Algorithmic compliance leverages automated systems and machine learning models to ensure adherence to regulatory standards, minimizing human error and enhancing accuracy in financial reporting. Internal controls consist of manual processes and organizational policies designed to prevent fraud, ensure accuracy, and maintain asset security within accounting practices. Explore how combining algorithmic compliance with internal controls can optimize your organization's financial integrity and regulatory adherence.
Why it is important
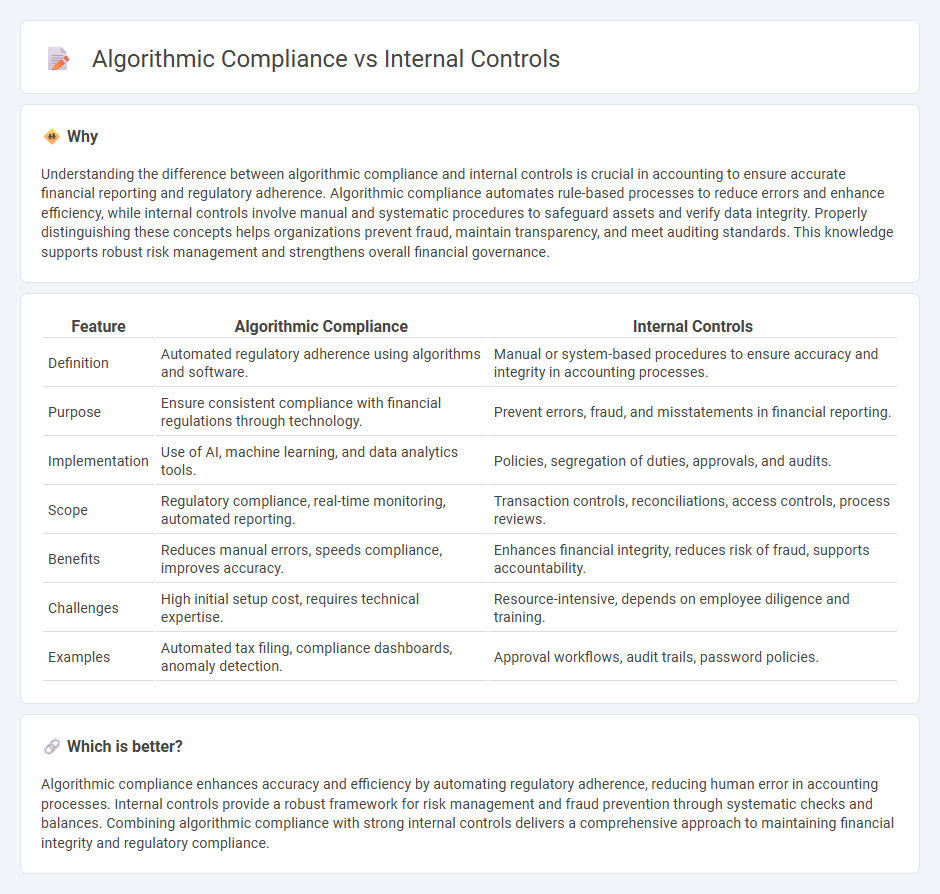
Understanding the difference between algorithmic compliance and internal controls is crucial in accounting to ensure accurate financial reporting and regulatory adherence. Algorithmic compliance automates rule-based processes to reduce errors and enhance efficiency, while internal controls involve manual and systematic procedures to safeguard assets and verify data integrity. Properly distinguishing these concepts helps organizations prevent fraud, maintain transparency, and meet auditing standards. This knowledge supports robust risk management and strengthens overall financial governance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Algorithmic Compliance | Internal Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated regulatory adherence using algorithms and software. | Manual or system-based procedures to ensure accuracy and integrity in accounting processes. |
| Purpose | Ensure consistent compliance with financial regulations through technology. | Prevent errors, fraud, and misstatements in financial reporting. |
| Implementation | Use of AI, machine learning, and data analytics tools. | Policies, segregation of duties, approvals, and audits. |
| Scope | Regulatory compliance, real-time monitoring, automated reporting. | Transaction controls, reconciliations, access controls, process reviews. |
| Benefits | Reduces manual errors, speeds compliance, improves accuracy. | Enhances financial integrity, reduces risk of fraud, supports accountability. |
| Challenges | High initial setup cost, requires technical expertise. | Resource-intensive, depends on employee diligence and training. |
| Examples | Automated tax filing, compliance dashboards, anomaly detection. | Approval workflows, audit trails, password policies. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic compliance enhances accuracy and efficiency by automating regulatory adherence, reducing human error in accounting processes. Internal controls provide a robust framework for risk management and fraud prevention through systematic checks and balances. Combining algorithmic compliance with strong internal controls delivers a comprehensive approach to maintaining financial integrity and regulatory compliance.
Connection
Algorithmic compliance integrates automated systems with accounting internal controls to enhance accuracy and regulatory adherence in financial reporting. By embedding predefined rules and checks within algorithms, organizations ensure continuous monitoring and timely detection of discrepancies or fraud. This synergy reduces human error, enforces consistent policy application, and streamlines audit processes in accounting operations.
Key Terms
Segregation of Duties
Internal controls establish a formal framework to enforce Segregation of Duties (SoD) by defining roles and responsibilities, preventing conflicts of interest and reducing fraud risk. Algorithmic compliance automates SoD enforcement using advanced software and machine learning models to continuously monitor transactions and flag violations in real-time. Explore how integrating both methods can enhance organizational governance and risk management strategies.
Automated Monitoring
Internal controls provide a framework for risk management and regulatory compliance through manual checks and policy enforcement, whereas algorithmic compliance utilizes automated monitoring systems powered by AI and machine learning to detect anomalies and ensure continuous adherence to regulations. Automated monitoring enhances accuracy, reduces human error, and accelerates compliance reporting by leveraging real-time data analysis and predictive analytics. Discover how integrating algorithmic compliance can revolutionize your compliance strategy and operational efficiency.
Exception Reporting
Internal controls are manual procedures and checks designed to prevent errors and fraud in business processes, whereas algorithmic compliance relies on automated systems to enforce regulations and detect anomalies through continuous monitoring. Exception reporting plays a crucial role by highlighting deviations from predefined standards, enabling timely identification and resolution of irregularities in both approaches. Explore more about leveraging exception reporting to enhance compliance and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
The Essential Guide to Internal Audit and Controls - This guide outlines internal controls as checks and balances to mitigate risk, comprising control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, and monitoring.
Internal Controls - Internal controls at UW Finance include a framework with control environment, risk assessment, and control activities that can be preventive or detective to ensure efficient operations.
Internal Controls - This resource defines internal controls as actions taken by management to manage risk and achieve objectives, with a focus on the control environment and COSO's framework components.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com