Microtransaction accounting focuses on tracking and recording numerous small financial transactions to ensure accuracy in revenue recognition and expense management. Cost allocation involves distributing indirect costs across various departments or products to better understand profitability and support budgeting decisions. Explore detailed strategies for optimizing both microtransaction accounting and cost allocation to enhance financial transparency and control.
Why it is important
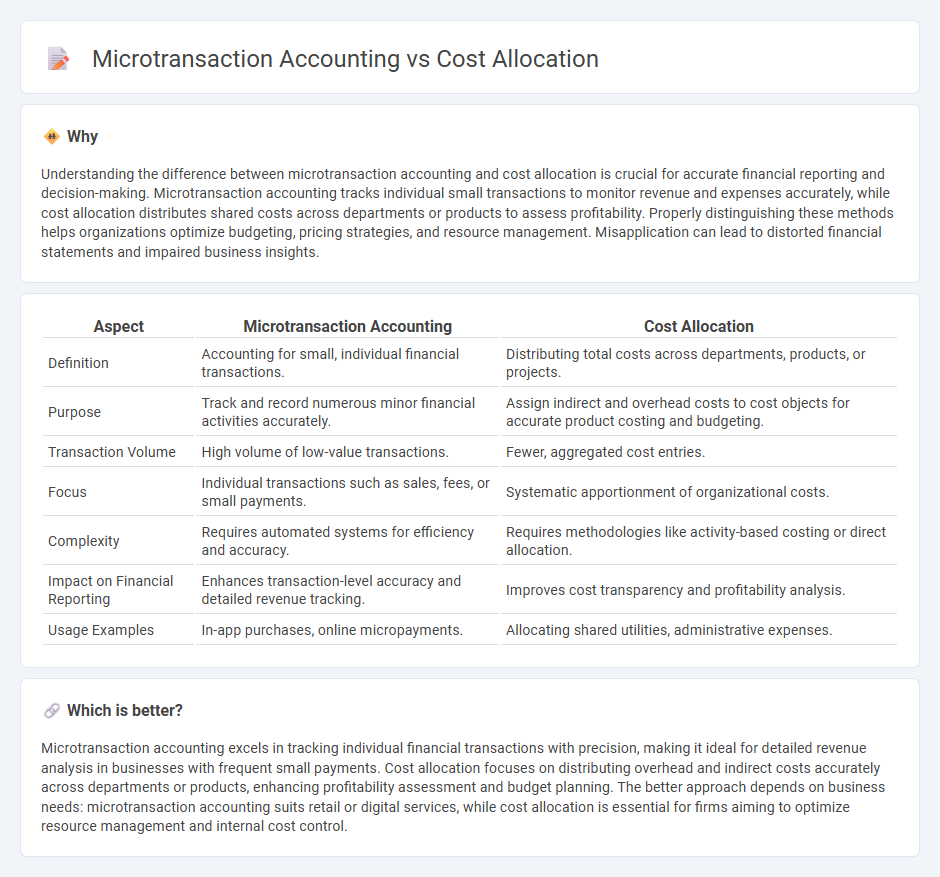
Understanding the difference between microtransaction accounting and cost allocation is crucial for accurate financial reporting and decision-making. Microtransaction accounting tracks individual small transactions to monitor revenue and expenses accurately, while cost allocation distributes shared costs across departments or products to assess profitability. Properly distinguishing these methods helps organizations optimize budgeting, pricing strategies, and resource management. Misapplication can lead to distorted financial statements and impaired business insights.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microtransaction Accounting | Cost Allocation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting for small, individual financial transactions. | Distributing total costs across departments, products, or projects. |
| Purpose | Track and record numerous minor financial activities accurately. | Assign indirect and overhead costs to cost objects for accurate product costing and budgeting. |
| Transaction Volume | High volume of low-value transactions. | Fewer, aggregated cost entries. |
| Focus | Individual transactions such as sales, fees, or small payments. | Systematic apportionment of organizational costs. |
| Complexity | Requires automated systems for efficiency and accuracy. | Requires methodologies like activity-based costing or direct allocation. |
| Impact on Financial Reporting | Enhances transaction-level accuracy and detailed revenue tracking. | Improves cost transparency and profitability analysis. |
| Usage Examples | In-app purchases, online micropayments. | Allocating shared utilities, administrative expenses. |
Which is better?
Microtransaction accounting excels in tracking individual financial transactions with precision, making it ideal for detailed revenue analysis in businesses with frequent small payments. Cost allocation focuses on distributing overhead and indirect costs accurately across departments or products, enhancing profitability assessment and budget planning. The better approach depends on business needs: microtransaction accounting suits retail or digital services, while cost allocation is essential for firms aiming to optimize resource management and internal cost control.
Connection
Microtransaction accounting involves recording and tracking small-value financial transactions with high frequency, which requires precise cost allocation to distribute expenses accurately across different departments or products. Effective cost allocation ensures that indirect expenses, such as administrative costs or shared services, are assigned to microtransactions appropriately, enhancing the accuracy of financial reporting and profitability analysis. This integration supports granular financial insights essential for businesses managing numerous, low-value transactions.
Key Terms
**Cost Allocation:**
Cost allocation involves systematically distributing indirect expenses to various departments or products based on predefined criteria, enhancing financial clarity and operational efficiency. This method ensures accurate cost tracking, aids in budgeting, and supports strategic decision-making within organizations. Discover how precise cost allocation can optimize your financial management and business performance.
Overhead Allocation
Cost allocation involves distributing overhead expenses across various departments or products based on predetermined criteria, ensuring accurate financial reporting and resource management. Microtransaction accounting focuses on tracking and recording small, individual financial transactions, often in digital platforms or gaming environments, to optimize revenue and user engagement. Explore more to understand how effective overhead allocation impacts financial transparency and operational efficiency.
Cost Driver
Cost allocation centers on identifying and assigning expenses to specific cost drivers, such as labor hours or machine usage, to accurately trace costs to products or departments. Microtransaction accounting emphasizes tracking small, frequent transactions linked to specific user behaviors or digital services as primary cost drivers, especially in gaming or app environments. Explore how understanding cost drivers enhances financial precision in diverse accounting approaches.
Source and External Links
Cost Allocation - Meaning, Types, Methods & Examples - Cost allocation is the process of identifying and distributing a company's costs to different cost objects (departments, products, or services) using appropriate allocation bases such as labor hours or square footage to reflect resource consumption accurately.
Cost allocation - Cost allocation involves assigning costs from shared service centers to internal clients that consume the services, enhancing financial discipline by making business units accountable for the costs of services they use, thus improving cost control and enabling better business decisions.
What is Cost Allocation? Definition, Methods, and Examples - Cost allocation helps businesses understand the true cost of products, services, projects, or departments by following steps such as identifying cost objects, calculating associated costs, and choosing a cost allocation method like direct allocation, step-down allocation, or activity-based costing depending on the scenario.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com