Algorithmic compliance leverages advanced software systems to automate the verification of financial data against regulatory standards, significantly reducing human error and increasing efficiency. Manual reconciliation involves accountants physically comparing and correcting records, which can be time-consuming and prone to discrepancies. Explore the benefits and challenges of both methods to optimize your accounting processes.
Why it is important
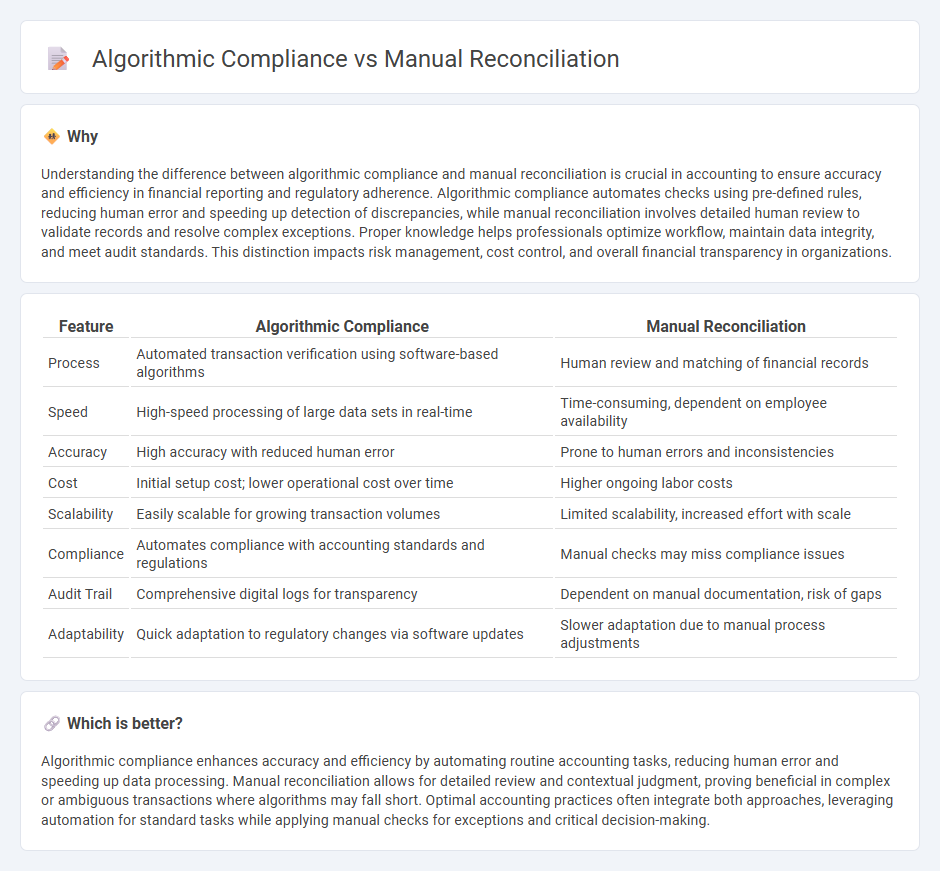
Understanding the difference between algorithmic compliance and manual reconciliation is crucial in accounting to ensure accuracy and efficiency in financial reporting and regulatory adherence. Algorithmic compliance automates checks using pre-defined rules, reducing human error and speeding up detection of discrepancies, while manual reconciliation involves detailed human review to validate records and resolve complex exceptions. Proper knowledge helps professionals optimize workflow, maintain data integrity, and meet audit standards. This distinction impacts risk management, cost control, and overall financial transparency in organizations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Algorithmic Compliance | Manual Reconciliation |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Automated transaction verification using software-based algorithms | Human review and matching of financial records |
| Speed | High-speed processing of large data sets in real-time | Time-consuming, dependent on employee availability |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with reduced human error | Prone to human errors and inconsistencies |
| Cost | Initial setup cost; lower operational cost over time | Higher ongoing labor costs |
| Scalability | Easily scalable for growing transaction volumes | Limited scalability, increased effort with scale |
| Compliance | Automates compliance with accounting standards and regulations | Manual checks may miss compliance issues |
| Audit Trail | Comprehensive digital logs for transparency | Dependent on manual documentation, risk of gaps |
| Adaptability | Quick adaptation to regulatory changes via software updates | Slower adaptation due to manual process adjustments |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance enhances accuracy and efficiency by automating routine accounting tasks, reducing human error and speeding up data processing. Manual reconciliation allows for detailed review and contextual judgment, proving beneficial in complex or ambiguous transactions where algorithms may fall short. Optimal accounting practices often integrate both approaches, leveraging automation for standard tasks while applying manual checks for exceptions and critical decision-making.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance in accounting leverages automated systems to ensure transactions adhere to regulatory standards, reducing errors and enhancing accuracy. Manual reconciliation serves as a critical verification step, where accountants review and validate algorithm-generated results to detect discrepancies and address exceptions. Combining algorithmic compliance with manual reconciliation optimizes financial reporting integrity and regulatory adherence by balancing automation with human oversight.
Key Terms
Data Matching
Manual reconciliation involves human effort to verify and match data across systems, often leading to longer processing times and higher error rates in large datasets. Algorithmic compliance leverages automated data matching algorithms to enhance accuracy, speed, and consistency by cross-referencing vast amounts of financial records and transactions. Discover how advanced data matching algorithms transform compliance processes and improve operational efficiency.
Error Detection
Manual reconciliation relies on human expertise to identify errors in financial records, often leading to slower detection and increased risk of oversight. Algorithmic compliance uses advanced data algorithms and machine learning to automate error detection, significantly enhancing accuracy and efficiency in spotting discrepancies. Explore how integrating algorithmic solutions can transform your error detection process and improve compliance outcomes.
Process Automation
Manual reconciliation involves labor-intensive data matching and error detection, leading to increased operational costs and slower processing times. Algorithmic compliance utilizes machine learning and AI-driven process automation to enhance accuracy, reduce human error, and streamline workflow efficiency in regulatory adherence. Discover how process automation transforms compliance strategies for superior operational performance.
Source and External Links
Problems with Manual Reconciliation - This article discusses the challenges associated with manual reconciliation, including the time-consuming comparison of ledgers and the potential for errors.
Manual vs. Automated Balance Sheet Reconciliation - This resource compares manual and automated reconciliation processes, highlighting the labor-intensive nature of manual reconciliation and its susceptibility to human errors.
How You Manually Reconcile a Bank Statement - This document guides users through the manual process of reconciling bank statements by matching system transactions with bank statement lines and addressing any discrepancies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com