Sustainability ledgers focus on tracking environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics with detailed, data-driven accounting to support corporate responsibility and transparency. Integrated reporting combines financial and sustainability performance into a unified framework, offering a holistic view of an organization's long-term value creation. Explore how these evolving accounting approaches shape strategic decision-making and stakeholder communication.
Why it is important
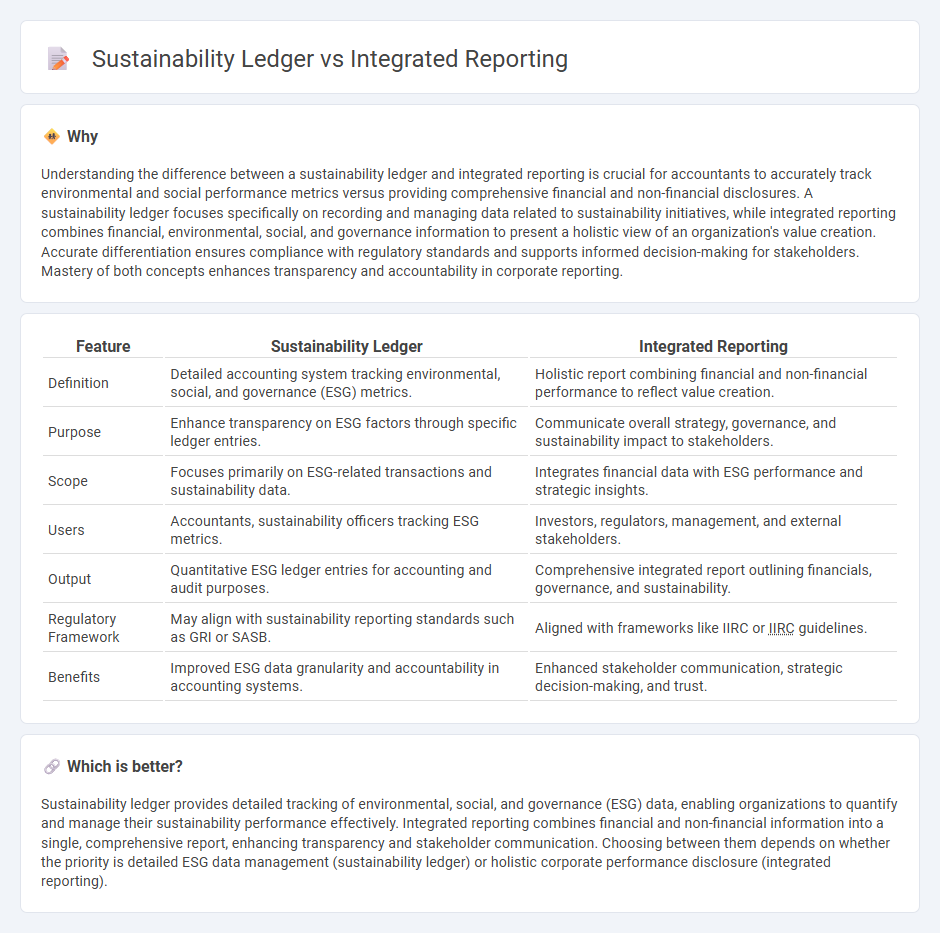
Understanding the difference between a sustainability ledger and integrated reporting is crucial for accountants to accurately track environmental and social performance metrics versus providing comprehensive financial and non-financial disclosures. A sustainability ledger focuses specifically on recording and managing data related to sustainability initiatives, while integrated reporting combines financial, environmental, social, and governance information to present a holistic view of an organization's value creation. Accurate differentiation ensures compliance with regulatory standards and supports informed decision-making for stakeholders. Mastery of both concepts enhances transparency and accountability in corporate reporting.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Sustainability Ledger | Integrated Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Detailed accounting system tracking environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics. | Holistic report combining financial and non-financial performance to reflect value creation. |
| Purpose | Enhance transparency on ESG factors through specific ledger entries. | Communicate overall strategy, governance, and sustainability impact to stakeholders. |
| Scope | Focuses primarily on ESG-related transactions and sustainability data. | Integrates financial data with ESG performance and strategic insights. |
| Users | Accountants, sustainability officers tracking ESG metrics. | Investors, regulators, management, and external stakeholders. |
| Output | Quantitative ESG ledger entries for accounting and audit purposes. | Comprehensive integrated report outlining financials, governance, and sustainability. |
| Regulatory Framework | May align with sustainability reporting standards such as GRI or SASB. | Aligned with frameworks like IIRC or IIRC guidelines. |
| Benefits | Improved ESG data granularity and accountability in accounting systems. | Enhanced stakeholder communication, strategic decision-making, and trust. |
Which is better?
Sustainability ledger provides detailed tracking of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data, enabling organizations to quantify and manage their sustainability performance effectively. Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial information into a single, comprehensive report, enhancing transparency and stakeholder communication. Choosing between them depends on whether the priority is detailed ESG data management (sustainability ledger) or holistic corporate performance disclosure (integrated reporting).
Connection
Sustainability ledger tracks environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics integrated into financial accounting systems, enabling comprehensive data collection for sustainability performance. Integrated reporting merges financial and sustainability information into a single framework to provide stakeholders with a holistic view of organizational value creation. This connection enhances transparency, supports regulatory compliance, and drives informed decision-making by linking ESG data with traditional financial metrics.
Key Terms
Value Creation
Integrated reporting combines financial and non-financial data to present a holistic view of how organizations create value over time, emphasizing capitals such as financial, manufactured, intellectual, human, social, and natural. Sustainability ledgers specifically track environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics, focusing on the impact of corporate activities on sustainable development and stakeholder accountability. Explore the distinctions and synergies to optimize value creation strategies in corporate reporting.
ESG (Environmental, Social, Governance)
Integrated reporting combines financial and ESG data to provide a holistic view of a company's performance and value creation over time, emphasizing transparency and stakeholder communication. The sustainability ledger focuses specifically on recording and tracking ESG metrics, enabling precise measurement and management of environmental, social, and governance impacts. Explore further to understand how these tools enhance corporate accountability and drive sustainable business practices.
Double Materiality
Integrated reporting emphasizes the importance of presenting financial and non-financial information together, focusing on how sustainability issues impact a company's ability to create value over time. Sustainability ledgers primarily track environmental, social, and governance (ESG) metrics but may lack the comprehensive linkage to financial outcomes highlighted by integrated reports. Explore how double materiality shapes both frameworks to gain deeper insights into corporate accountability and stakeholder communication.
Source and External Links
Integrated reporting - Wikipedia - Integrated reporting is a concise communication process about how an organization's strategy, governance, performance, and prospects lead to value creation over time, combining financial and other value-relevant information to guide long-term decision making, mainly for providers of financial capital.
What is Integrated Reporting? - ESG - Integrated reporting provides a comprehensive view of a company's financial and non-financial factors, emphasizing ESG issues, governance, and how the company creates sustainable value, helping investors and stakeholders understand long-term performance beyond traditional financial statements.
IFRS - Integrated Reporting Framework - IFRS Foundation - The IFRS Foundation's Integrated Reporting Framework defines an integrated report as a concise communication about an organization's strategy, governance, performance, and prospects in the context of its external environment, showing how it creates short, medium, and long-term value, supporting alignment with financial reporting standards.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com