Continuous assurance leverages real-time data monitoring to proactively identify discrepancies and risks within financial processes, enhancing accuracy and compliance. Detective control, by contrast, involves periodic reviews and audits conducted after transactions occur to uncover errors or fraud. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches impact financial integrity and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
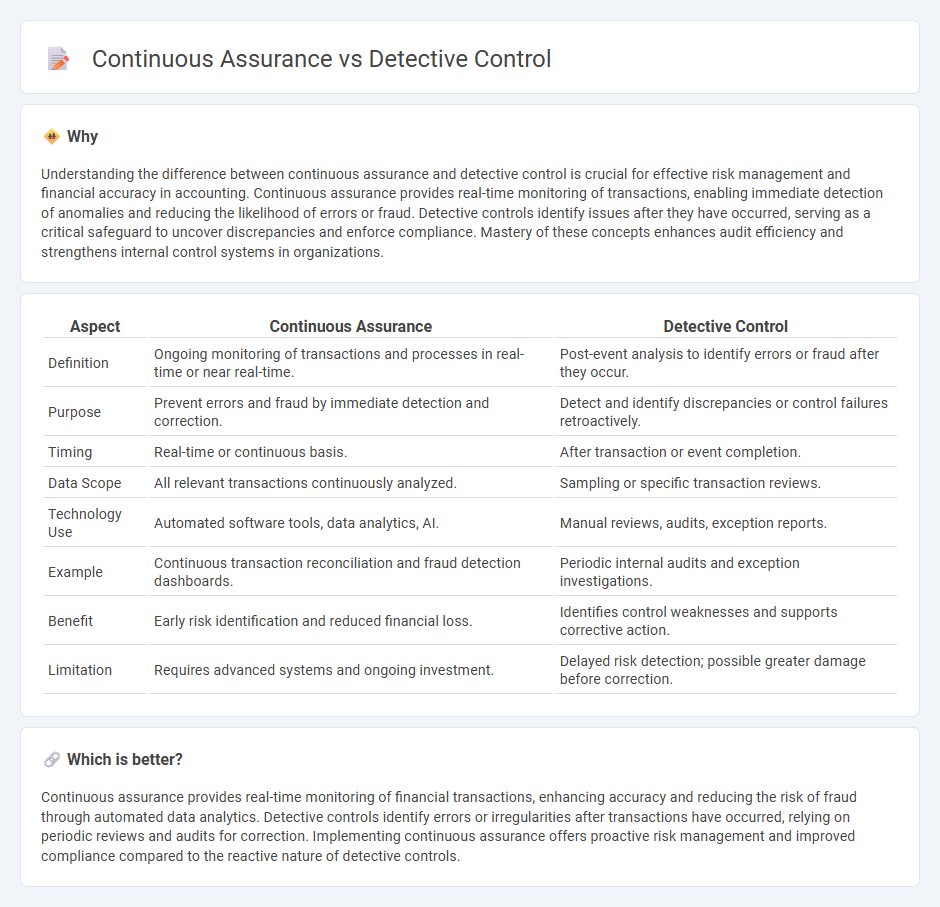
Understanding the difference between continuous assurance and detective control is crucial for effective risk management and financial accuracy in accounting. Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring of transactions, enabling immediate detection of anomalies and reducing the likelihood of errors or fraud. Detective controls identify issues after they have occurred, serving as a critical safeguard to uncover discrepancies and enforce compliance. Mastery of these concepts enhances audit efficiency and strengthens internal control systems in organizations.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Assurance | Detective Control |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing monitoring of transactions and processes in real-time or near real-time. | Post-event analysis to identify errors or fraud after they occur. |
| Purpose | Prevent errors and fraud by immediate detection and correction. | Detect and identify discrepancies or control failures retroactively. |
| Timing | Real-time or continuous basis. | After transaction or event completion. |
| Data Scope | All relevant transactions continuously analyzed. | Sampling or specific transaction reviews. |
| Technology Use | Automated software tools, data analytics, AI. | Manual reviews, audits, exception reports. |
| Example | Continuous transaction reconciliation and fraud detection dashboards. | Periodic internal audits and exception investigations. |
| Benefit | Early risk identification and reduced financial loss. | Identifies control weaknesses and supports corrective action. |
| Limitation | Requires advanced systems and ongoing investment. | Delayed risk detection; possible greater damage before correction. |
Which is better?
Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring of financial transactions, enhancing accuracy and reducing the risk of fraud through automated data analytics. Detective controls identify errors or irregularities after transactions have occurred, relying on periodic reviews and audits for correction. Implementing continuous assurance offers proactive risk management and improved compliance compared to the reactive nature of detective controls.
Connection
Continuous assurance continuously monitors financial transactions using automated tools to detect anomalies in real-time, enhancing the effectiveness of detective controls. Detective controls identify and investigate irregularities or errors after they occur, relying on data flagged through ongoing assurance processes. Integration of continuous assurance with detective controls enables timely identification and remediation of accounting discrepancies, improving overall financial accuracy and compliance.
Key Terms
Reconciliation
Reconciliation is a critical focus in both detective control and continuous assurance, ensuring accuracy between financial records and actual transactions to prevent discrepancies. Detective control identifies errors or fraud after transactions occur through periodic reviews, while continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring for immediate issue detection. Explore how integrating these approaches enhances financial integrity and operational efficiency.
Exception Reporting
Detective control primarily involves identifying and investigating exceptions after transactions have occurred, relying heavily on exception reporting to highlight anomalies or discrepancies for corrective action. Continuous assurance integrates real-time monitoring and exception reporting to provide ongoing validation of controls, enabling proactive detection and remediation of issues. Explore how these approaches optimize risk management and operational efficiency through exception reporting insights.
Real-time Monitoring
Detective control identifies anomalies and errors after they occur, relying on periodic reviews that may delay issue resolution. Continuous assurance employs real-time monitoring with automated data analytics, enabling immediate detection and response to discrepancies as transactions happen. Explore how integrating continuous assurance can transform your organization's risk management and compliance strategies.
Source and External Links
Detective control definition - AccountingTools - A detective control is designed to locate problems after they have occurred, allowing management to take corrective action to mitigate future risks; examples include bank reconciliations, internal audits, and exception reports, and these controls are complementary to preventive controls that aim to stop problems before they happen.
Detective controls - AWS Prescriptive Guidance - Detective controls are security measures that detect, log, and alert after an event has occurred, providing a second line of defense by notifying security teams of issues that bypass preventive controls and enabling faster incident response and investigation.
Detective controls // Division of Finance & Business Services - Detective controls attempt to detect undesirable acts after they occur and provide evidence of losses or errors, with examples including supervisory reviews, physical inventories, and control self-assessments to identify and address discrepancies or weaknesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com