Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting evaluates a company's performance based on sustainability, ethical practices, and social responsibility metrics, while Carbon accounting specifically quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to measure environmental impact. ESG accounting integrates broader criteria, including labor practices and community engagement, offering a holistic view of corporate responsibility beyond carbon footprints. Explore how these distinct accounting approaches drive transparency and sustainable business strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting and Carbon accounting is crucial for businesses to accurately measure and report their sustainability performance and regulatory compliance. ESG accounting evaluates a broad range of non-financial factors including social responsibility, corporate governance, and environmental impact, whereas Carbon accounting specifically quantifies greenhouse gas emissions. Accurate differentiation ensures targeted strategies for risk management, investment decisions, and stakeholder communication aligned with global standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Greenhouse Gas Protocol. Companies leveraging both practices can enhance transparency, drive sustainable growth, and meet evolving investor and regulatory expectations.
Comparison Table
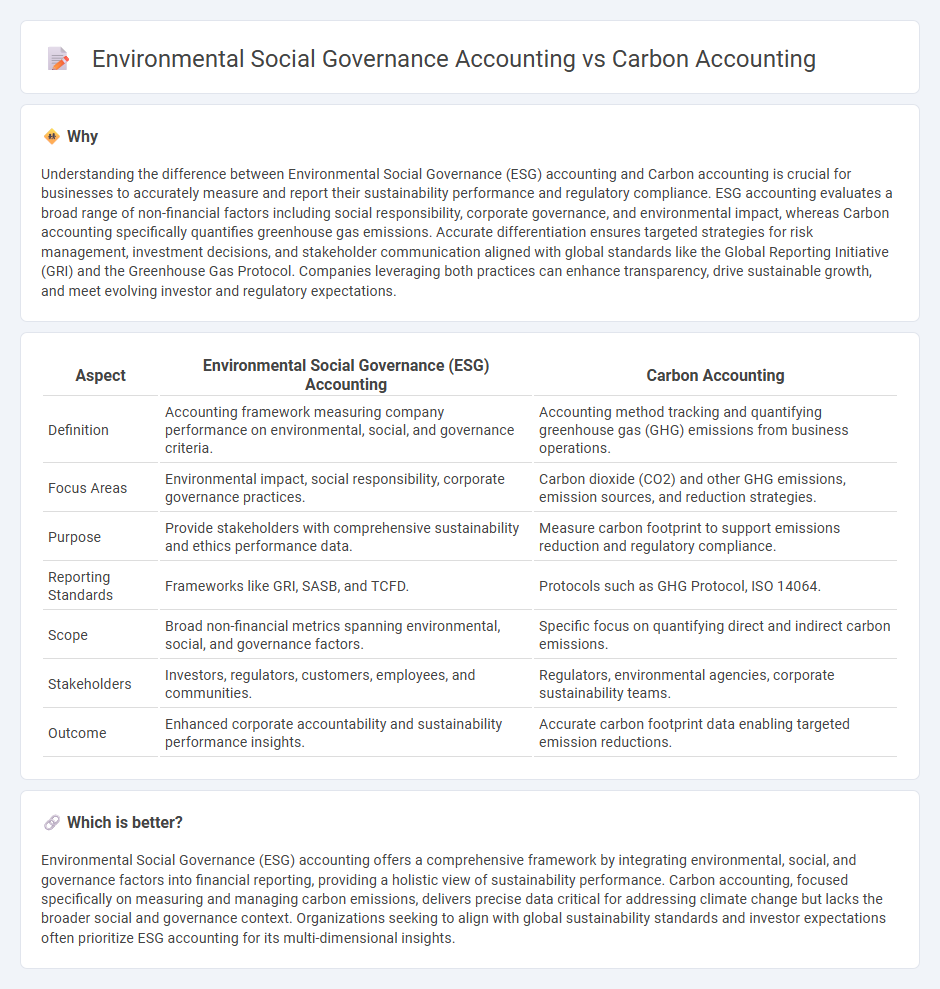
| Aspect | Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Accounting | Carbon Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting framework measuring company performance on environmental, social, and governance criteria. | Accounting method tracking and quantifying greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions from business operations. |
| Focus Areas | Environmental impact, social responsibility, corporate governance practices. | Carbon dioxide (CO2) and other GHG emissions, emission sources, and reduction strategies. |
| Purpose | Provide stakeholders with comprehensive sustainability and ethics performance data. | Measure carbon footprint to support emissions reduction and regulatory compliance. |
| Reporting Standards | Frameworks like GRI, SASB, and TCFD. | Protocols such as GHG Protocol, ISO 14064. |
| Scope | Broad non-financial metrics spanning environmental, social, and governance factors. | Specific focus on quantifying direct and indirect carbon emissions. |
| Stakeholders | Investors, regulators, customers, employees, and communities. | Regulators, environmental agencies, corporate sustainability teams. |
| Outcome | Enhanced corporate accountability and sustainability performance insights. | Accurate carbon footprint data enabling targeted emission reductions. |
Which is better?
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting offers a comprehensive framework by integrating environmental, social, and governance factors into financial reporting, providing a holistic view of sustainability performance. Carbon accounting, focused specifically on measuring and managing carbon emissions, delivers precise data critical for addressing climate change but lacks the broader social and governance context. Organizations seeking to align with global sustainability standards and investor expectations often prioritize ESG accounting for its multi-dimensional insights.
Connection
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting and Carbon accounting are interconnected through their focus on measuring and reporting sustainability-related financial impacts. ESG accounting integrates environmental metrics, including carbon emissions, into financial disclosures to inform stakeholders about an organization's ecological footprint and risk management. Carbon accounting specifically quantifies greenhouse gas emissions, providing detailed data that enhances ESG reporting accuracy and supports compliance with regulatory frameworks like the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD).
Key Terms
**Carbon Accounting:**
Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to measure an organization's carbon footprint and its impact on climate change, using frameworks like the Greenhouse Gas Protocol. It supports regulatory compliance, carbon trading, and sustainability reporting by providing accurate emissions data. Discover how implementing robust carbon accounting can enhance environmental accountability and drive strategic decarbonization efforts.
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions
Carbon accounting specifically measures and tracks Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions to quantify an organization's carbon footprint, enabling targeted reductions and regulatory compliance. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) accounting incorporates GHG emissions as one part of a broader framework assessing environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance practices. Explore in-depth methodologies and benefits of integrating GHG data within ESG frameworks for comprehensive sustainability management.
Carbon Footprint
Carbon accounting specifically measures greenhouse gas emissions, quantifying the carbon footprint of organizations, products, and activities to gauge their impact on climate change. Environmental social governance (ESG) accounting encompasses a broader scope, integrating carbon footprint metrics with social and governance factors to evaluate overall sustainability performance. Explore how these distinct accounting frameworks drive corporate responsibility and influence strategic decision-making.
Source and External Links
What Is Carbon Accounting? | IBM - Carbon accounting is the process of quantifying greenhouse gas emissions produced directly and indirectly by an organization, using CO2 equivalent (CO2e) for all major gases, helping companies understand their climate impact and set emission reduction goals, often following the Greenhouse Gas Protocol's classification of emissions into three scopes.
Carbon accounting, explained - Carbon accounting calculates an organization's greenhouse gas emissions to quantify its climate impact, enabling companies to identify emission hotspots, reduce emissions, comply with reporting requirements, and support their journey to net zero by measuring and managing carbon footprints like financial accounting tracks financial impact.
Carbon Accounting | CarbonNeutral - Carbon accounting involves measuring and tracking greenhouse gas emissions from a company's activities to understand emission sources, implement reduction strategies, and communicate results to stakeholders; it is increasingly becoming a legal requirement in many countries with mandatory reporting laws expanding globally.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com