Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring of financial transactions to enhance accuracy and compliance, while transaction sampling reviews selected data sets to identify errors or irregularities after the fact. Continuous assurance relies on automated systems and data analytics for ongoing verification, whereas transaction sampling involves manual or statistical evaluation of representative transactions. Explore these approaches further to understand their impact on financial auditing and risk management.
Why it is important
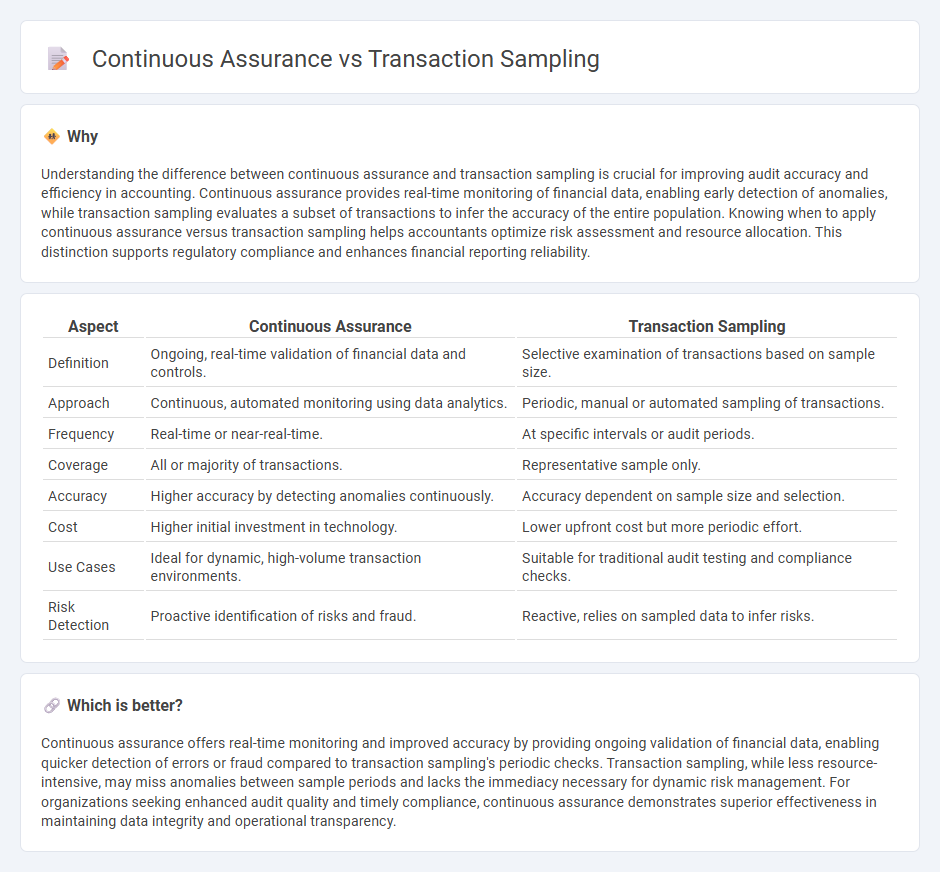
Understanding the difference between continuous assurance and transaction sampling is crucial for improving audit accuracy and efficiency in accounting. Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring of financial data, enabling early detection of anomalies, while transaction sampling evaluates a subset of transactions to infer the accuracy of the entire population. Knowing when to apply continuous assurance versus transaction sampling helps accountants optimize risk assessment and resource allocation. This distinction supports regulatory compliance and enhances financial reporting reliability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Continuous Assurance | Transaction Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing, real-time validation of financial data and controls. | Selective examination of transactions based on sample size. |
| Approach | Continuous, automated monitoring using data analytics. | Periodic, manual or automated sampling of transactions. |
| Frequency | Real-time or near-real-time. | At specific intervals or audit periods. |
| Coverage | All or majority of transactions. | Representative sample only. |
| Accuracy | Higher accuracy by detecting anomalies continuously. | Accuracy dependent on sample size and selection. |
| Cost | Higher initial investment in technology. | Lower upfront cost but more periodic effort. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for dynamic, high-volume transaction environments. | Suitable for traditional audit testing and compliance checks. |
| Risk Detection | Proactive identification of risks and fraud. | Reactive, relies on sampled data to infer risks. |
Which is better?
Continuous assurance offers real-time monitoring and improved accuracy by providing ongoing validation of financial data, enabling quicker detection of errors or fraud compared to transaction sampling's periodic checks. Transaction sampling, while less resource-intensive, may miss anomalies between sample periods and lacks the immediacy necessary for dynamic risk management. For organizations seeking enhanced audit quality and timely compliance, continuous assurance demonstrates superior effectiveness in maintaining data integrity and operational transparency.
Connection
Continuous assurance enhances accounting accuracy by enabling real-time monitoring of financial transactions, while transaction sampling allows auditors to evaluate a representative subset of these transactions for anomalies or errors. The integration of continuous assurance with transaction sampling improves the efficiency and reliability of audit processes by providing timely insights and reducing the volume of data needing detailed examination. This connection supports more effective risk assessment and fraud detection within accounting systems.
Key Terms
Audit Evidence
Transaction sampling involves examining a subset of transactions to infer the accuracy of the entire dataset, providing selective audit evidence that may miss anomalies. Continuous assurance offers real-time monitoring of transactions, delivering comprehensive audit evidence and enhancing the detection of irregularities throughout the audit period. Explore the key differences to understand how each method impacts the reliability of audit evidence.
Real-time Monitoring
Transaction sampling analyzes a specific subset of transactions to identify errors or anomalies, offering periodic insights into financial activities. Continuous assurance employs real-time monitoring techniques to provide ongoing verification and immediate detection of irregularities across the entire transaction flow. Explore the benefits and implementation strategies of continuous assurance in enhancing audit accuracy and operational efficiency.
Sampling Risk
Transaction sampling involves examining a subset of transactions to infer conclusions about the entire dataset, which introduces sampling risk--the possibility that the sample may not represent the population accurately. Continuous assurance utilizes real-time data monitoring and automated controls to minimize sampling risk by assessing all transactions continuously rather than relying on samples. Explore more on how these approaches impact audit reliability and risk management strategies.
Source and External Links
Sampling | Sentry for JavaScript - Transaction sampling can be configured using either a static sample rate or a dynamic sampling function, with decisions inherited from parent transactions or explicitly set, to provide an even cross-section of transactions in an application.
apm/specs/agents/tracing-sampling.md at main * elastic/apm - Transaction sampling involves "head-based sampling," where a sampling decision is made at the start of a distributed trace probabilistically, to reduce processing and storage overhead, with sample rates configurable between 0 and 1.
Transaction sampling | APM Overview [7.15] - Elastic APM uses head-based probability sampling where the initiating service decides which transactions to sample, and all downstream services respect this decision, allowing control of the percentage of traces fully retained and analyzed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com