Forensic analytics utilizes advanced data analysis techniques to detect fraud, financial discrepancies, and legal evidence within accounting records. In contrast, cost accounting focuses on analyzing, recording, and controlling costs related to production and operations to enhance profitability and efficiency. Explore more insights to understand how each method uniquely supports financial decision-making.
Why it is important
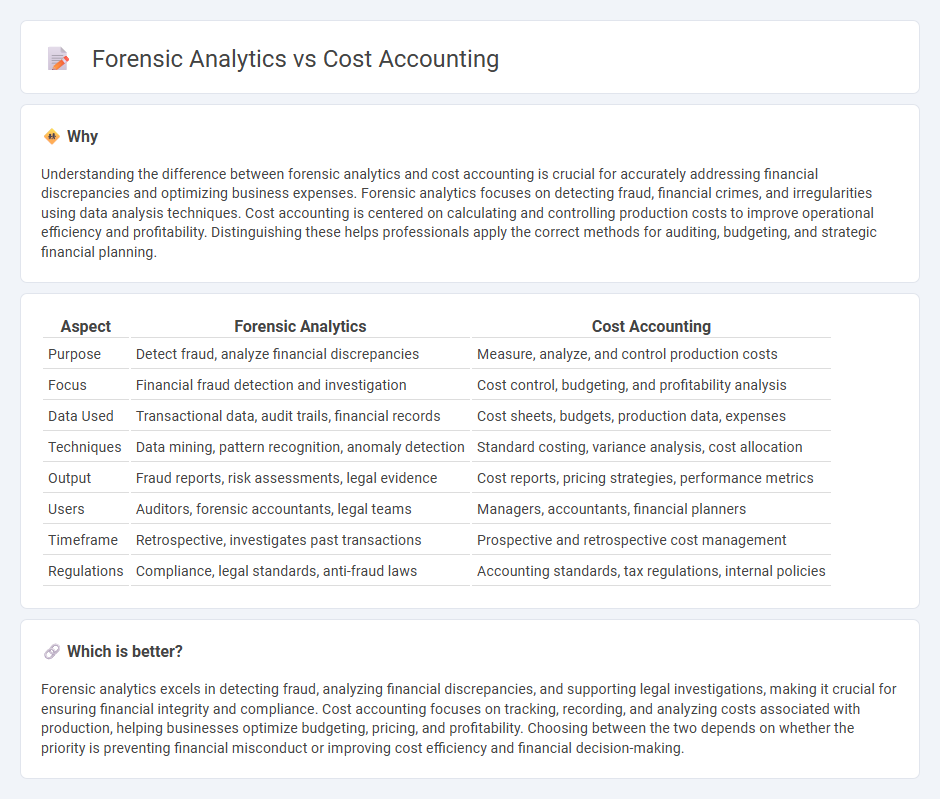
Understanding the difference between forensic analytics and cost accounting is crucial for accurately addressing financial discrepancies and optimizing business expenses. Forensic analytics focuses on detecting fraud, financial crimes, and irregularities using data analysis techniques. Cost accounting is centered on calculating and controlling production costs to improve operational efficiency and profitability. Distinguishing these helps professionals apply the correct methods for auditing, budgeting, and strategic financial planning.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Forensic Analytics | Cost Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Detect fraud, analyze financial discrepancies | Measure, analyze, and control production costs |
| Focus | Financial fraud detection and investigation | Cost control, budgeting, and profitability analysis |
| Data Used | Transactional data, audit trails, financial records | Cost sheets, budgets, production data, expenses |
| Techniques | Data mining, pattern recognition, anomaly detection | Standard costing, variance analysis, cost allocation |
| Output | Fraud reports, risk assessments, legal evidence | Cost reports, pricing strategies, performance metrics |
| Users | Auditors, forensic accountants, legal teams | Managers, accountants, financial planners |
| Timeframe | Retrospective, investigates past transactions | Prospective and retrospective cost management |
| Regulations | Compliance, legal standards, anti-fraud laws | Accounting standards, tax regulations, internal policies |
Which is better?
Forensic analytics excels in detecting fraud, analyzing financial discrepancies, and supporting legal investigations, making it crucial for ensuring financial integrity and compliance. Cost accounting focuses on tracking, recording, and analyzing costs associated with production, helping businesses optimize budgeting, pricing, and profitability. Choosing between the two depends on whether the priority is preventing financial misconduct or improving cost efficiency and financial decision-making.
Connection
Forensic analytics enhances cost accounting by identifying discrepancies, fraud, and inefficiencies within financial records and cost data. By applying data analysis techniques to cost accounting information, organizations can detect irregularities in expenses, inventory valuations, and cost allocations. This integration supports accurate financial reporting and strengthens internal controls to prevent financial losses.
Key Terms
**Cost accounting:**
Cost accounting systematically tracks, records, and analyzes production costs to optimize financial efficiency and support strategic decision-making in businesses. It provides detailed insights into direct and indirect costs, enabling companies to control expenses and price products competitively. Explore more about how cost accounting drives profitability and operational excellence.
Overhead allocation
Cost accounting allocates overhead by assigning indirect costs to products or departments using methods such as activity-based costing or predetermined overhead rates, enabling accurate product costing. Forensic analytics examines overhead allocation for anomalies or irregularities that may indicate fraud, inefficiencies, or misallocation of expenses. Explore how integrating forensic analytics with cost accounting enhances the accuracy and integrity of overhead cost management.
Standard costing
Standard costing in cost accounting involves setting predetermined costs for materials, labor, and overhead to measure performance and control expenses within manufacturing processes. Forensic analytics applies investigative techniques to analyze financial data and identify discrepancies or fraud related to cost variances and standard costing deviations. Explore how integrating standard costing with forensic analytics enhances accuracy and transparency in financial management.
Source and External Links
What Is Cost Accounting | A Guide for Businesses - BPM - Cost accounting is a specialized field that analyzes, standardizes, forecasts, and compares cost data to determine the true cost of products or services, aiding management in strategic pricing, reducing waste, and improving profitability.
Cost Accounting Defined: What It Is & Why It Matters - NetSuite - Cost accounting tracks, analyzes, and summarizes all fixed and variable input costs related to production, helping companies control expenses and inform pricing decisions for internal management use.
Cost accounting - Wikipedia - Cost accounting involves systematic procedures for recording and reporting measurements of the cost of manufacturing goods and performing services, often using techniques like standard costing to compare actual and predefined costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com