Smart contracts accounting automates financial transactions using blockchain technology, ensuring real-time accuracy and reducing human errors, while internal controls rely on traditional manual processes and organizational policies to safeguard assets and ensure compliance. The integration of smart contracts streamlines audit trails and enhances transparency, contrasting with the periodic and often cumbersome paper-based internal control audits. Explore how combining smart contracts with internal controls can revolutionize accounting practices and improve financial governance.
Why it is important
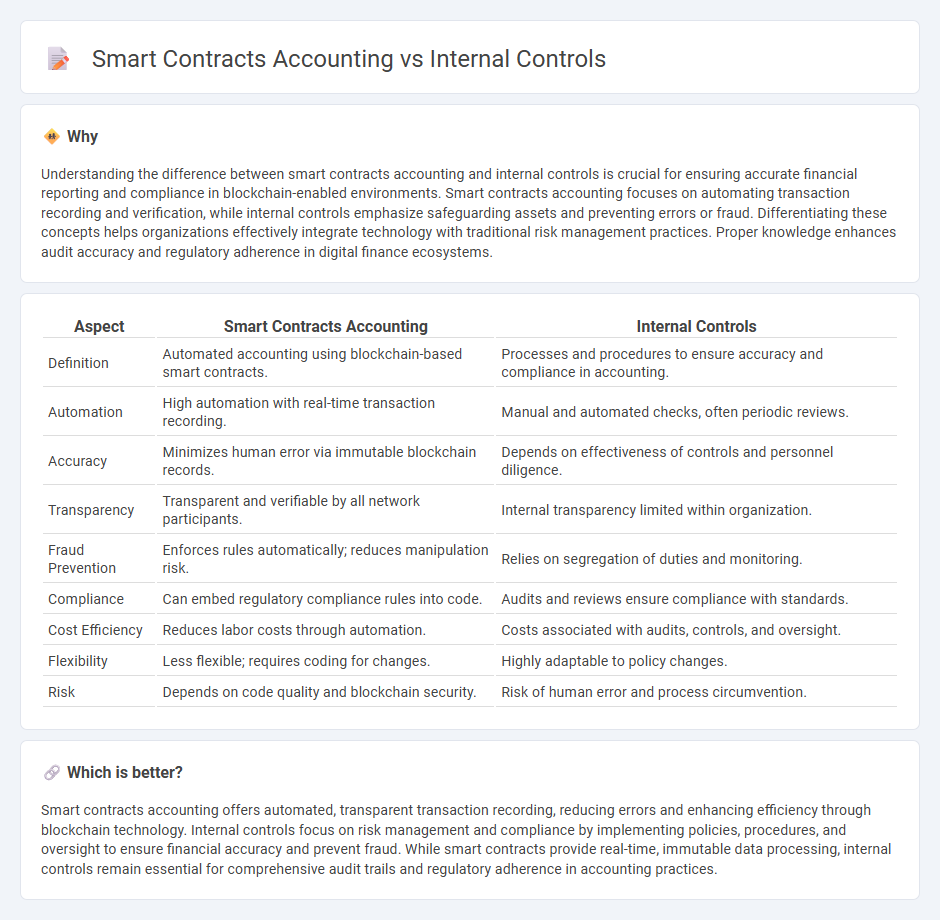
Understanding the difference between smart contracts accounting and internal controls is crucial for ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance in blockchain-enabled environments. Smart contracts accounting focuses on automating transaction recording and verification, while internal controls emphasize safeguarding assets and preventing errors or fraud. Differentiating these concepts helps organizations effectively integrate technology with traditional risk management practices. Proper knowledge enhances audit accuracy and regulatory adherence in digital finance ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Contracts Accounting | Internal Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated accounting using blockchain-based smart contracts. | Processes and procedures to ensure accuracy and compliance in accounting. |
| Automation | High automation with real-time transaction recording. | Manual and automated checks, often periodic reviews. |
| Accuracy | Minimizes human error via immutable blockchain records. | Depends on effectiveness of controls and personnel diligence. |
| Transparency | Transparent and verifiable by all network participants. | Internal transparency limited within organization. |
| Fraud Prevention | Enforces rules automatically; reduces manipulation risk. | Relies on segregation of duties and monitoring. |
| Compliance | Can embed regulatory compliance rules into code. | Audits and reviews ensure compliance with standards. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces labor costs through automation. | Costs associated with audits, controls, and oversight. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible; requires coding for changes. | Highly adaptable to policy changes. |
| Risk | Depends on code quality and blockchain security. | Risk of human error and process circumvention. |
Which is better?
Smart contracts accounting offers automated, transparent transaction recording, reducing errors and enhancing efficiency through blockchain technology. Internal controls focus on risk management and compliance by implementing policies, procedures, and oversight to ensure financial accuracy and prevent fraud. While smart contracts provide real-time, immutable data processing, internal controls remain essential for comprehensive audit trails and regulatory adherence in accounting practices.
Connection
Smart contracts enhance internal controls by automating transaction verification and ensuring real-time accuracy in accounting records, reducing human error and fraud risks. These contracts provide immutable audit trails that strengthen compliance and transparency within financial reporting processes. Integration of smart contracts streamlines audit procedures and enforces predefined accounting rules, improving operational efficiency and control effectiveness.
Key Terms
Segregation of Duties
Internal controls emphasize Segregation of Duties by dividing critical accounting tasks among multiple individuals to prevent errors and fraud, ensuring accuracy and accountability in financial reporting. Smart contracts automate these controls through blockchain technology, embedding Segregation of Duties directly into code to enforce predefined rules and reduce human intervention. Explore how integrating smart contracts can revolutionize internal controls and enhance accounting security.
Automated Execution
Internal controls in accounting rely on manual processes and periodic audits to ensure transaction accuracy and compliance, while smart contracts automate execution by embedding business rules directly into blockchain protocols, reducing human error and enhancing transparency. Smart contracts provide real-time enforcement of financial terms, enabling instantaneous validation and settlement of transactions without intermediaries. Explore how integrating smart contracts can revolutionize your accounting accuracy and efficiency.
Audit Trail
Internal controls in accounting establish a systematic framework to ensure transaction accuracy and prevent fraud, emphasizing the maintenance of a reliable audit trail through manual and automated processes. Smart contracts leverage blockchain technology to create immutable, transparent records of financial activities, enhancing audit trail integrity by automatically recording every transaction in real-time without human intervention. Explore how integrating smart contracts with traditional internal controls can revolutionize audit trails and enhance financial accountability.
Source and External Links
The Essential Guide to Internal Audit and Controls - AuditBoard - Internal controls are policies and procedures designed to mitigate risk, including control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring to ensure effectiveness across an organization.
Internal control - Wikipedia - Internal control directs and monitors organizational risks, with responsibilities shared among management, board of directors, and employees to establish an ethical control environment and effective controls across corporate governance.
Top Ten Things to Strengthen Internal Controls in the Office - Key steps to strengthen internal controls include segregation of duties, adequate physical controls, written procedures, reconciliations, and approval processes to prevent errors and fraud in operations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com