Cryptocurrency auditing focuses on verifying digital asset transactions and ensuring blockchain integrity, requiring specialized knowledge of cryptographic technologies and regulatory compliance. Internal auditing involves evaluating an organization's financial processes, risk management, and control systems to enhance operational efficiency and safeguard assets. Discover more about the distinctions and key practices in cryptocurrency auditing and internal auditing.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between cryptocurrency auditing and internal auditing is crucial because cryptocurrency auditing involves specialized knowledge of blockchain technology, digital wallets, and transactional transparency, whereas internal auditing focuses on evaluating an organization's internal controls, risk management, and compliance processes. Cryptocurrency auditing requires expertise in cryptographic security and decentralized ledger verification, enabling auditors to accurately assess digital asset integrity. Internal auditing ensures the effectiveness and efficiency of business operations, helping prevent fraud and ensuring regulatory compliance across all departments. Recognizing these distinctions allows organizations to implement appropriate audit strategies that safeguard both traditional financial processes and emerging digital assets.
Comparison Table
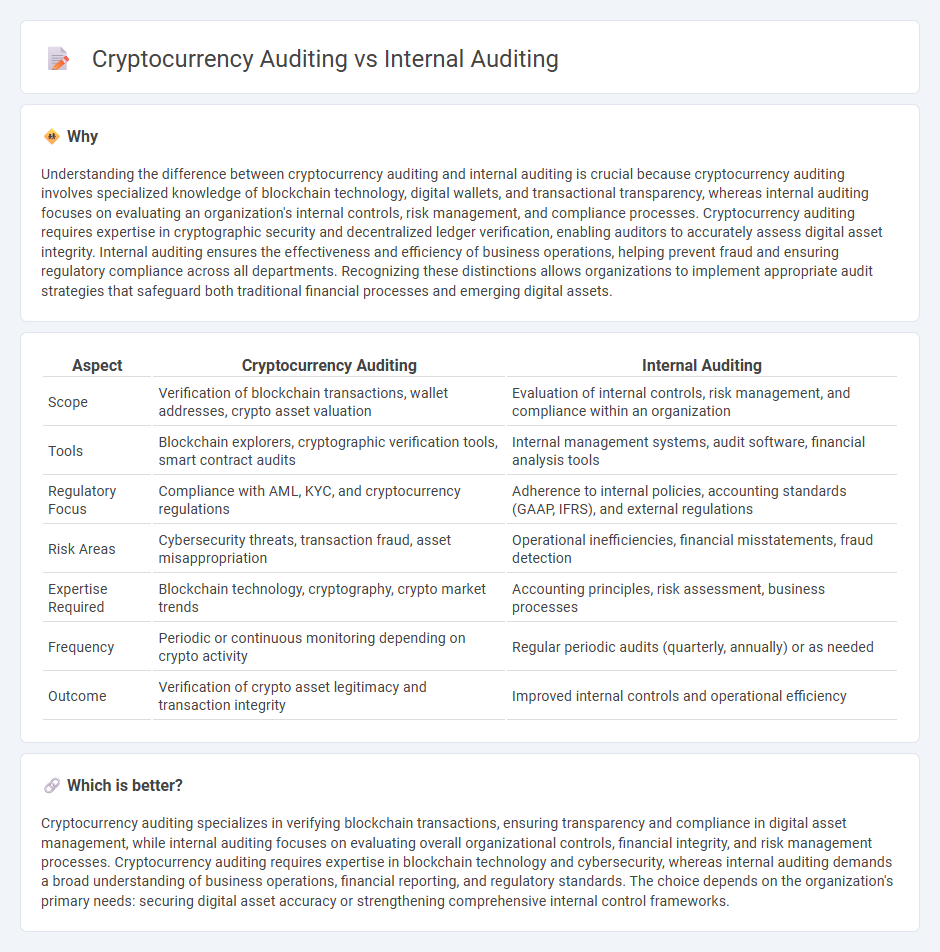
| Aspect | Cryptocurrency Auditing | Internal Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Verification of blockchain transactions, wallet addresses, crypto asset valuation | Evaluation of internal controls, risk management, and compliance within an organization |
| Tools | Blockchain explorers, cryptographic verification tools, smart contract audits | Internal management systems, audit software, financial analysis tools |
| Regulatory Focus | Compliance with AML, KYC, and cryptocurrency regulations | Adherence to internal policies, accounting standards (GAAP, IFRS), and external regulations |
| Risk Areas | Cybersecurity threats, transaction fraud, asset misappropriation | Operational inefficiencies, financial misstatements, fraud detection |
| Expertise Required | Blockchain technology, cryptography, crypto market trends | Accounting principles, risk assessment, business processes |
| Frequency | Periodic or continuous monitoring depending on crypto activity | Regular periodic audits (quarterly, annually) or as needed |
| Outcome | Verification of crypto asset legitimacy and transaction integrity | Improved internal controls and operational efficiency |
Which is better?
Cryptocurrency auditing specializes in verifying blockchain transactions, ensuring transparency and compliance in digital asset management, while internal auditing focuses on evaluating overall organizational controls, financial integrity, and risk management processes. Cryptocurrency auditing requires expertise in blockchain technology and cybersecurity, whereas internal auditing demands a broad understanding of business operations, financial reporting, and regulatory standards. The choice depends on the organization's primary needs: securing digital asset accuracy or strengthening comprehensive internal control frameworks.
Connection
Cryptocurrency auditing integrates blockchain analysis and transaction verification to ensure the accuracy of digital asset records within financial statements. Internal auditing evaluates the effectiveness of an organization's control environment, including risk management procedures related to cryptocurrency holdings and transactions. Both processes collaborate to enhance transparency, compliance, and fraud prevention in the evolving landscape of digital finance.
Key Terms
Internal Auditing:
Internal auditing involves evaluating an organization's internal controls, risk management, and governance processes to ensure operational efficiency and regulatory compliance. It systematically examines financial and operational activities, identifying discrepancies and potential fraud to enhance organizational accountability. Explore deeper insights into the principles, methodologies, and benefits of internal auditing for comprehensive organizational integrity.
Risk Assessment
Internal auditing centers on evaluating organizational controls and financial integrity to identify operational risks, ensuring regulatory compliance and preventing fraud. Cryptocurrency auditing involves analyzing blockchain transactions and smart contracts to assess digital asset security, transparency, and exposure to cyber threats or market volatility risks. Discover how these auditing processes uniquely address risk assessment challenges in modern financial environments.
Internal Controls
Internal auditing rigorously evaluates an organization's internal controls to ensure accuracy, compliance, and risk management, focusing on financial statements and operational processes. Cryptocurrency auditing emphasizes verifying blockchain transactions, wallet security, and smart contract integrity, addressing unique challenges like decentralized ledgers and cryptographic proof. Discover how these distinct auditing approaches safeguard assets and enhance transparency by exploring more detailed insights.
Source and External Links
Internal Audit 101: Everything You Need to Know - AuditBoard - Internal auditing is an independent, objective review of a company's systems, processes, and procedures to provide assurance over the effectiveness of risk management, controls, and operations, helping organizations identify issues, improve efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance.
What is Internal Auditing? - Sacramento State - Internal auditing is an independent, objective assurance and consulting activity designed to add value and improve an organization's operations by systematically evaluating and enhancing the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes.
What is Internal Audit? Types, Value, Process & Standards - Internal audit involves unbiased, independent reviews of various organizational areas--including financial, compliance, environmental, IT, operational, and performance audits--to ensure accuracy, regulatory adherence, and operational efficiency.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com