting | Factoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Early payment discount offered by buyers to suppliers based on invoice due dates. | Financial transaction where a business sells its invoices to a third party (factor) to receive immediate cash. |
| Purpose | Optimize working capital by accelerating supplier payments at a discounted rate. | Improve cash flow by converting accounts receivable into immediate funds. |
| Parties Involved | Buyer and supplier. | Seller (business) and factoring company. |
| Cost Structure | Discount percentage negotiated based on early payment timing. | Fees and interest charged by the factoring company, typically a percentage of invoice value. |
| Impact on Balance Sheet | No change in liabilities; improves supplier cash flow. | Reduces accounts receivable; can increase liabilities if recourse factoring. |
| Credit Risk | Remains with the buyer or supplier depending on agreement. | Transferred to factor in non-recourse factoring; retained by seller in recourse factoring. |
| Control Over Receivables | Supplier controls receivables; payment terms remain. | Factor controls collection process once invoices are sold. |
| Typical Use Cases | Large buyers managing supplier payment terms to improve financial efficiency. | Companies needing immediate cash flow without waiting for invoice payment. |
Which is better?
Dynamic discounting offers companies flexible early payment options directly with suppliers, improving cash flow management and reducing reliance on external financing. Factoring involves selling accounts receivable to a third party at a discount, providing immediate liquidity but often at higher costs and potential loss of customer control. Businesses seeking cost-effective, supplier-driven financing typically benefit more from dynamic discounting than traditional factoring solutions.
Connection
Dynamic discounting and factoring both enhance cash flow management by accelerating receivables collection, but they operate differently: dynamic discounting allows buyers to pay suppliers early in exchange for a discount, while factoring involves a third party purchasing invoices at a discount to provide immediate funds. Businesses leverage dynamic discounting to reduce procurement costs and improve supplier relationships, whereas factoring offers quick liquidity without waiting for invoice maturity. Integrating these financial strategies supports optimized working capital and improved financial stability in accounting practices.
Key Terms
Accounts Receivable
Factoring involves selling accounts receivable to a third party at a discount to improve immediate cash flow, while dynamic discounting enables buyers to offer early payment to suppliers in exchange for a variable discount, enhancing working capital efficiency. Both methods serve as accounts receivable financing solutions but differ in ownership transfer and cost structure, with factoring often involving external financiers and dynamic discounting managed internally through supplier agreements. Explore how these strategies impact cash flow management and supplier relationships in your business.
Cash Flow
Factoring provides immediate cash flow by selling invoices to a third party at a discount, enabling businesses to convert receivables into working capital quickly. Dynamic discounting allows buyers to pay suppliers early in exchange for variable discounts, optimizing cash flow based on available liquidity and payment terms flexibility. Explore deeper insights on factoring and dynamic discounting to enhance your cash flow management strategies.
Early Payment
Factoring involves selling invoices to a third party at a discount to receive immediate cash, while dynamic discounting allows buyers to pay suppliers early in exchange for variable discounts based on payment timing. Early payment solutions enhance cash flow management by accelerating receivables via flexible financial arrangements tailored to both parties' needs. Explore how these mechanisms optimize working capital and supplier relationships for your business success.
Source and External Links
Factoring (finance) - A financial transaction where businesses sell their accounts receivable to a third party at a discount to meet immediate cash needs.
Factoring in Algebra - A process of splitting an algebraic expression into a product of simpler expressions.
Algebra - Factoring Polynomials - A method of breaking down polynomials into simpler factors, often using techniques like grouping or finding common factors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com