Data lake reconciliation automates the process by integrating vast financial datasets into a centralized repository, enhancing accuracy and real-time analysis. Manual reconciliation relies on manual data entry and cross-verification, increasing the risk of errors and consuming significant time. Explore the advantages of data lake reconciliation to optimize your accounting processes.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between Data Lake Reconciliation and Manual Reconciliation is crucial in accounting to enhance accuracy and efficiency in financial data verification. Data Lake Reconciliation leverages automated processes to handle large volumes of financial data from various sources, reducing human error and saving time. Manual Reconciliation involves human intervention to cross-check transactions, which is essential for resolving discrepancies that automated systems may not detect. Mastery of both methods ensures comprehensive financial integrity, compliance, and informed decision-making in accounting practices.
Comparison Table
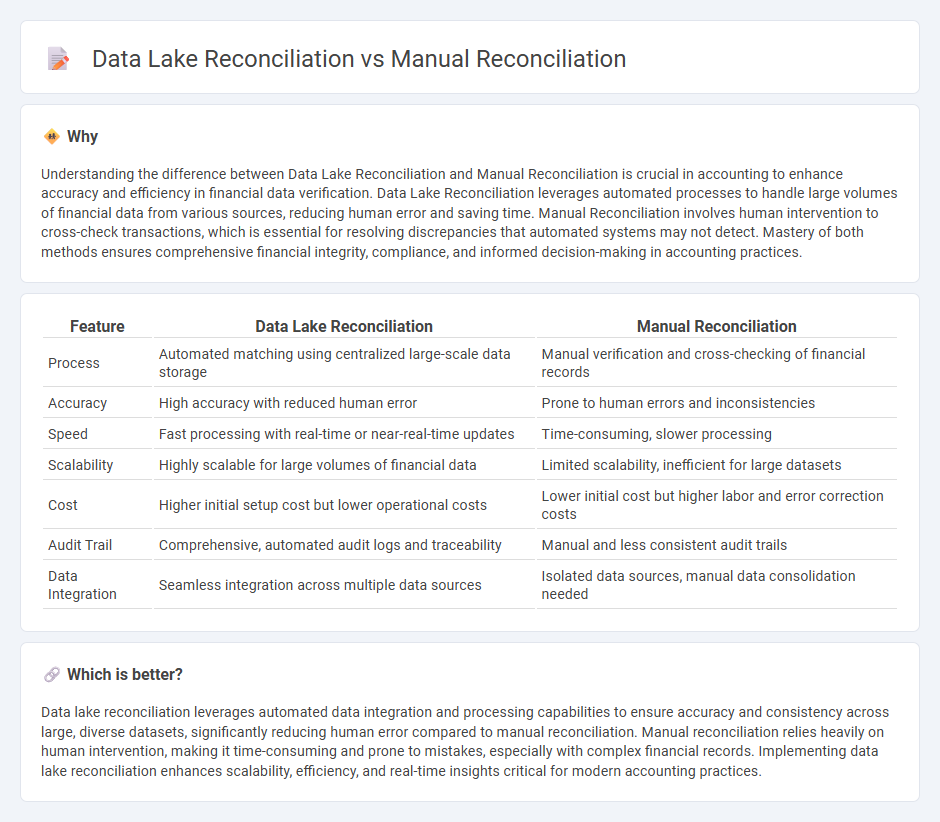
| Feature | Data Lake Reconciliation | Manual Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Automated matching using centralized large-scale data storage | Manual verification and cross-checking of financial records |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with reduced human error | Prone to human errors and inconsistencies |
| Speed | Fast processing with real-time or near-real-time updates | Time-consuming, slower processing |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large volumes of financial data | Limited scalability, inefficient for large datasets |
| Cost | Higher initial setup cost but lower operational costs | Lower initial cost but higher labor and error correction costs |
| Audit Trail | Comprehensive, automated audit logs and traceability | Manual and less consistent audit trails |
| Data Integration | Seamless integration across multiple data sources | Isolated data sources, manual data consolidation needed |
Which is better?
Data lake reconciliation leverages automated data integration and processing capabilities to ensure accuracy and consistency across large, diverse datasets, significantly reducing human error compared to manual reconciliation. Manual reconciliation relies heavily on human intervention, making it time-consuming and prone to mistakes, especially with complex financial records. Implementing data lake reconciliation enhances scalability, efficiency, and real-time insights critical for modern accounting practices.
Connection
Data lake reconciliation and manual reconciliation intersect in accounting by ensuring data accuracy and consistency across diverse financial systems. Data lake reconciliation automates the aggregation and comparison of large volumes of transactional data from multiple sources, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency. Manual reconciliation complements this process by addressing exceptions and anomalies that require human judgment and detailed verification for compliance and audit purposes.
Key Terms
Source Documents
Manual reconciliation relies heavily on physical source documents such as invoices, receipts, and transaction records to verify financial data, which can be time-consuming and prone to human error. Data lake reconciliation utilizes centralized, scalable data repositories that integrate multiple digital source documents, enabling faster, automated verification and improved data accuracy. Explore more insights on optimizing reconciliation processes with data lakes.
Data Integration
Manual reconciliation relies on human intervention to compare and verify data sets, often leading to increased errors and slower processing times in data integration workflows. Data lake reconciliation automates the process by using advanced algorithms and scalable storage, enabling seamless integration of diverse data sources and ensuring data consistency. Explore how data lake reconciliation revolutionizes data integration for enhanced accuracy and efficiency.
Automation
Manual reconciliation involves labor-intensive processes prone to human error and inefficiencies, whereas data lake reconciliation leverages automated tools to streamline data integration and validation across multiple sources. Automation in data lake reconciliation enhances accuracy, scalability, and real-time data consistency, significantly reducing operational costs and improving decision-making speed. Explore how automated reconciliation in data lakes revolutionizes data management and boosts organizational performance.
Source and External Links
Why Manual Reconciliation Fails Accounting Teams - Teampay - Manual reconciliation is the process where accounting professionals manually compare ledgers and transactions to ensure the books are balanced, involving stages like comparing records, identifying open payments, and making adjustments, covering types such as one-step vs. multi-step and bank vs. non-bank reconciliation.
Manual vs Automated Balance Sheet Reconciliation - DataSnipper - Manual reconciliation requires auditors to gather data and manually verify account balances and transactions, which is time-consuming and error-prone compared to automated methods that streamline and reduce errors using technology.
How You Manually Reconcile a Bank Statement - Oracle Help Center - Manual bank statement reconciliation involves selecting and clearing transactions manually, including handling bank errors through reversal and adjustment methods to correct discrepancies on statements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com