Continuous assurance enhances financial transparency by providing real-time monitoring of accounting data through automated systems, ensuring ongoing accuracy and compliance. Exception reporting focuses on identifying and flagging deviations or anomalies within financial transactions, enabling targeted investigation of potential issues. Discover how integrating these methods can optimize accounting practices and reduce risks effectively.
Why it is important
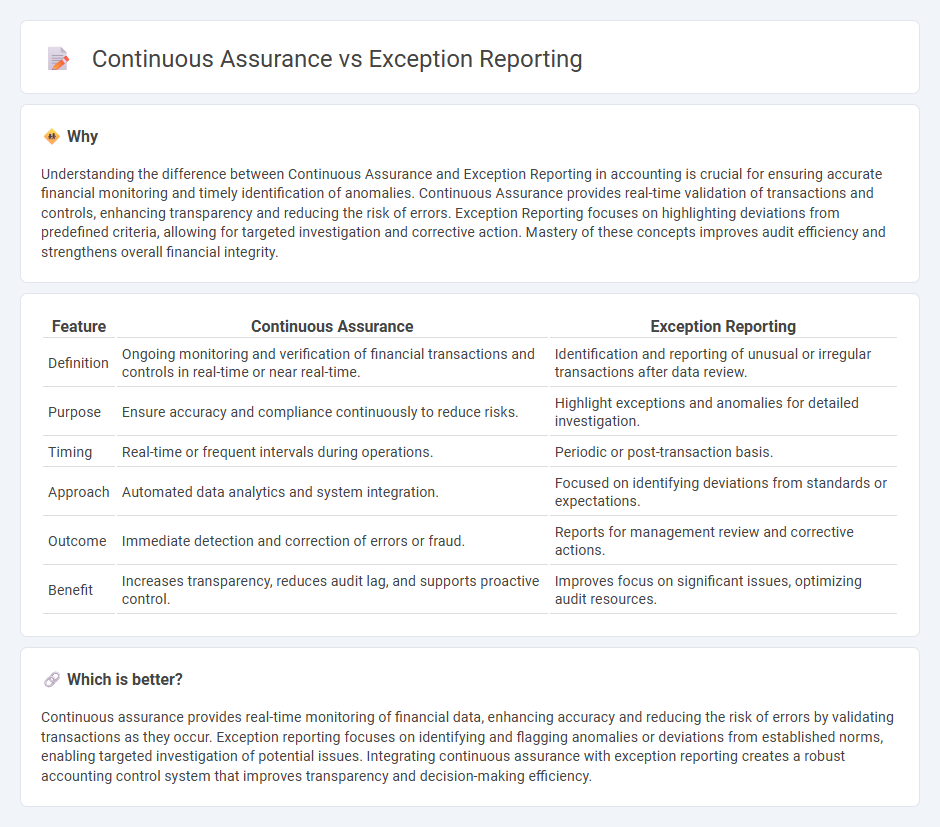
Understanding the difference between Continuous Assurance and Exception Reporting in accounting is crucial for ensuring accurate financial monitoring and timely identification of anomalies. Continuous Assurance provides real-time validation of transactions and controls, enhancing transparency and reducing the risk of errors. Exception Reporting focuses on highlighting deviations from predefined criteria, allowing for targeted investigation and corrective action. Mastery of these concepts improves audit efficiency and strengthens overall financial integrity.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Continuous Assurance | Exception Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ongoing monitoring and verification of financial transactions and controls in real-time or near real-time. | Identification and reporting of unusual or irregular transactions after data review. |
| Purpose | Ensure accuracy and compliance continuously to reduce risks. | Highlight exceptions and anomalies for detailed investigation. |
| Timing | Real-time or frequent intervals during operations. | Periodic or post-transaction basis. |
| Approach | Automated data analytics and system integration. | Focused on identifying deviations from standards or expectations. |
| Outcome | Immediate detection and correction of errors or fraud. | Reports for management review and corrective actions. |
| Benefit | Increases transparency, reduces audit lag, and supports proactive control. | Improves focus on significant issues, optimizing audit resources. |
Which is better?
Continuous assurance provides real-time monitoring of financial data, enhancing accuracy and reducing the risk of errors by validating transactions as they occur. Exception reporting focuses on identifying and flagging anomalies or deviations from established norms, enabling targeted investigation of potential issues. Integrating continuous assurance with exception reporting creates a robust accounting control system that improves transparency and decision-making efficiency.
Connection
Continuous assurance enhances accounting accuracy by providing real-time verification of financial data, enabling early detection of discrepancies. Exception reporting complements this by automatically highlighting deviations from established accounting standards or thresholds, facilitating prompt investigation. Together, they improve the reliability and transparency of financial reporting through proactive monitoring and targeted alerts.
Key Terms
Anomalies
Exception reporting detects anomalies by highlighting deviations from predefined thresholds or standards, providing targeted insights into potential issues that require immediate attention. Continuous assurance employs real-time data monitoring and advanced analytics, including machine learning algorithms, to continuously identify and assess anomalies across complex systems for proactive risk management. Explore further to understand how these methodologies enhance anomaly detection and organizational decision-making.
Real-time monitoring
Exception reporting highlights anomalies by identifying deviations from expected performance metrics, enabling swift response to specific issues. Continuous assurance employs real-time monitoring techniques to provide ongoing validation of financial transactions and internal controls, reducing risk exposure through constant oversight. Explore how integrating real-time monitoring enhances both exception reporting and continuous assurance for proactive risk management.
Audit trails
Exception reporting highlights deviations from pre-set thresholds within audit trails, enabling auditors to quickly identify anomalies and potential risks. Continuous assurance leverages real-time audit trail analysis to provide ongoing validation of transaction integrity and compliance, enhancing transparency and reducing the risk of fraud. Explore the detailed differences in audit trail management to optimize your organization's risk mitigation strategies.
Source and External Links
Understanding the Exception Report in Project Management - An exception report documents deviations and problems in a project to help quickly identify and address issues before they escalate, ensuring team accountability and data quality in project management processes.
Exception report definition - AccountingTools - An exception report highlights significant deviations from expected performance, focusing management's attention on problems such as budget overruns or production shortfalls that require immediate correction.
Exception Reports for Banks & Credit Unions - How Are They Used? - Exception reports in banking identify missing, expired, or problematic documents, using manual methods or automated software to help institutions track and resolve compliance and operational exceptions efficiently.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com