Continuous auditing integrates automated data analytics to enable real-time financial monitoring and risk management, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in detecting discrepancies. Information systems auditing focuses on evaluating the controls, security, and integrity of IT infrastructures that support financial reporting and operations. Explore the nuances of these auditing approaches to strengthen your organization's financial oversight.
Why it is important
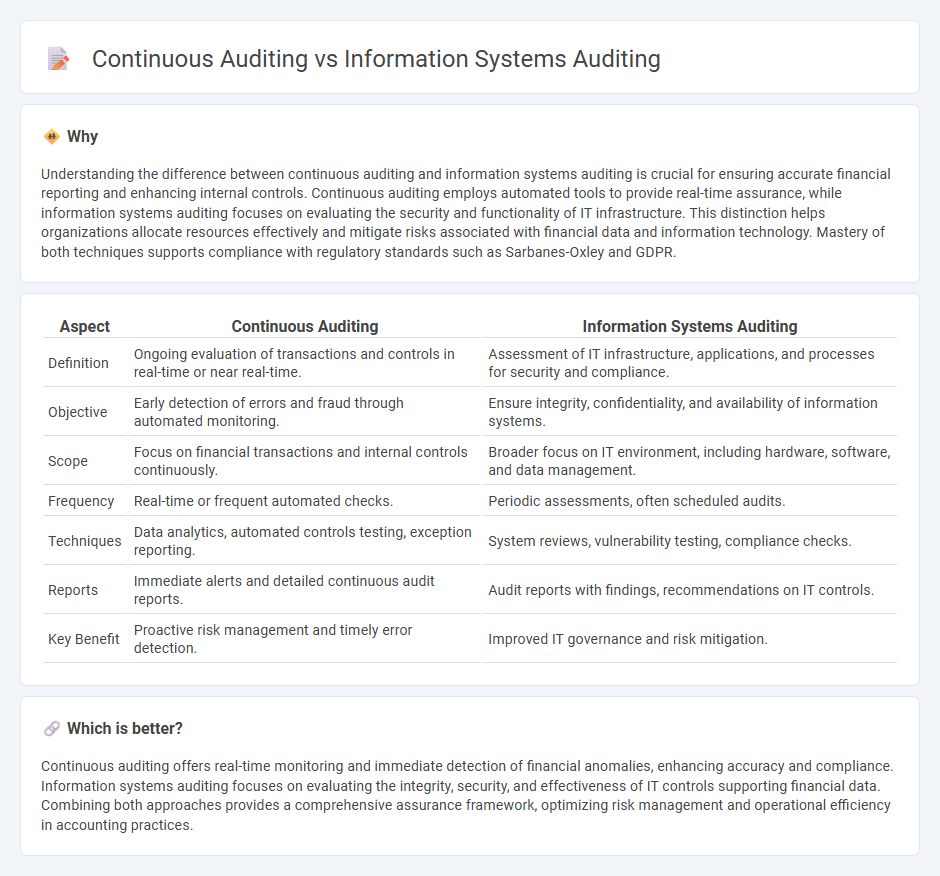
Understanding the difference between continuous auditing and information systems auditing is crucial for ensuring accurate financial reporting and enhancing internal controls. Continuous auditing employs automated tools to provide real-time assurance, while information systems auditing focuses on evaluating the security and functionality of IT infrastructure. This distinction helps organizations allocate resources effectively and mitigate risks associated with financial data and information technology. Mastery of both techniques supports compliance with regulatory standards such as Sarbanes-Oxley and GDPR.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Auditing | Information Systems Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing evaluation of transactions and controls in real-time or near real-time. | Assessment of IT infrastructure, applications, and processes for security and compliance. |
| Objective | Early detection of errors and fraud through automated monitoring. | Ensure integrity, confidentiality, and availability of information systems. |
| Scope | Focus on financial transactions and internal controls continuously. | Broader focus on IT environment, including hardware, software, and data management. |
| Frequency | Real-time or frequent automated checks. | Periodic assessments, often scheduled audits. |
| Techniques | Data analytics, automated controls testing, exception reporting. | System reviews, vulnerability testing, compliance checks. |
| Reports | Immediate alerts and detailed continuous audit reports. | Audit reports with findings, recommendations on IT controls. |
| Key Benefit | Proactive risk management and timely error detection. | Improved IT governance and risk mitigation. |
Which is better?
Continuous auditing offers real-time monitoring and immediate detection of financial anomalies, enhancing accuracy and compliance. Information systems auditing focuses on evaluating the integrity, security, and effectiveness of IT controls supporting financial data. Combining both approaches provides a comprehensive assurance framework, optimizing risk management and operational efficiency in accounting practices.
Connection
Continuous auditing integrates with information systems auditing by leveraging automated data analysis tools to perform real-time evaluations of financial transactions and controls. Information systems auditing assesses the effectiveness, security, and integrity of IT environments that support accounting processes, enabling continuous auditing to monitor compliance and detect anomalies promptly. This connection enhances risk management and ensures accurate, timely financial reporting through ongoing assessment of internal controls within enterprise information systems.
Key Terms
**Information Systems Auditing:**
Information systems auditing involves systematically evaluating an organization's IT infrastructure, policies, and operations to ensure data integrity, security, and compliance with regulatory standards like ISO 27001 and GDPR. This audit process typically includes risk assessments, control evaluations, and the verification of information systems' effectiveness at specific intervals. Explore more to understand how information systems auditing safeguards digital assets and enhances organizational resilience.
Controls Assessment
Information systems auditing evaluates the effectiveness of controls through periodic, comprehensive assessments to ensure data integrity and security compliance. Continuous auditing employs automated tools and real-time data analysis to provide ongoing monitoring and rapid identification of control deficiencies. Explore the advantages and methodologies of both approaches in controls assessment for enhanced audit accuracy.
IT Governance
Information systems auditing entails a comprehensive evaluation of IT governance frameworks, controls, and risk management processes to ensure compliance and effectiveness of information systems. Continuous auditing leverages automated tools and real-time data analysis to provide ongoing assurance and immediate detection of anomalies within IT governance activities. Explore the evolving methodologies in IT governance auditing to enhance organizational oversight and control.
Source and External Links
Information Systems Auditing | EBSCO Research Starters - Information Systems Auditing (IS Auditing) is a critical process that evaluates management controls within information systems to ensure their security, integrity, and effective use, often using frameworks like COBIT and following ethical guidelines from organizations such as ISACA.
01.01. An Introduction to Information Systems (IS) Auditing - IS Auditing focuses on assessing the controls and processes around IT systems, providing assurance that they support business objectives, comply with regulations, and manage risks, while also addressing ethical considerations related to data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Information technology audit - Wikipedia - An information technology (or systems) audit examines management controls within IT infrastructure to determine if systems safeguard assets, maintain data integrity, and operate effectively to achieve organizational goals, often conducted alongside financial or internal audits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com