Zero-knowledge proofs in accounting enable verification of financial statements without disclosing sensitive data, enhancing confidentiality beyond traditional IFRS requirements. IFRS focuses on standardized financial reporting principles to ensure transparency and comparability, while zero-knowledge proofs revolutionize data privacy during audits. Explore how zero-knowledge proofs can transform compliance and reporting processes within IFRS frameworks.
Why it is important
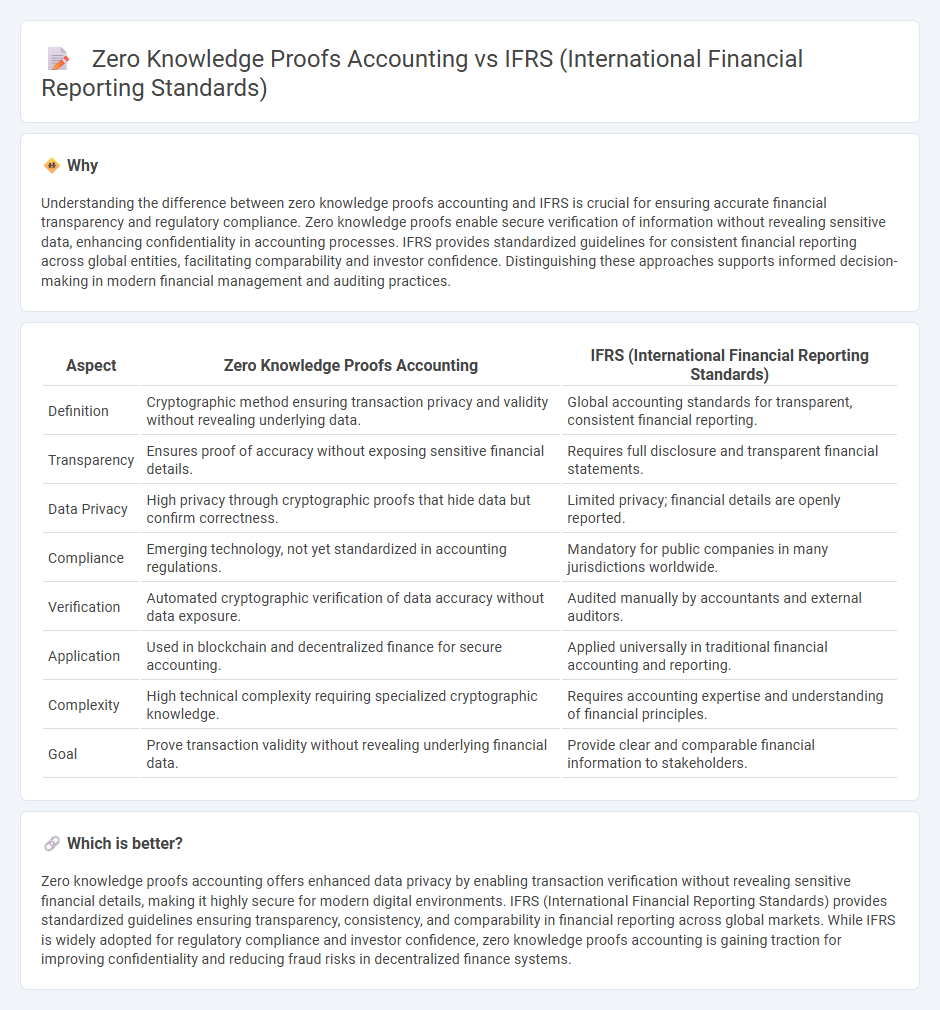
Understanding the difference between zero knowledge proofs accounting and IFRS is crucial for ensuring accurate financial transparency and regulatory compliance. Zero knowledge proofs enable secure verification of information without revealing sensitive data, enhancing confidentiality in accounting processes. IFRS provides standardized guidelines for consistent financial reporting across global entities, facilitating comparability and investor confidence. Distinguishing these approaches supports informed decision-making in modern financial management and auditing practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero Knowledge Proofs Accounting | IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic method ensuring transaction privacy and validity without revealing underlying data. | Global accounting standards for transparent, consistent financial reporting. |
| Transparency | Ensures proof of accuracy without exposing sensitive financial details. | Requires full disclosure and transparent financial statements. |
| Data Privacy | High privacy through cryptographic proofs that hide data but confirm correctness. | Limited privacy; financial details are openly reported. |
| Compliance | Emerging technology, not yet standardized in accounting regulations. | Mandatory for public companies in many jurisdictions worldwide. |
| Verification | Automated cryptographic verification of data accuracy without data exposure. | Audited manually by accountants and external auditors. |
| Application | Used in blockchain and decentralized finance for secure accounting. | Applied universally in traditional financial accounting and reporting. |
| Complexity | High technical complexity requiring specialized cryptographic knowledge. | Requires accounting expertise and understanding of financial principles. |
| Goal | Prove transaction validity without revealing underlying financial data. | Provide clear and comparable financial information to stakeholders. |
Which is better?
Zero knowledge proofs accounting offers enhanced data privacy by enabling transaction verification without revealing sensitive financial details, making it highly secure for modern digital environments. IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) provides standardized guidelines ensuring transparency, consistency, and comparability in financial reporting across global markets. While IFRS is widely adopted for regulatory compliance and investor confidence, zero knowledge proofs accounting is gaining traction for improving confidentiality and reducing fraud risks in decentralized finance systems.
Connection
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance accounting by enabling secure verification of financial data without revealing underlying details, aligning with IFRS's emphasis on transparency and accuracy. This cryptographic method supports compliance by ensuring confidential transaction validation while maintaining auditor confidence in financial statements. Integrating zero-knowledge proofs with IFRS frameworks strengthens data integrity and confidentiality in financial reporting processes.
Key Terms
Fair Value Measurement
IFRS Fair Value Measurement relies on market-based inputs and observable data to determine asset values, ensuring transparency and comparability in financial reporting. Zero-knowledge proofs accounting introduces cryptographic validation of asset valuations without revealing sensitive data, enhancing privacy and security in financial disclosures. Explore how combining IFRS standards with zero-knowledge proofs can revolutionize fair value measurement and financial transparency.
Transparency
IFRS ensures transparency in financial reporting by standardizing how companies disclose financial information, promoting comparability and accountability across global markets. Zero knowledge proofs (ZKPs) enhance transparency differently by enabling verification of financial data without revealing sensitive details, ensuring privacy while maintaining trustworthiness. Explore how these technologies reshape transparency in modern accounting practices.
Verifiability
IFRS emphasizes transparency and comparability by requiring standardized financial disclosures that allow stakeholders to verify company performance through audited financial statements. Zero knowledge proofs accounting enhances verifiability by enabling parties to validate the accuracy of transactions without revealing sensitive data, ensuring confidentiality alongside trust. Explore how integrating these frameworks can revolutionize financial reporting verifiability in regulated and privacy-conscious environments.
Source and External Links
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) - EBSCO - IFRS are a set of accounting guidelines aimed at creating a universal framework for financial reporting across nations.
International Financial Reporting Standards - Wikipedia - IFRS are accounting standards issued by the IFRS Foundation and the International Accounting Standards Board, offering a standardized way to describe financial performance across international boundaries.
What are the IFRS Standards in Accounting - IFRS standards are a set of accounting rules that determine how transactions and other accounting events are required to be reported in financial statements, promoting transparency and comparability.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com